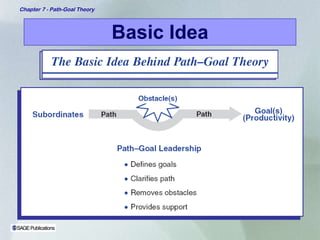
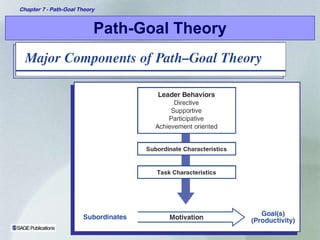
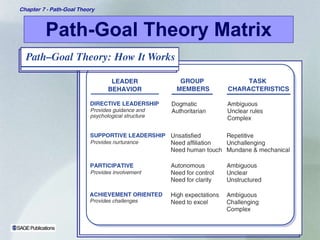
Path-goal theory proposes that a leader's job is to help subordinates reach their goals by directing, guiding, and coaching them based on an evaluation of subordinate and task characteristics. The theory suggests which leadership styles of directive, supportive, participative, or achievement-oriented are most appropriate given the characteristics of the subordinates and the task. Path-goal theory provides a framework to understand how leadership behaviors can motivate subordinates by influencing their expectations and perceptions of work goals, pathways, and environmental factors.