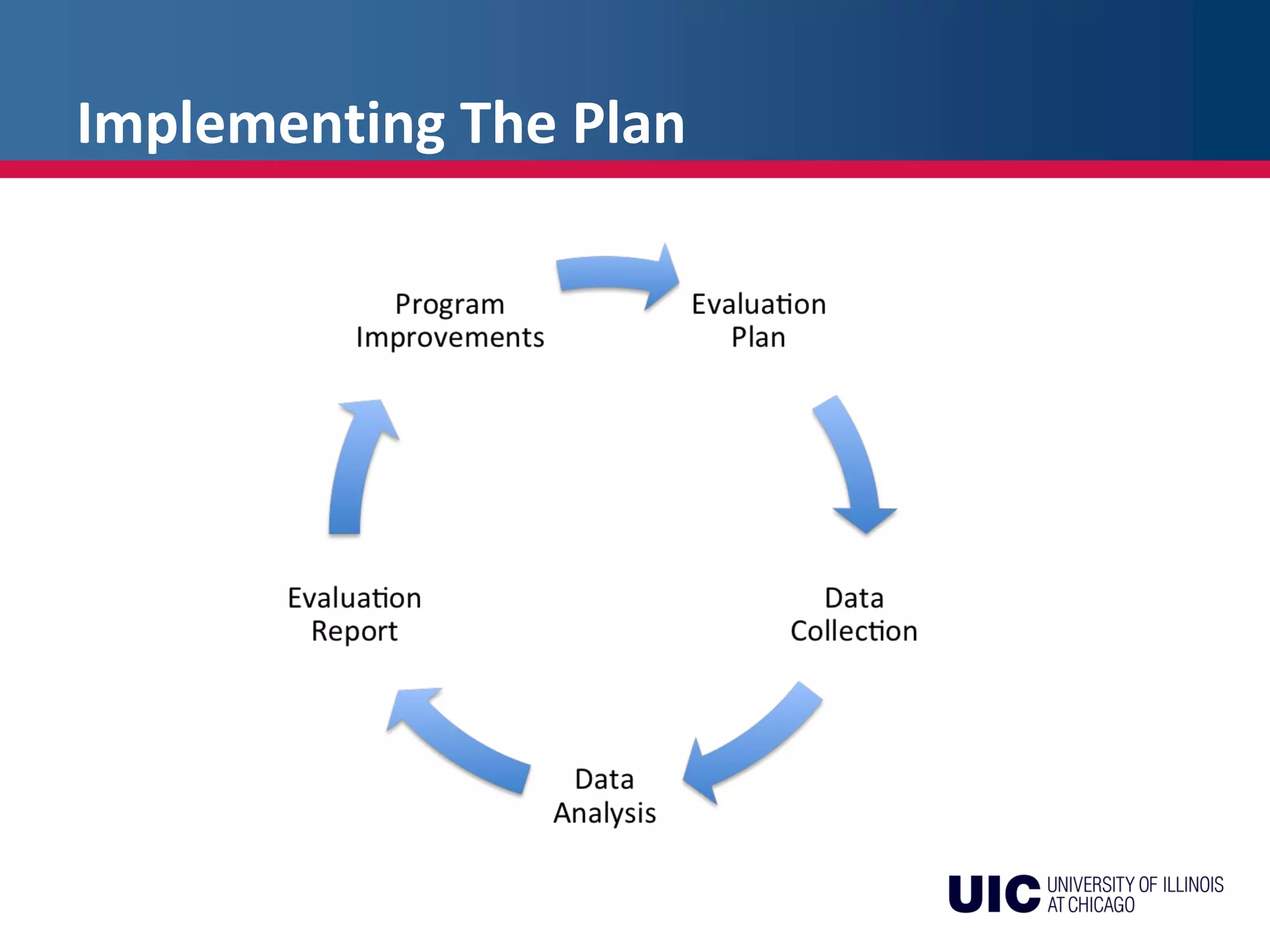
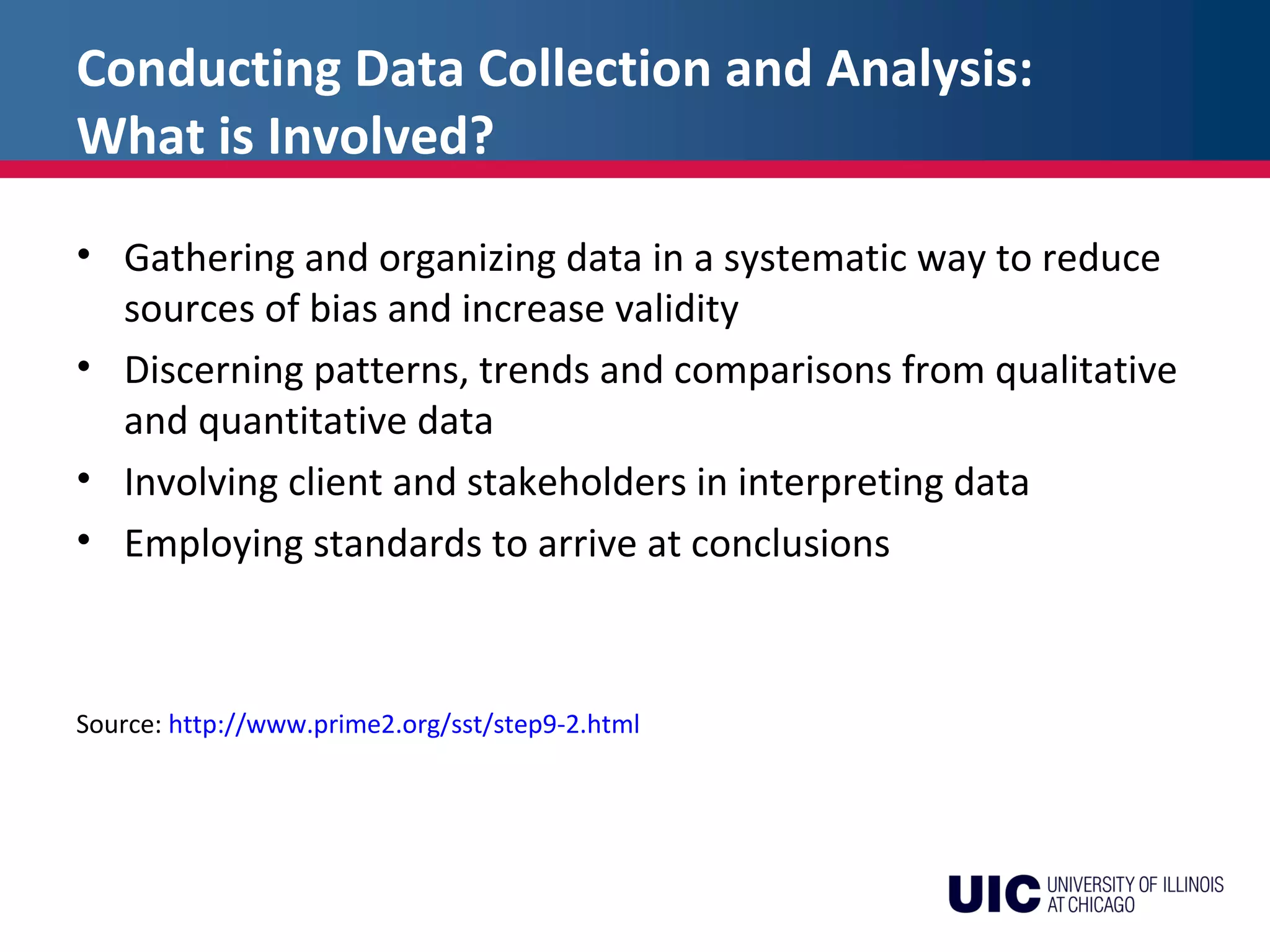
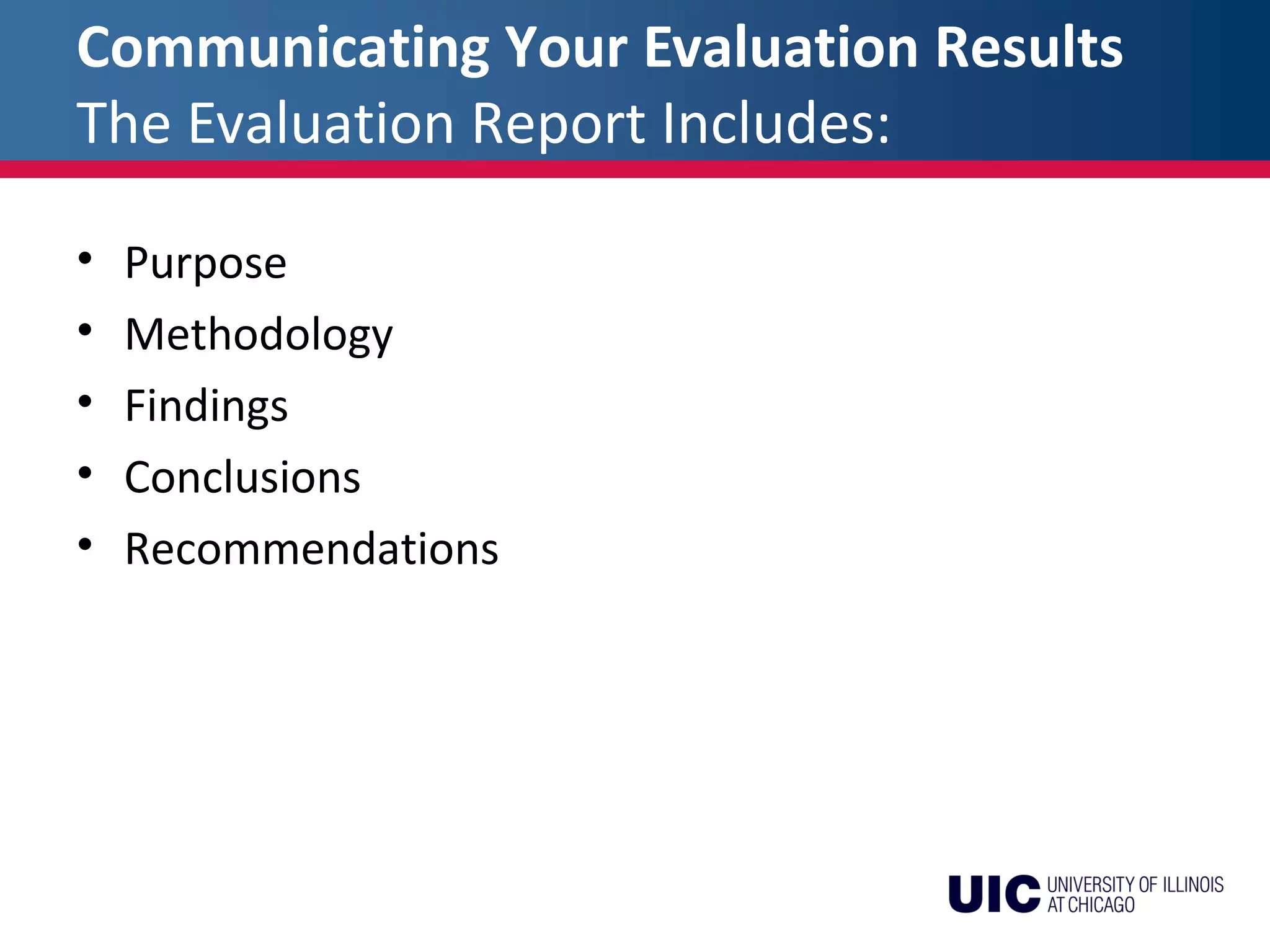
The document discusses the key steps in developing an effective evaluation plan, including identifying stakeholders, budgeting, establishing procedures, collecting and analyzing data, reporting results, and using the evaluation to improve programs. An evaluation plan should identify evaluation questions, data needs, collection methods, timelines, and staffing. It should produce a report that clearly presents changes, their causes, costs, and recommendations for strengthening the program. Avoiding pitfalls like attribution errors and using all collected data helps ensure an useful evaluation.