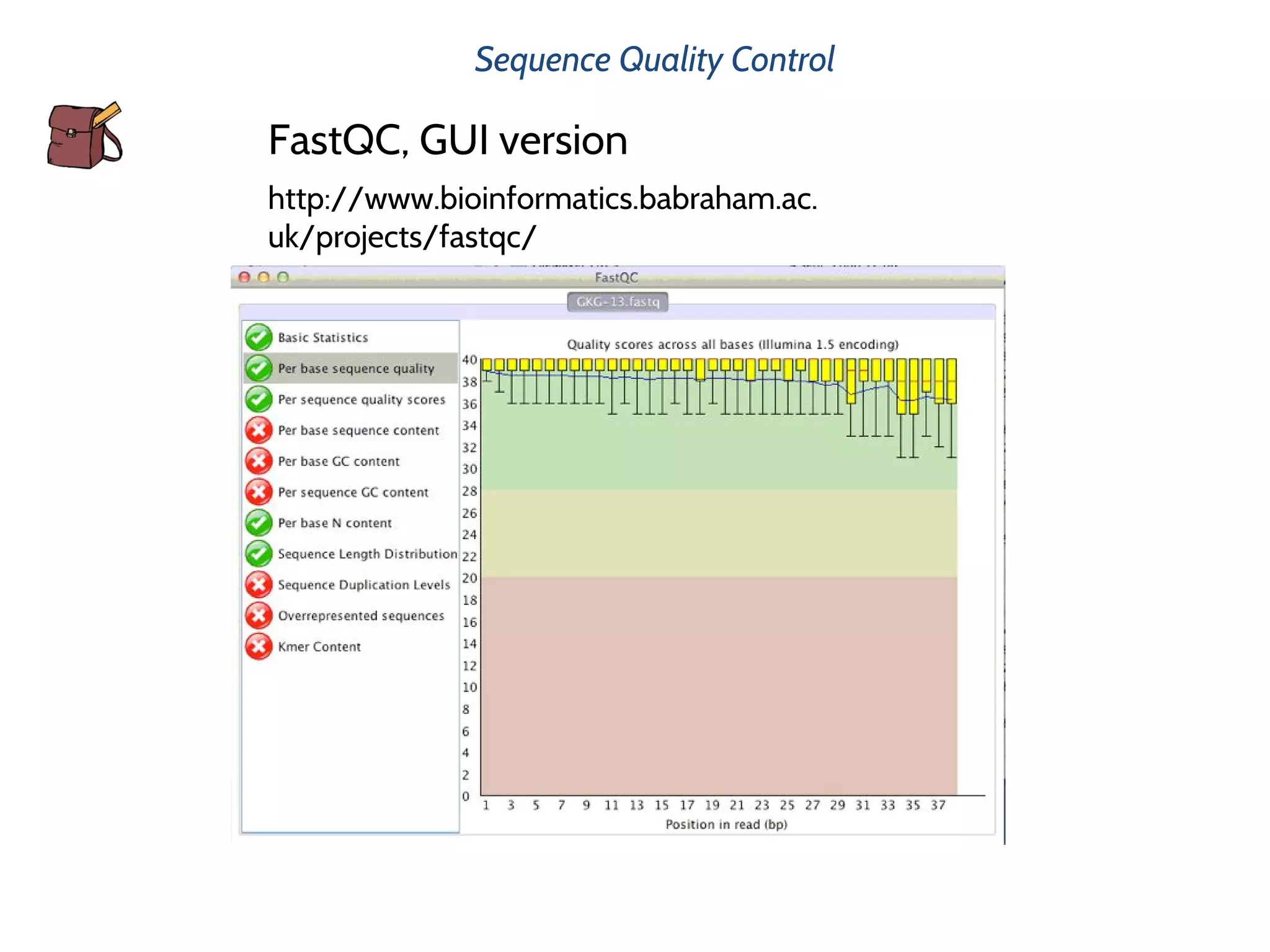
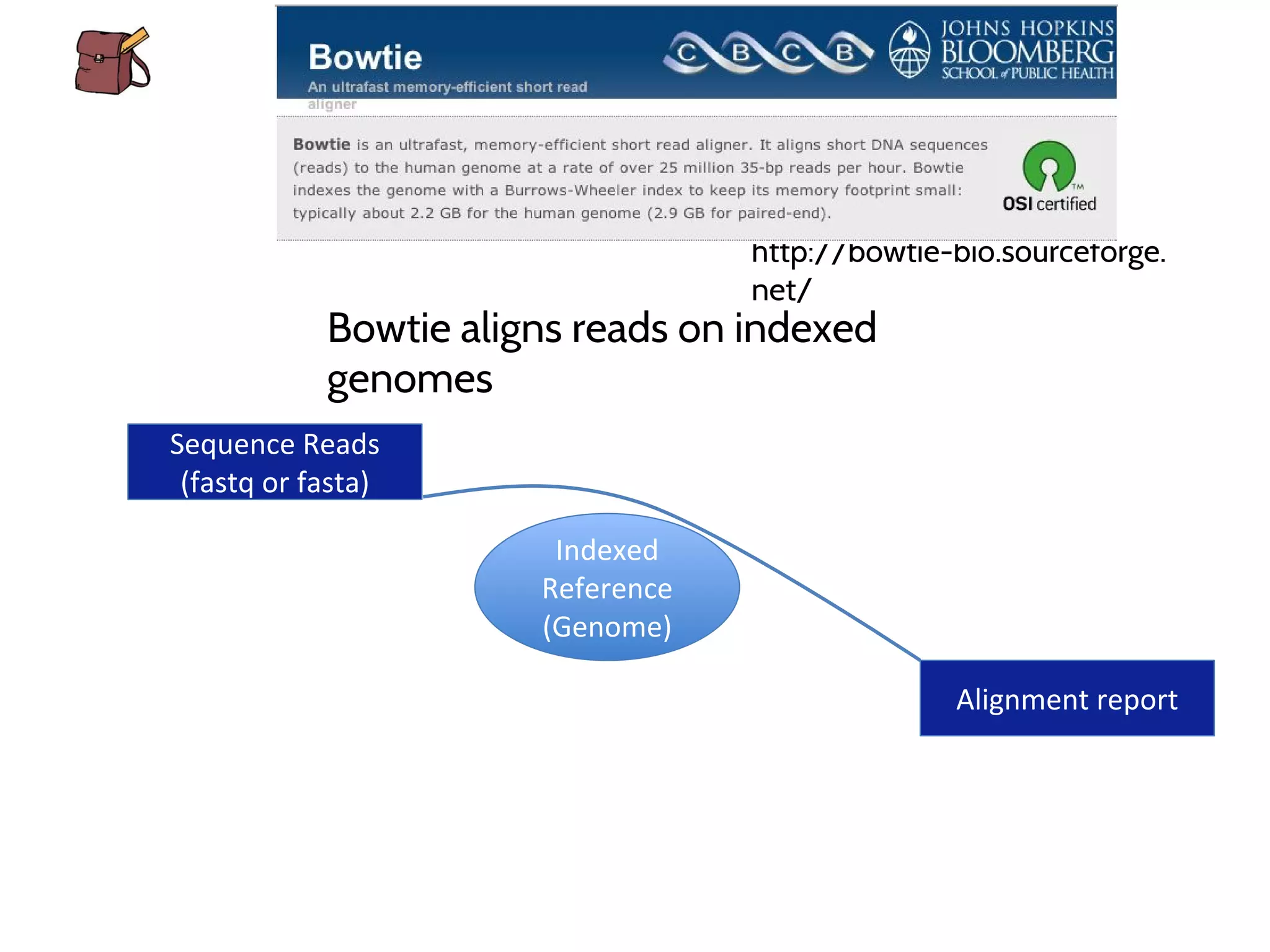
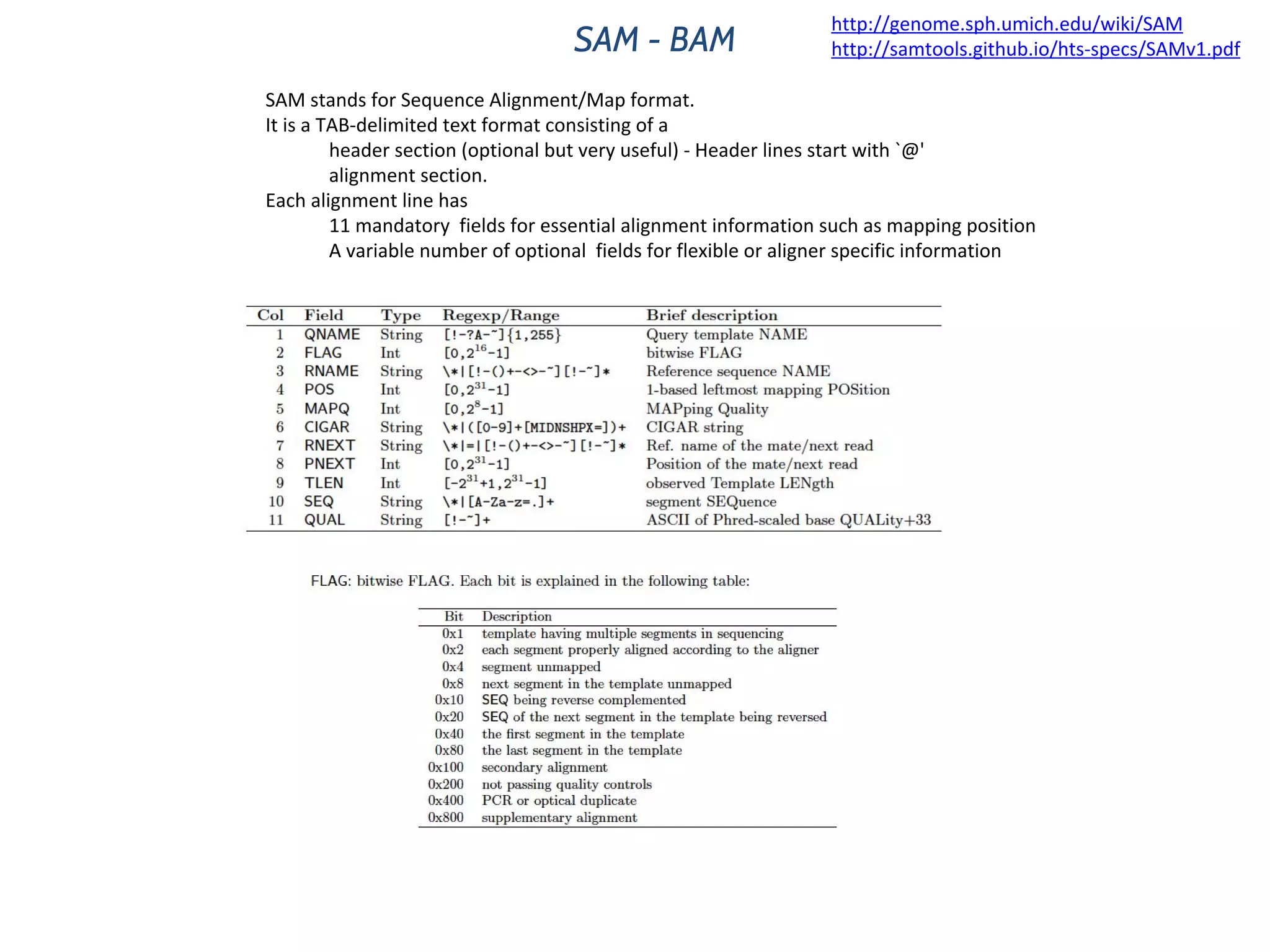
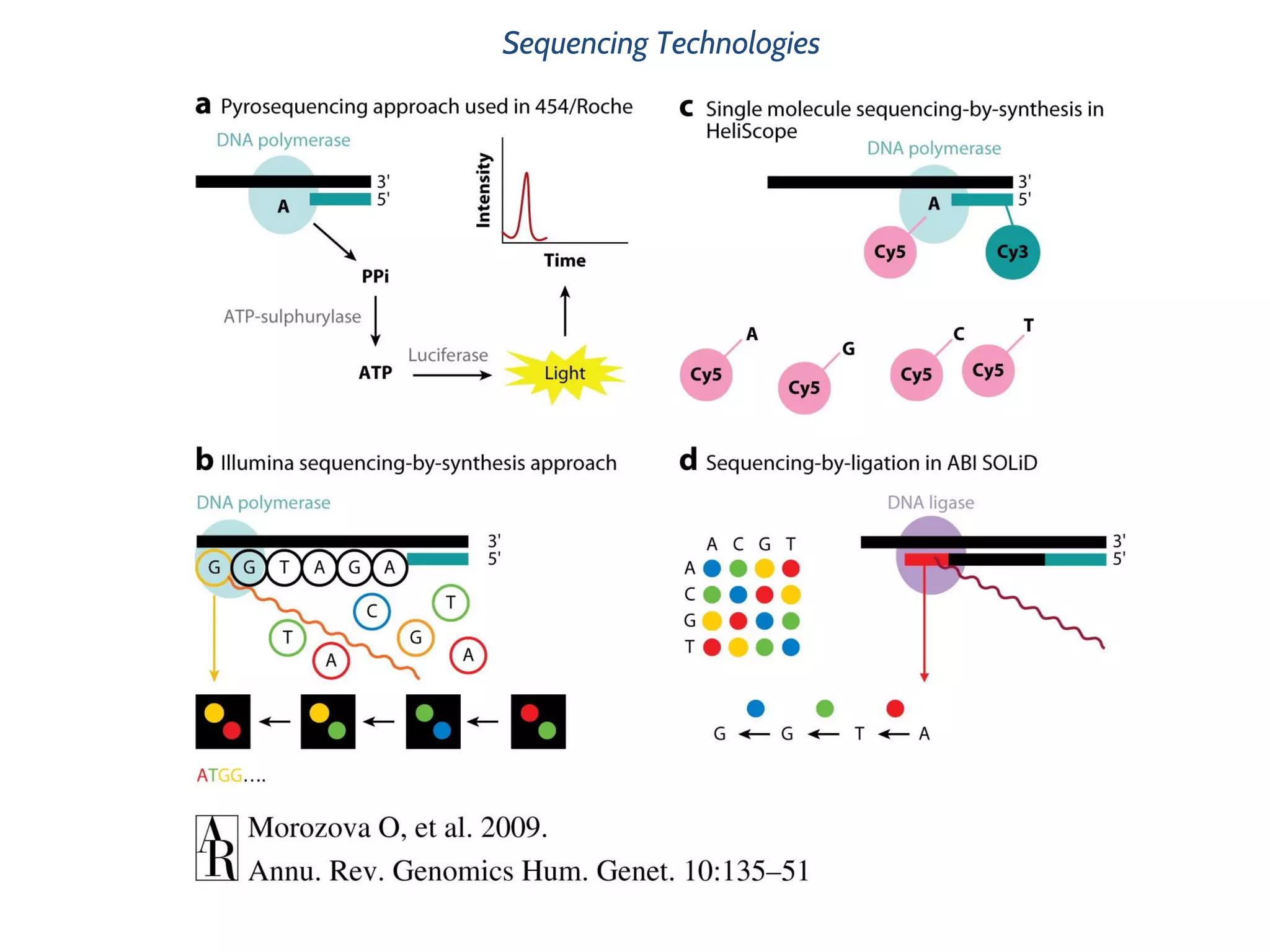
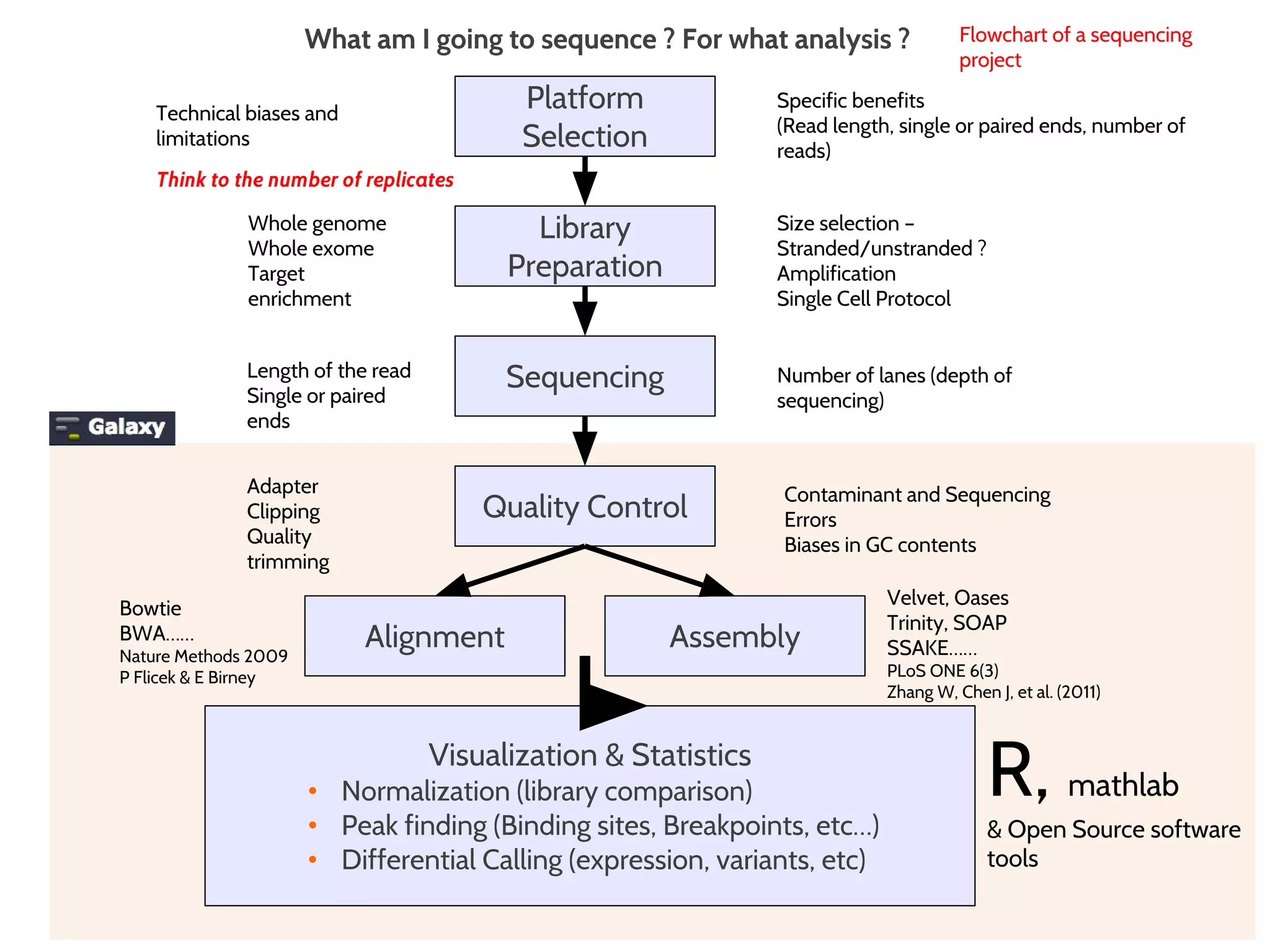
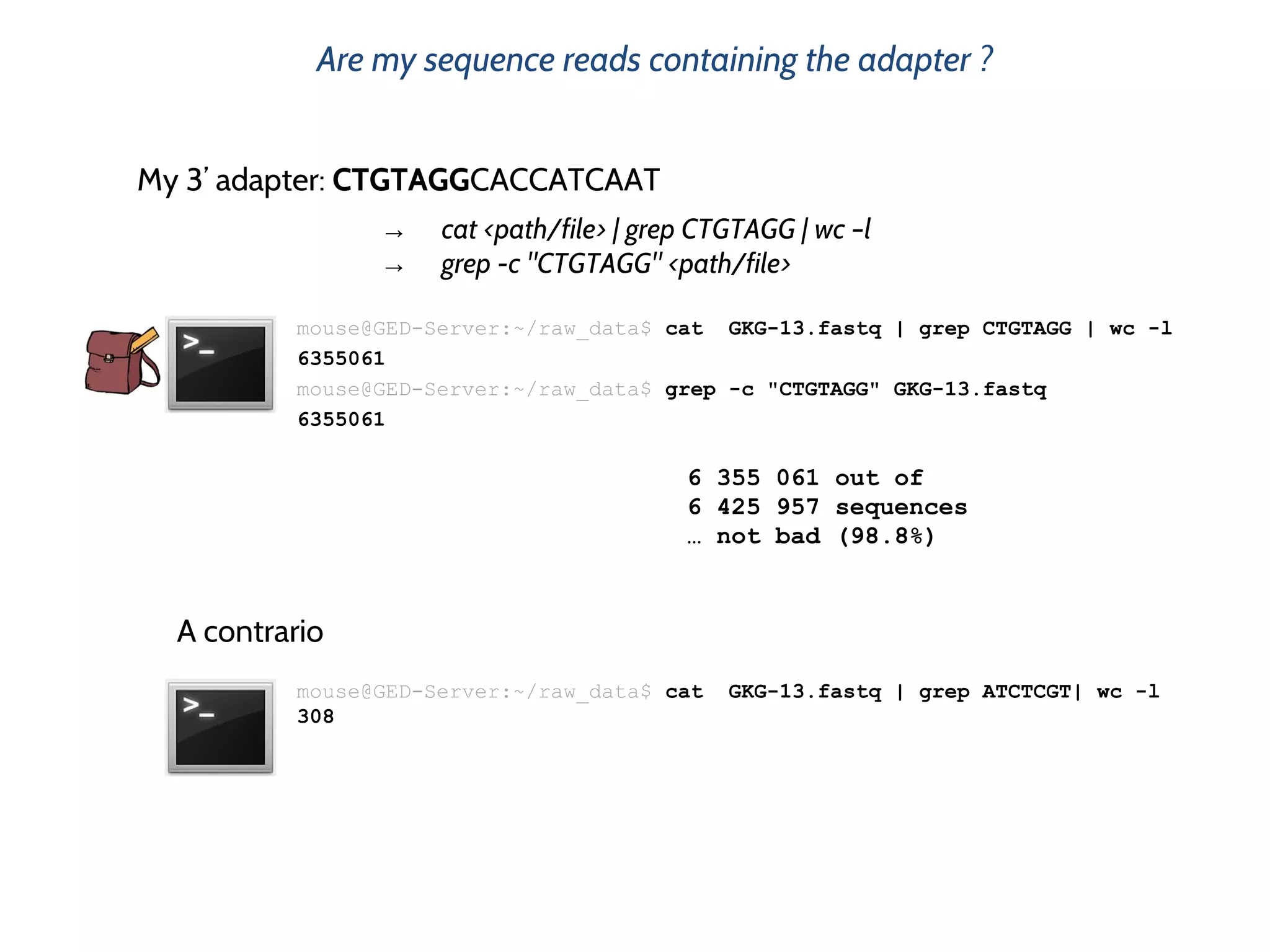
This document provides an overview of deep sequencing data analysis. It discusses sequencing technologies like Ion Torrent and Illumina, library preparation, alignment, and common file formats. It also demonstrates commands for quality control like FastQC, alignment with Bowtie, and working with the output files including SAM, BAM, pileup formats. Next steps discussed are accessing the Galaxy analysis framework and server to perform an NGS analysis project.







![What is this big* fastq file containning ?
→
→
…
…
...
mouse@GED-Server:~/raw_data$ more GKG-13.fastq
@HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:3019:1114#AGAAGA/1 Header
TNGGAACTTCATACCGTGCTCTCTGTAGGCACCATCAA Sequence
+HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:3019:1114#AGAAGA/1 Header
bBb`bfffffhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhfhhhhhhgh Sequence Quality (ASCII encoded)
@HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:3925:1114#AGAAGA/1
TNCTTGGACTACATATGGTTGAGGGTTGTACTGTAGGC
+HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:3925:1114#AGAAGA/1
]B]VWaaaaaagggfggggggcggggegdgfgeggbab
@HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:6220:1114#AGAAGA/1
TNGGAACTTCATACCGTGCTCTCTGTAGGCACCATCAA
+HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:6220:1114#AGAAGA/1
aB^^afffffhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhchhhh
@HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:6252:1115#AGAAGA/1
TNCTTGGACTACATATGGTTGAGGGTTGTACTGTAGGC
+HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:6252:1115#AGAAGA/1
aBa^ddeeehhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhghhhhhhhefff
@HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:6534:1114#AGAAGA/1
TNAATGCACTATCTGGTACGACTGTAGGCACCATCAAT
+HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:6534:1114#AGAAGA/1
aB^^eeeeegcggfffffffcfffgcgcfffffR^^]
@HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:8869:1114#AGAAGA/1
GNGGACTGAAGTGGAGCTGTAGGCACCATCAATAGATC
+HWIEAS210R_0028:2:1:8869:1114#AGAAGA/1
aBaaaeeeeehhhhhhhhhhhhfgfhhgfhhhhgga^^](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pasteurdeepseqanalysistheory2016-160117215845/75/Pasteur-deep-seq_analysis_theory_2016-14-2048.jpg)

![$mouse@GED-Server:~/raw_data$ cat GKG-13.fastq | perl -ne 'print if /^[ATGCN]{22}CTGTAGG/' | wc -l
Outputs the content
of a file, line by line
The output is passed
to the input of the
next command
perl interpreter is called
with –ne options (loop
& execute)
In line perl code
Regular expression
The output is passed
to the input of the
next command
wc with –l option
counts the lines
A more advanced example of combining Unix
commands
1 675 469 22nt long reads with 3’ flanking CTGTAGG adapter sequence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pasteurdeepseqanalysistheory2016-160117215845/75/Pasteur-deep-seq_analysis_theory_2016-17-2048.jpg)
![Clipping adapter sequences
Unix Operating Systems already contain powerful native tools for sequence analyses
cat GKG-13.fastq | perl -ne 'if (/^(.+CTGTAGG)/) {print "$1n"}' | more
mouse@GED-Server:~/raw_data$
cat GKG-13.fastq | perl -ne 'if (/^([GATC]{18,})CTGTAGG/) {$count++; print ">$countn"; print
"$1n"}' > clipped_GKG13.fasta
Final command line clipper](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pasteurdeepseqanalysistheory2016-160117215845/75/Pasteur-deep-seq_analysis_theory_2016-18-2048.jpg)