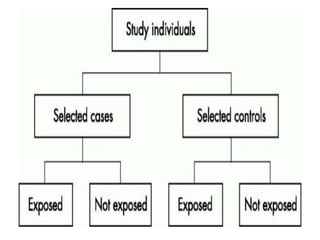
This document defines epidemiology and describes its aims and methods. Epidemiology is defined as the study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states in populations and the application of this study to control health problems. The main aims of epidemiology are to describe population health status, explain disease etiology, predict disease occurrence, control disease distribution, and promote health. Descriptive epidemiology involves describing diseases in terms of time, place, and person, while analytical epidemiology aims to determine causal factors through observational studies like cohort and case-control studies.