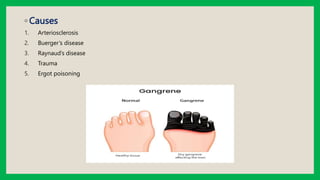
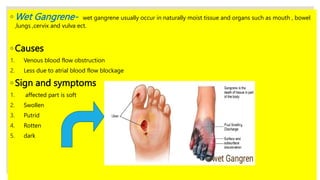
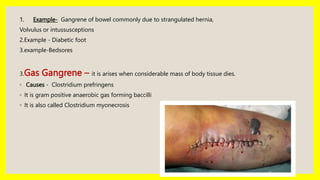
Gangrene is the death of body tissue due to reduced blood flow or infection. There are three main types: dry gangrene caused by blocked arteries, wet gangrene which affects moist tissues from blocked veins, and gas gangrene caused by Clostridium bacteria. Signs include black, shrunken tissue in dry gangrene; soft, swollen tissue in wet gangrene; and blisters with foul smell in gas gangrene. Treatment involves antibiotics, supportive care like IV fluids, and potentially amputation or angioplasty depending on the severity and type of gangrene.