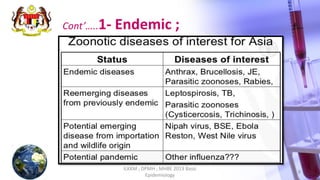
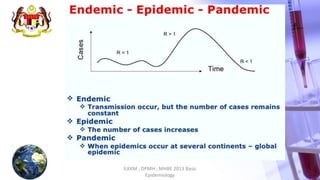
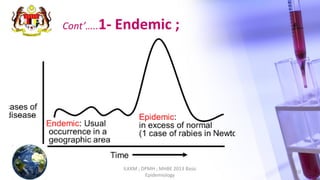
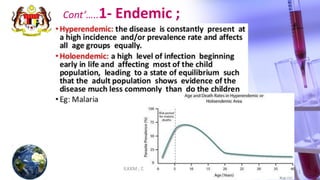
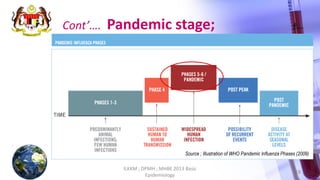
This document discusses patterns of disease occurrence, including endemic, epidemic, and pandemic diseases. It defines each term and provides examples. Endemic diseases have a constant presence in a population within an area. Epidemics occur when a disease exceeds normal levels in a community or region. Pandemics are global epidemics that spread over multiple countries. The document outlines the World Health Organization's phases of a pandemic and describes pandemics such as the 2009 H1N1 influenza outbreak. It recommends references for further reading on epidemiology concepts.