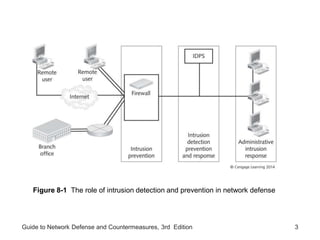
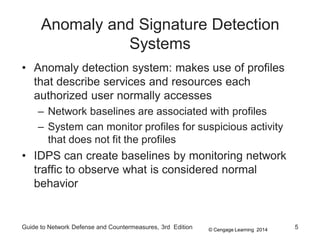
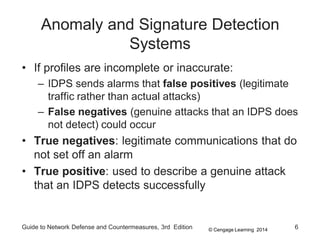
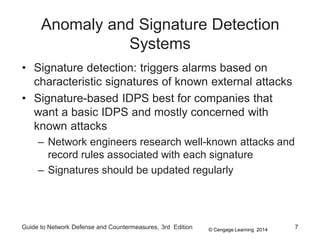
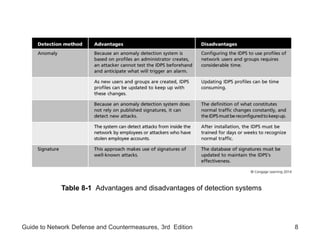
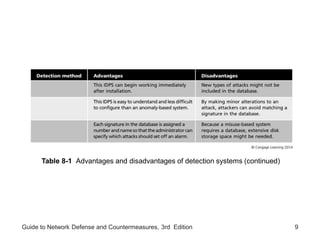
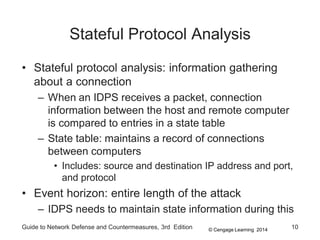
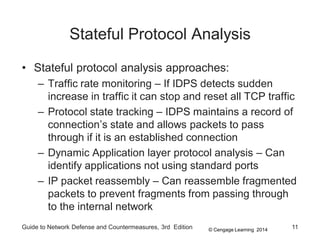
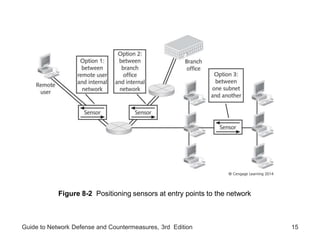
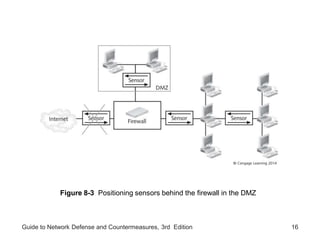
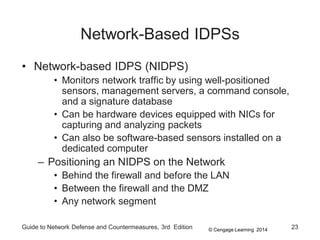
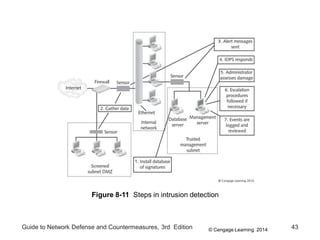
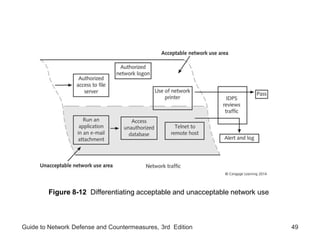
Chapter 8 of the 'Guide to Network Defense and Countermeasures' focuses on Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS), outlining their goals and functionalities such as detecting unauthorized access and generating logs. It discusses different detection methods, including anomaly and signature detection, as well as the roles of various components like network sensors, command consoles, and action responses to detected threats. The chapter emphasizes the importance of regular updates to detection signatures and the configuration of IDPS to enhance network security effectively.