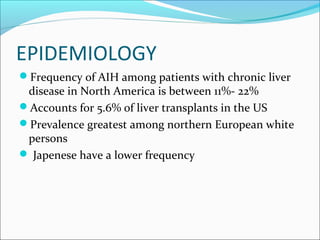
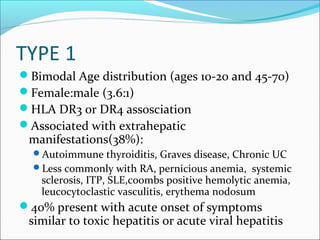
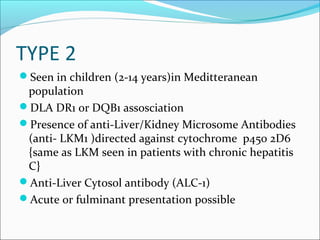
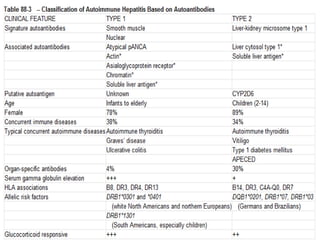
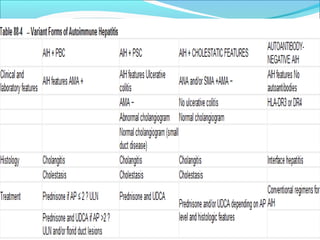
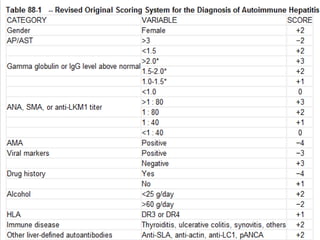
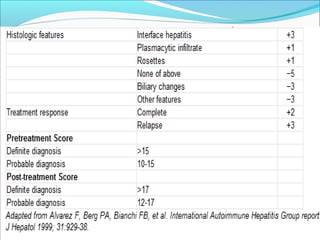
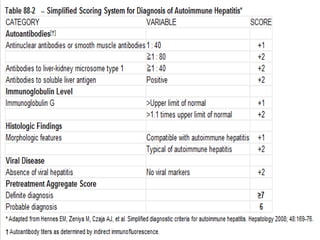
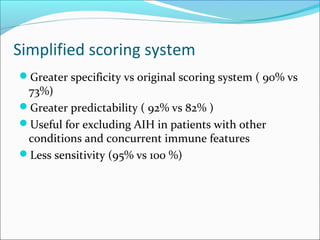
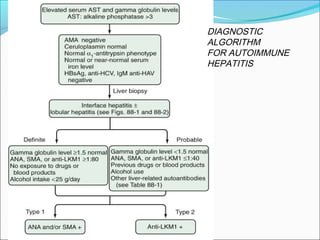
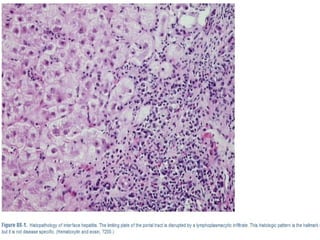
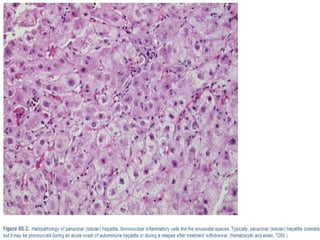
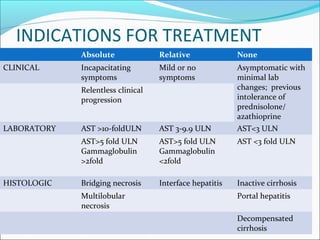
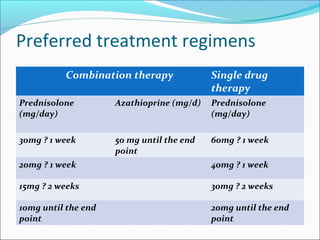
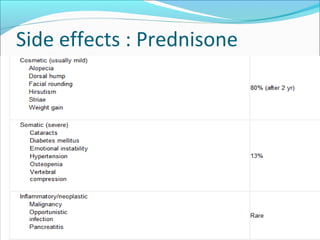
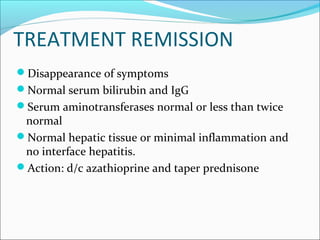
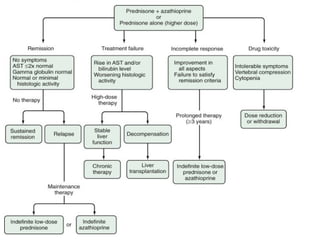
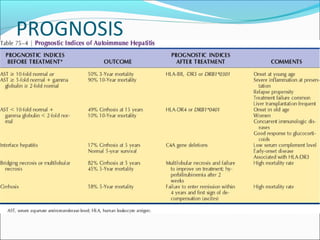
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver disease characterized by autoimmune destruction of the liver. It is diagnosed based on the presence of autoantibodies, elevated serum globulins, and evidence of hepatitis on liver biopsy after excluding other causes. The disease affects women more than men and can progress to cirrhosis if untreated. Treatment involves immunosuppression with corticosteroids and azathioprine to induce and maintain remission.