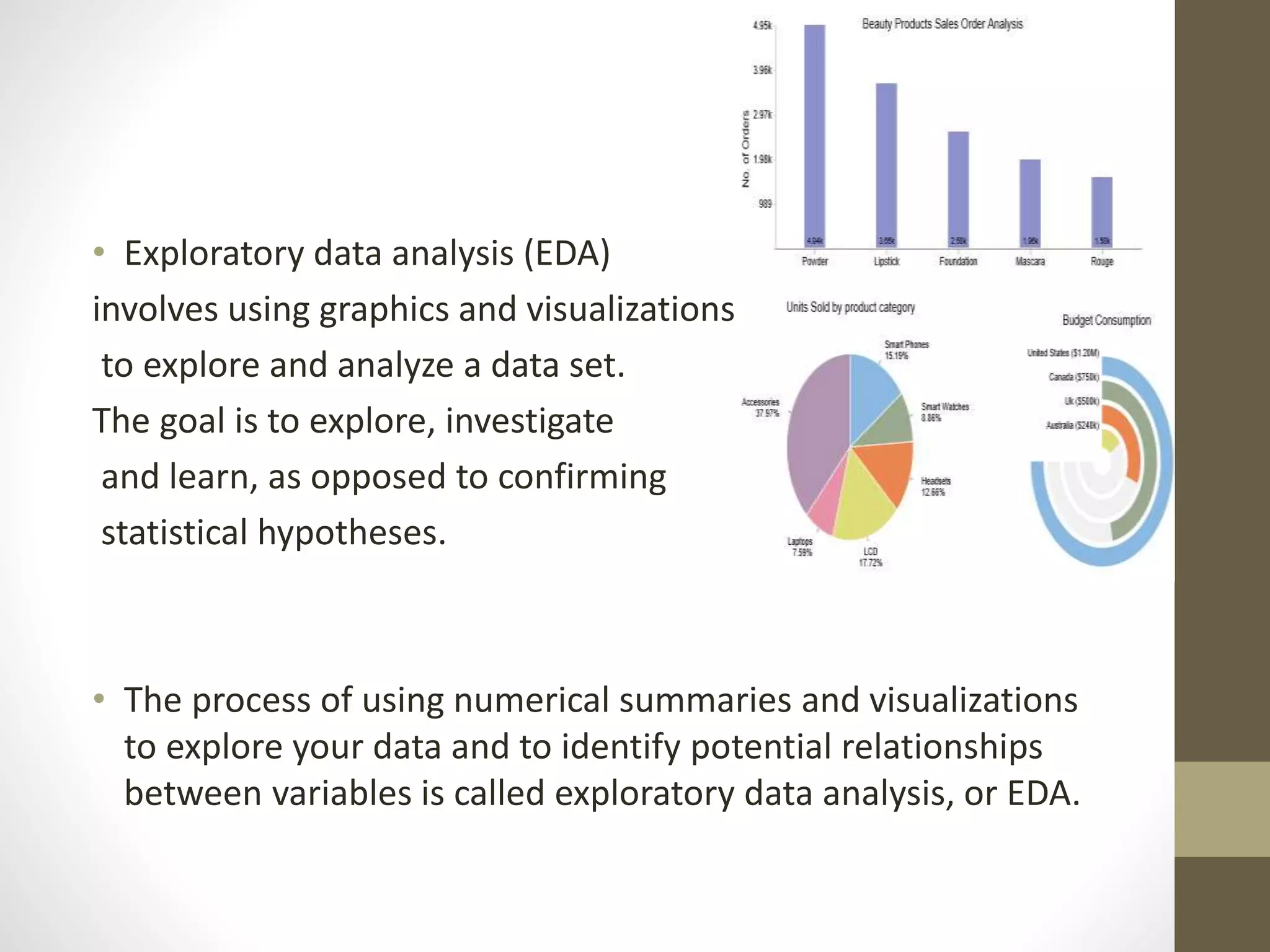
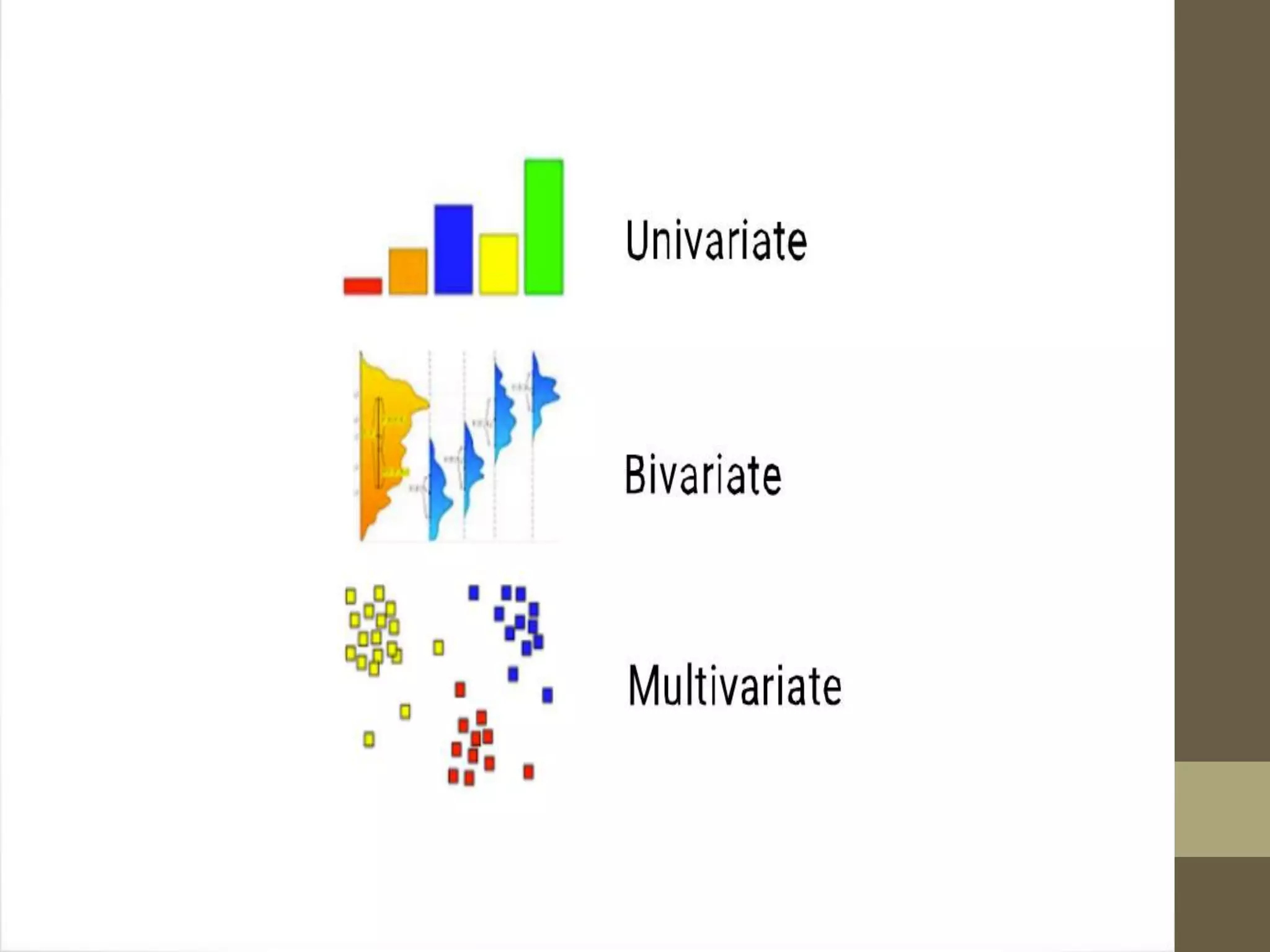
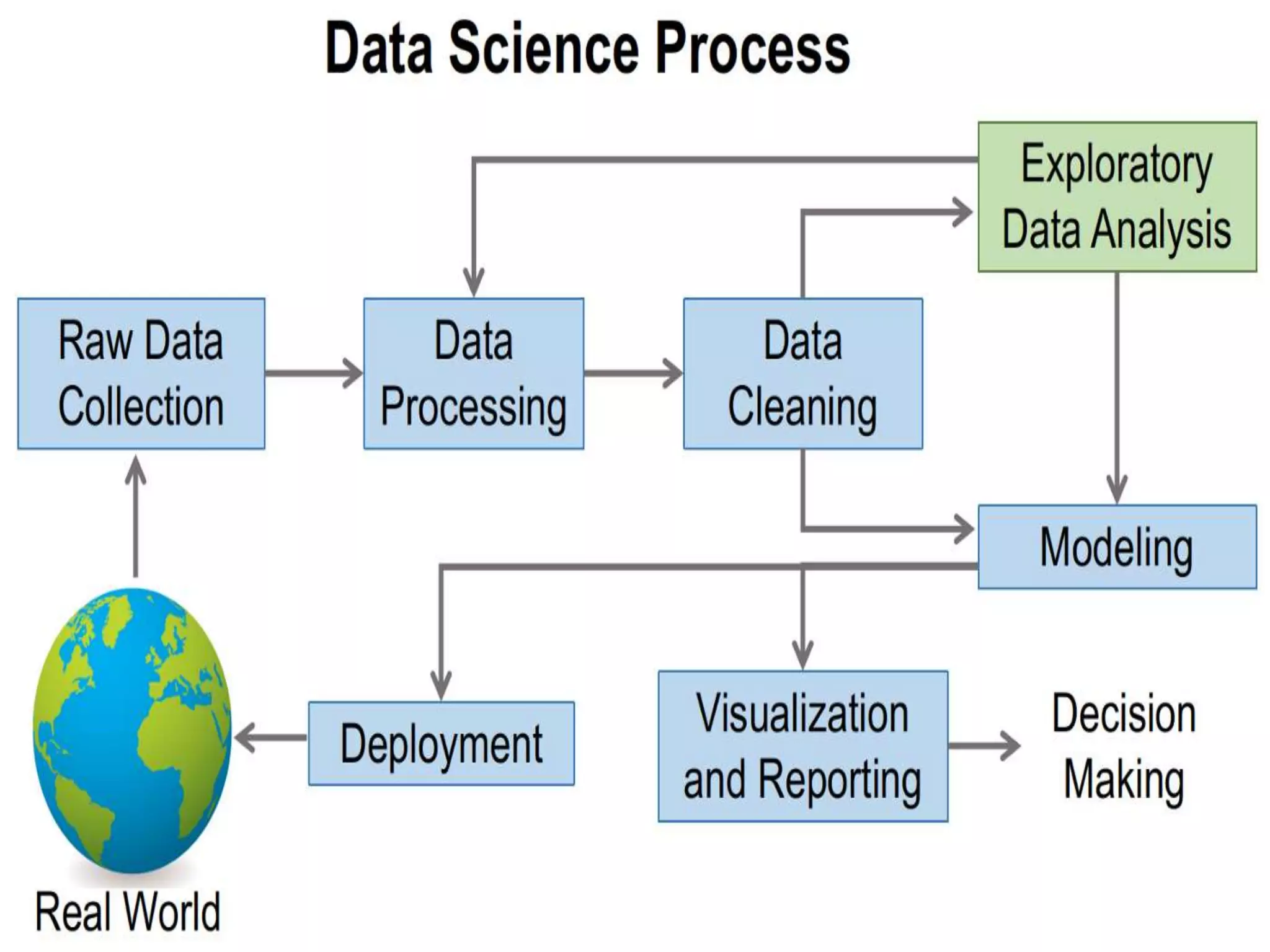
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) involves using graphics and visualizations to explore and analyze a data set without confirming statistical hypotheses. EDA uses numerical summaries and visualizations to explore relationships between variables and identify potential relationships. EDA techniques include univariate and multivariate graphical and non-graphical analysis to understand variable distributions, relationships, outliers, and patterns over time. Common EDA tools include R and Python for tasks like missing data analysis, clustering, and dimension reduction.