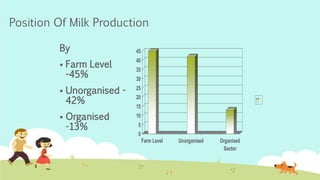
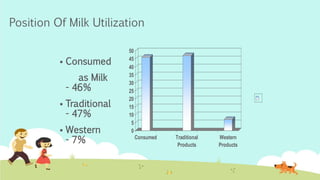
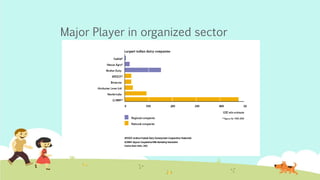
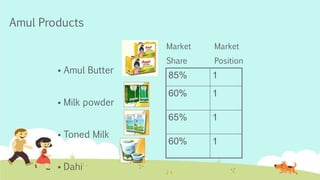
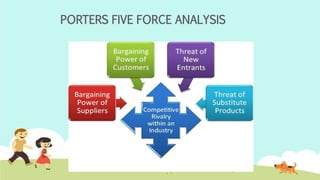
India is the largest producer of milk in the world. The dairy industry is one of the fastest growing sectors in India, valued at over $26 billion. Amul is the largest player in the organized sector, with market shares of over 80% for products like butter and cheese. It was formed in 1946 as a cooperative and now has over 2.5 million producer members. Mother Dairy is the largest regional player, sourcing milk from dairy cooperatives and marketing products under its brand. The dairy industry faces high competitive rivalry due to numerous competitors and undifferentiated products.