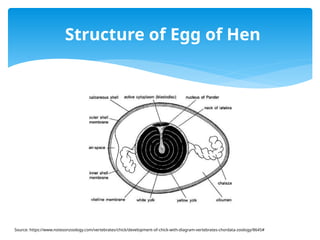
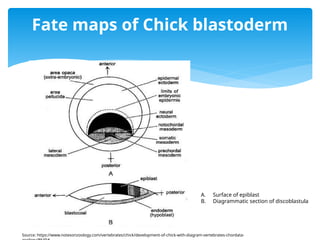
The document discusses the significance of chick embryos (Gallus gallus domesticus) in developmental biology, particularly concerning axes and pattern formation during early development. Key processes include the establishment of the anterior-posterior, dorsal-ventral, and left-right axes, which are guided by signaling centers such as the primitive streak and Hensen's node. Additionally, factors like BMP signaling, nodal expression, and the influence of the zone of polarizing activity are highlighted in the context of organ symmetry and limb patterning.