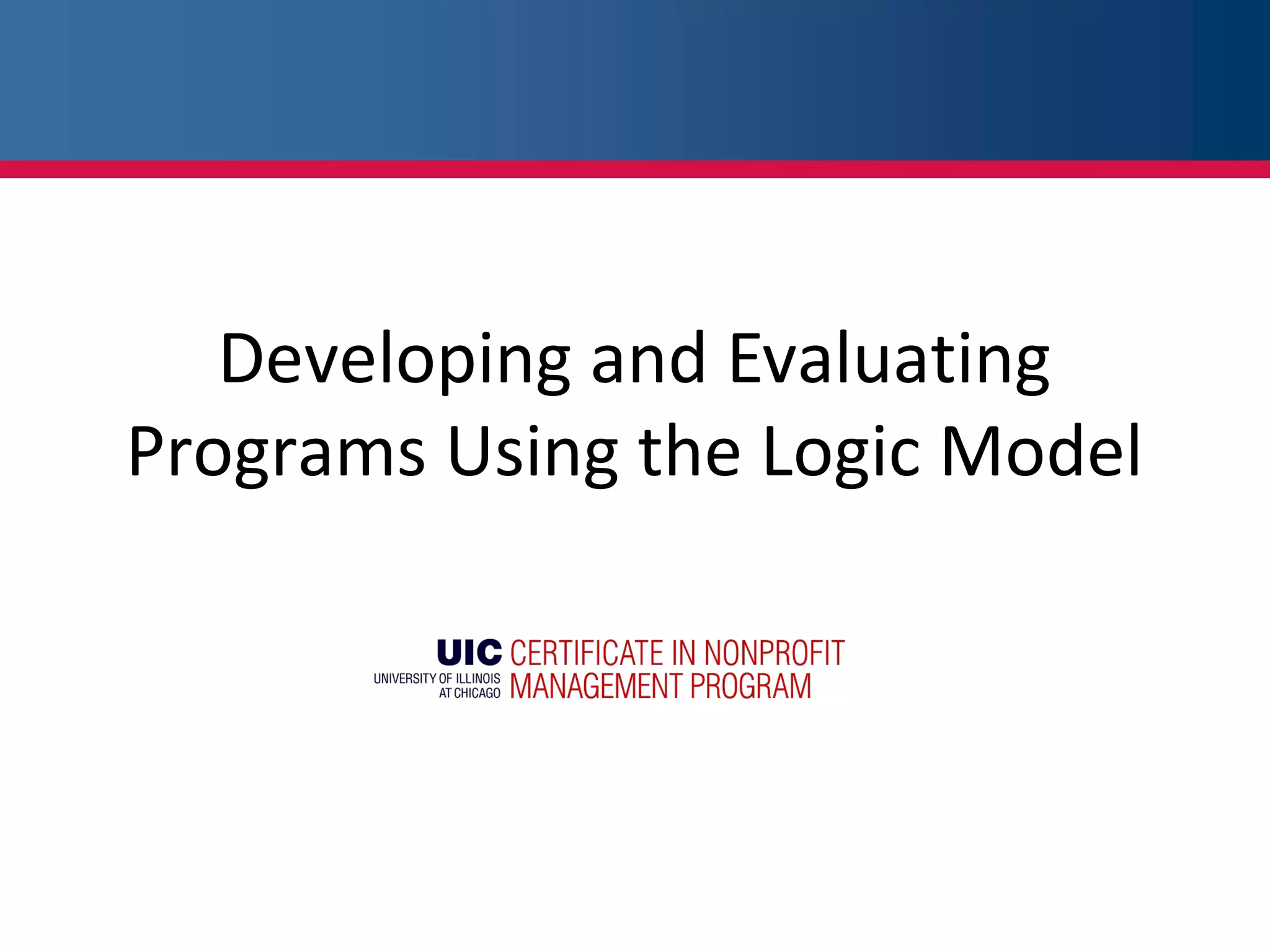
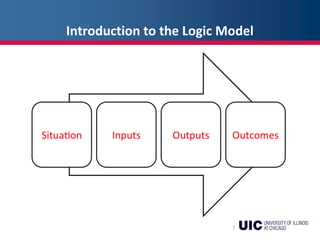
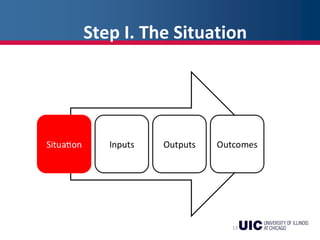
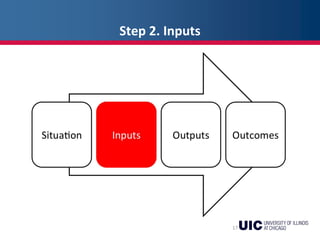
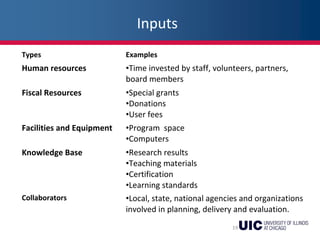
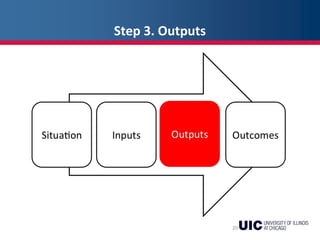
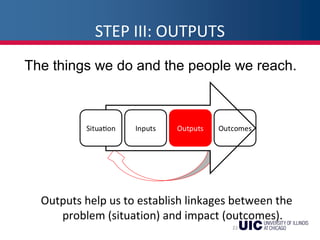
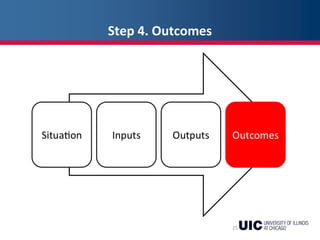
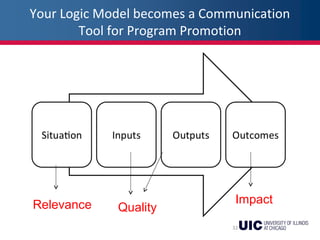
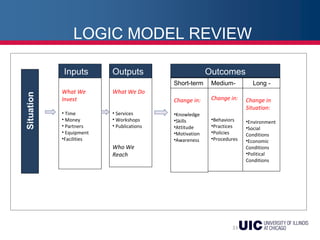
This document provides an overview of logic models and their components for program planning and evaluation. It defines the key elements of a logic model as the situation, inputs, outputs, outcomes, and assumptions. The situation establishes the problem a program aims to address. Inputs refer to the resources invested in the program. Outputs are the activities and people reached. Outcomes are the short-term, intermediate, and long-term results of the program. Assumptions recognize beliefs about how the program will work. A logic model displays the relationships between these elements and can be used as a communication tool.