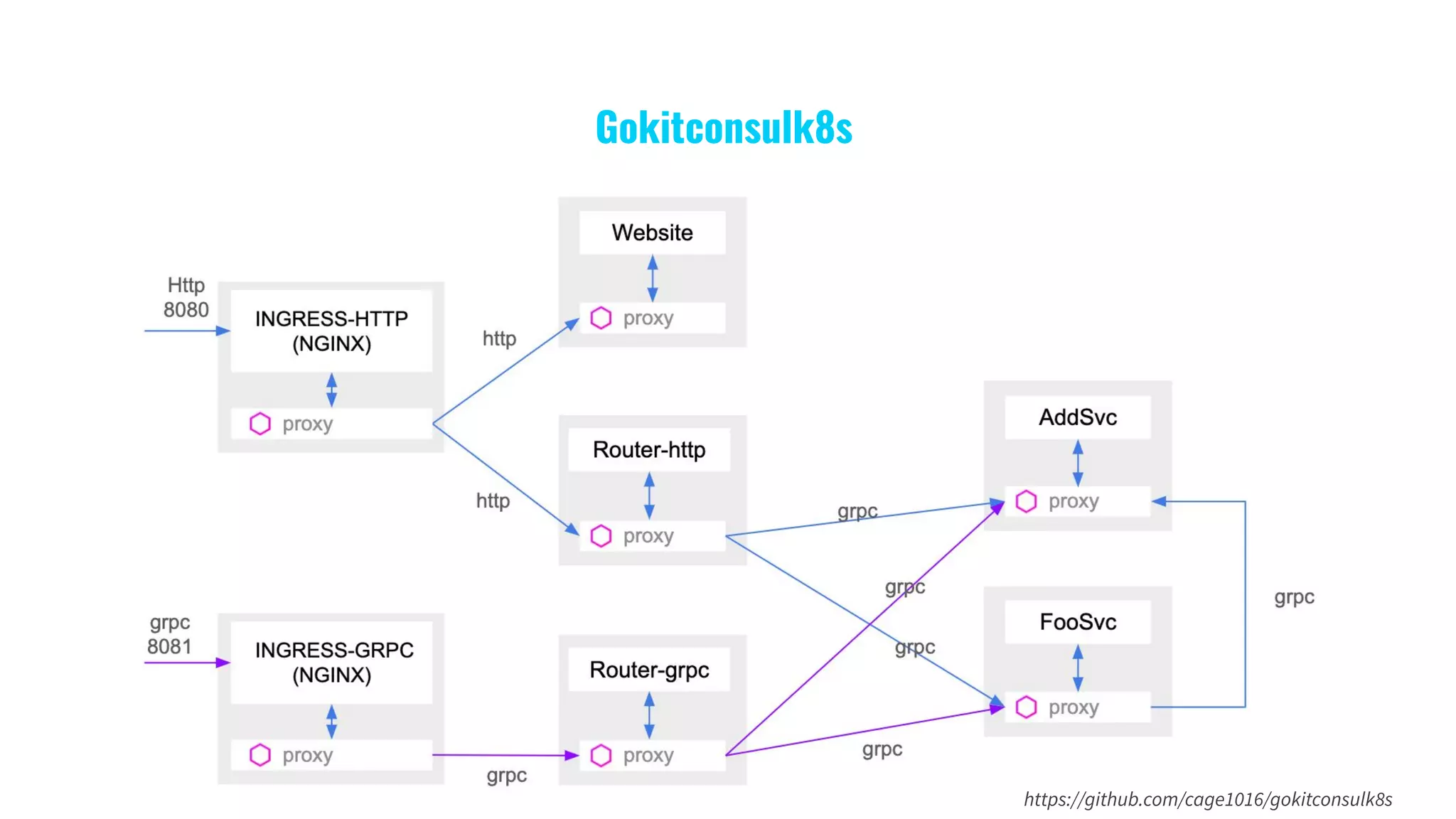
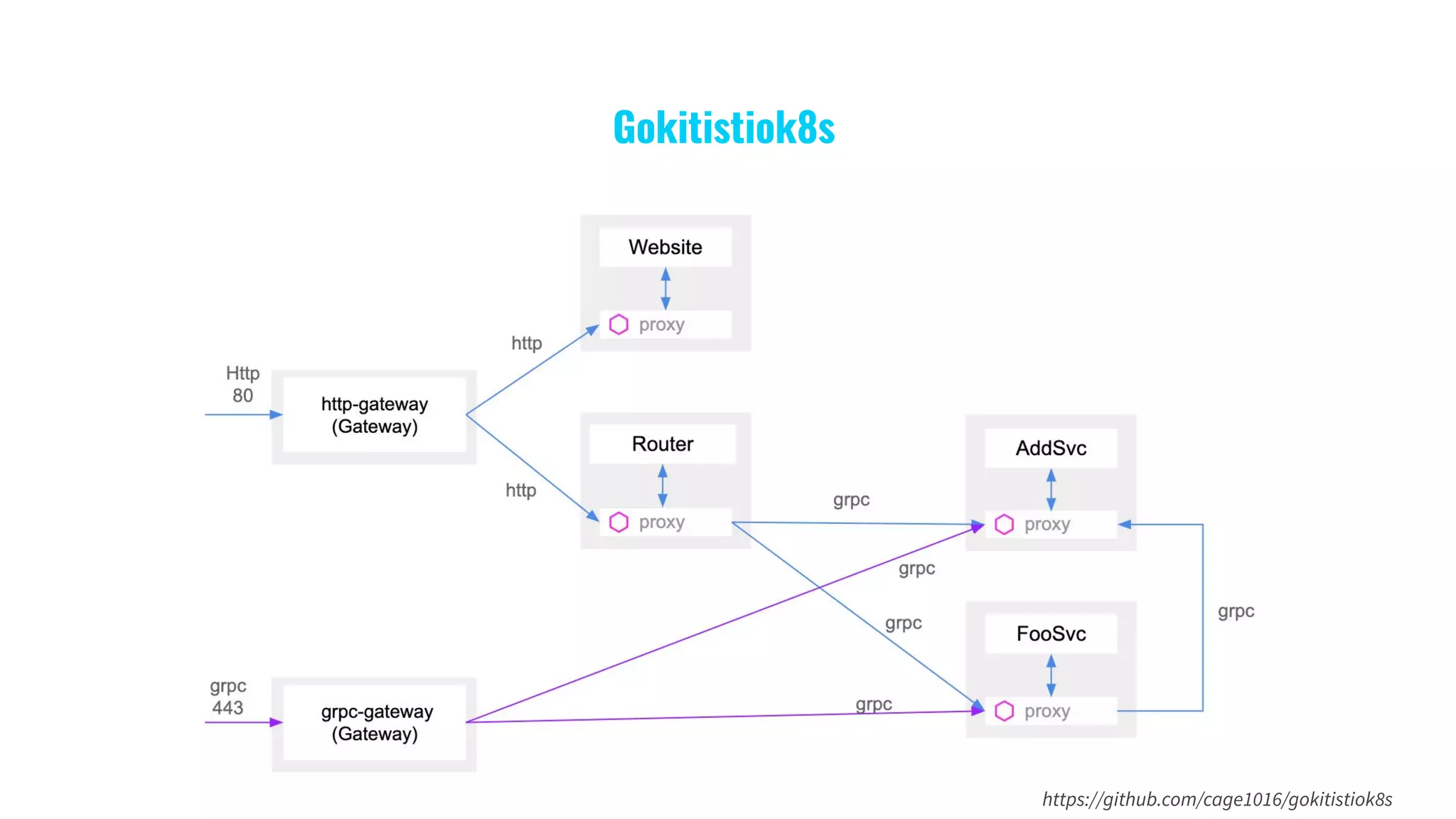
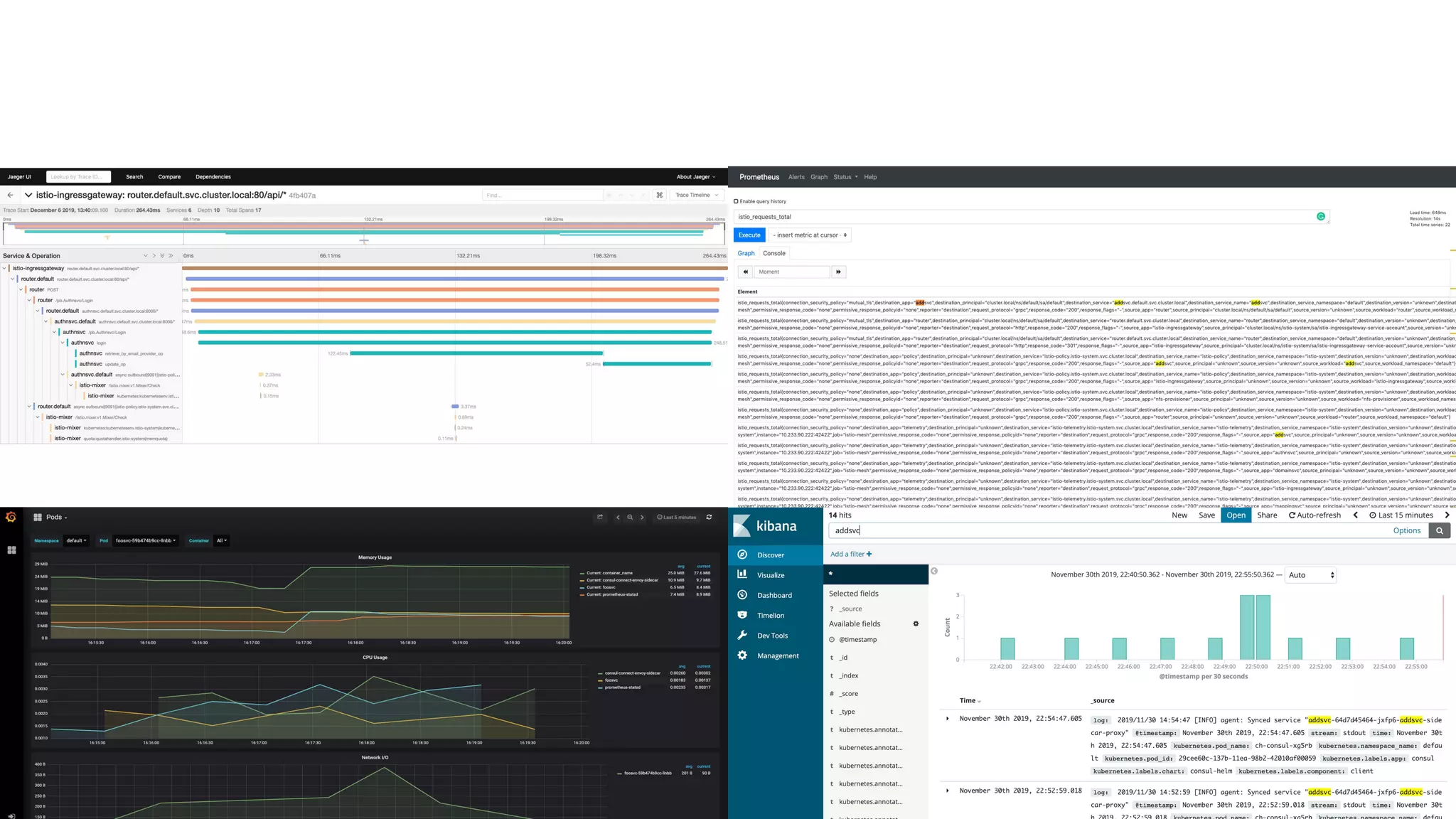
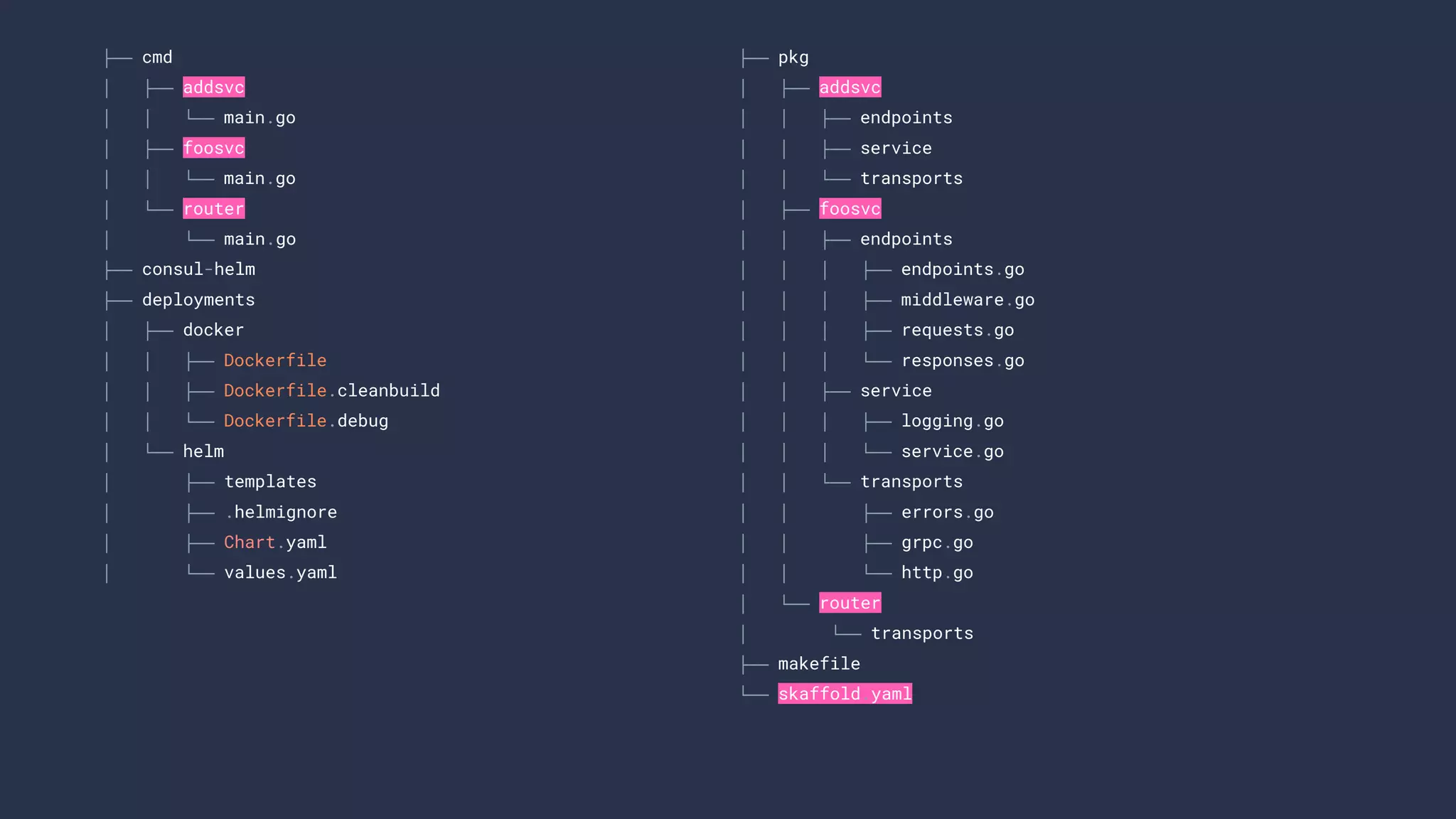
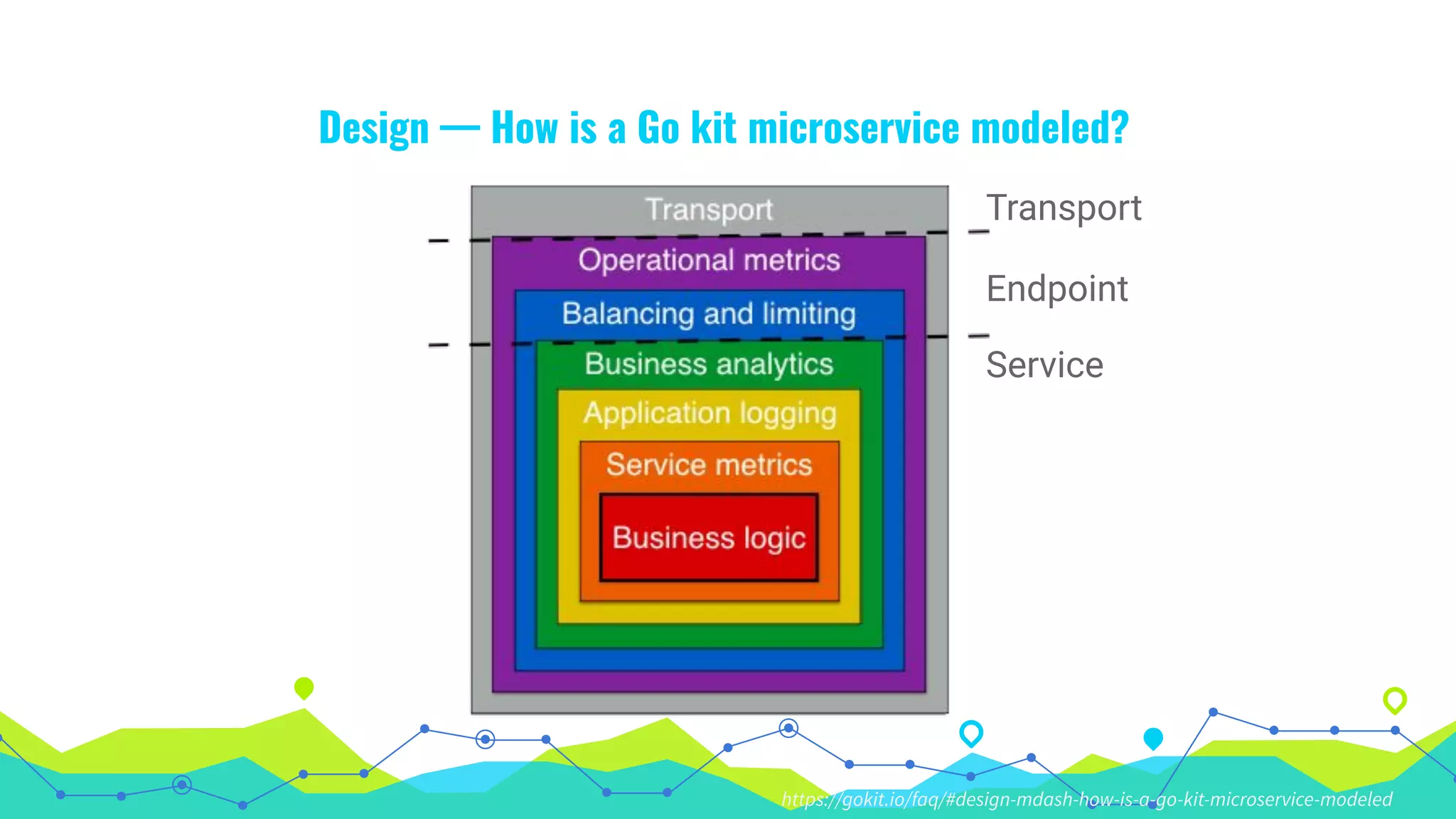
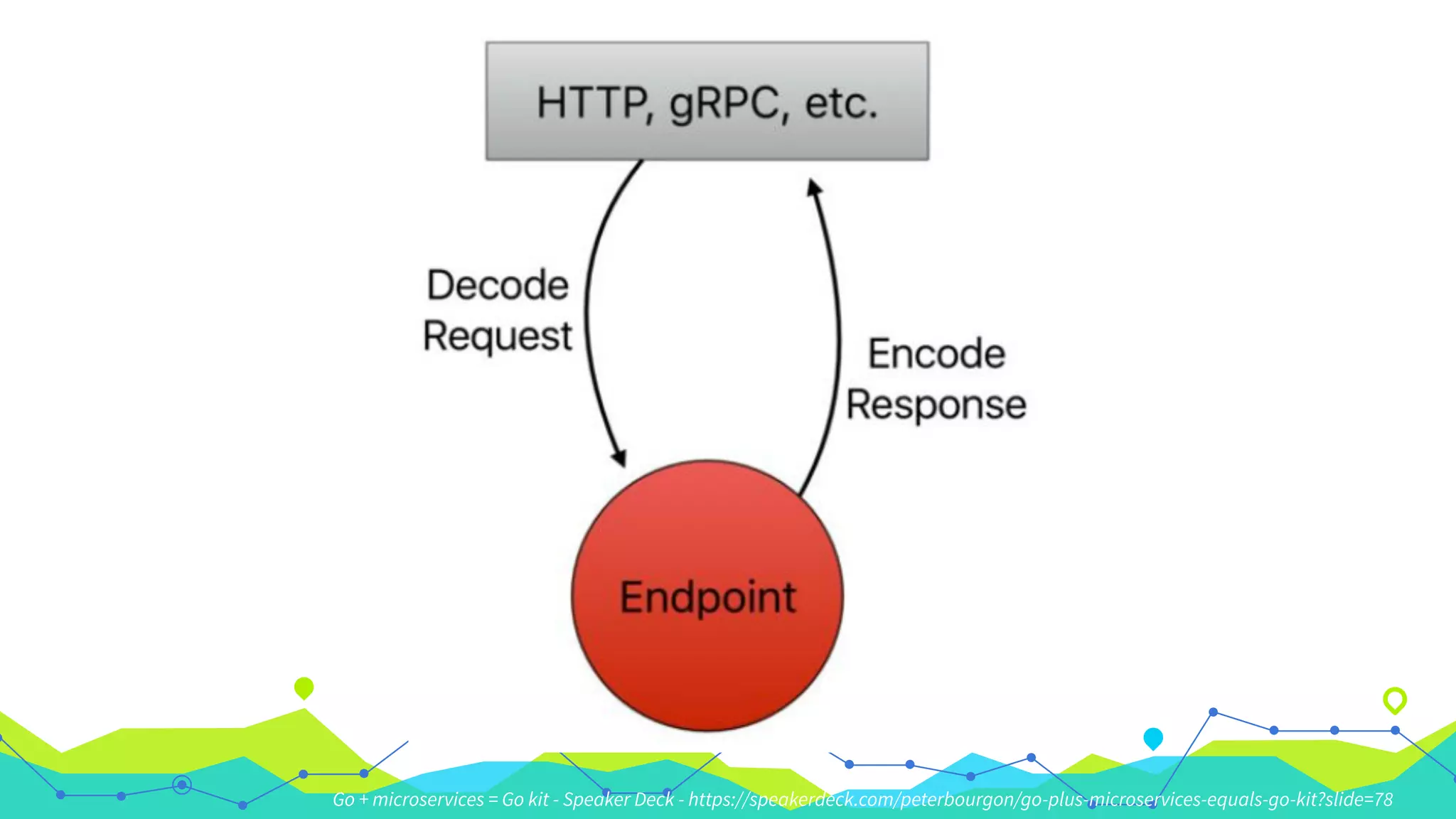
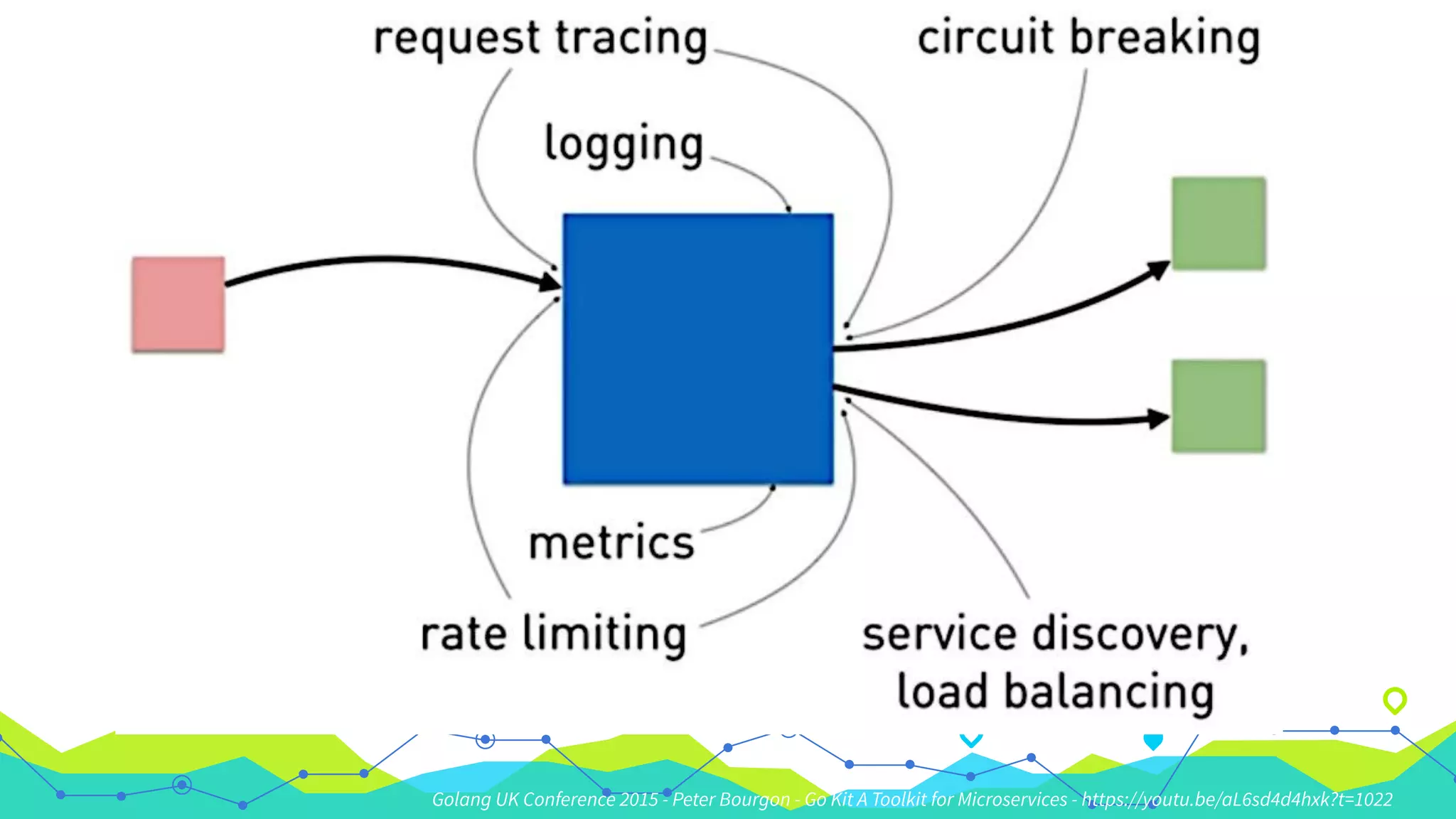
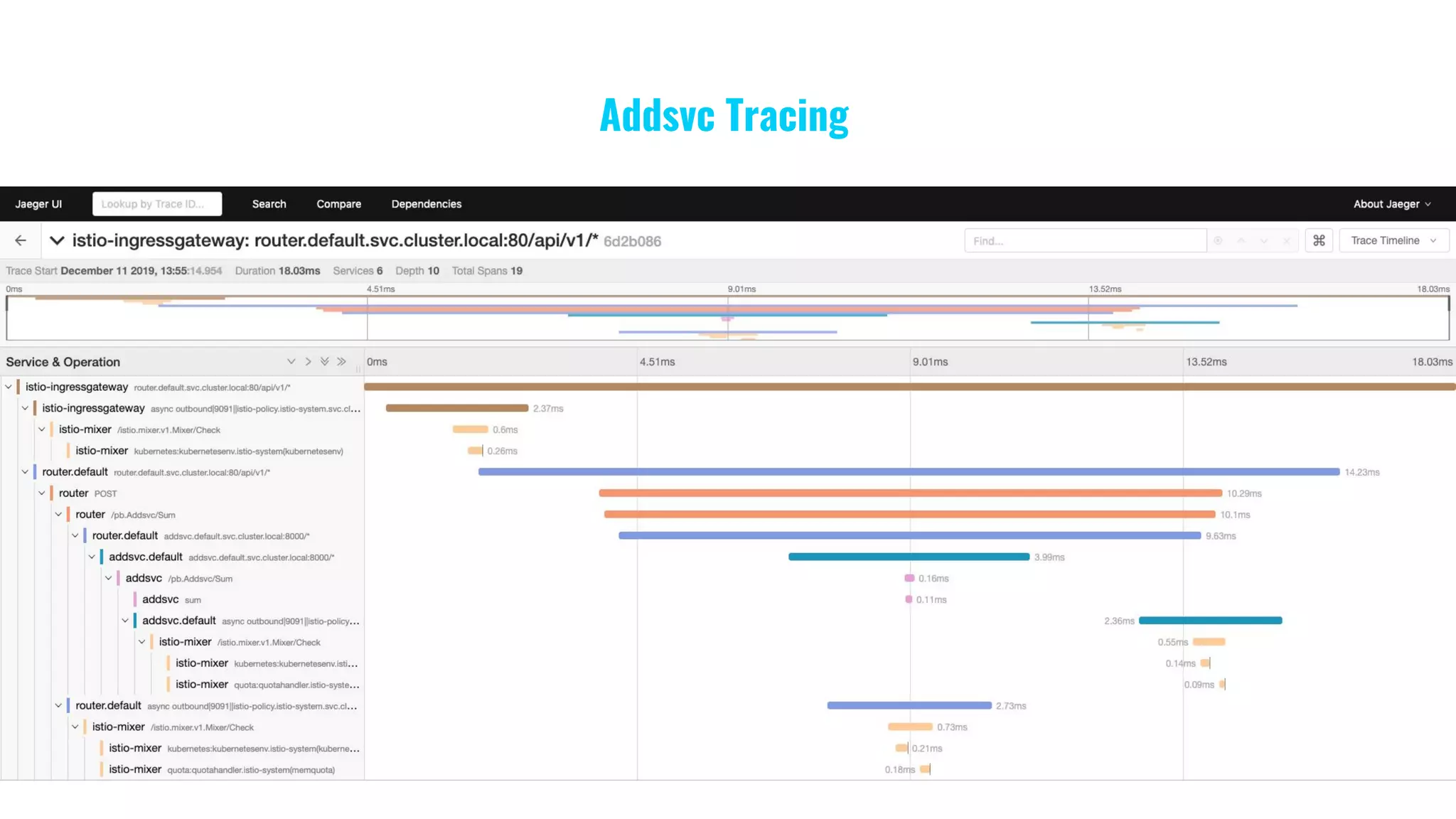
The document presents a comprehensive overview of building microservices using Go Kit and Kubernetes, integrating components such as Istio for service mesh, Jaeger for tracing, and various monitoring tools. It illustrates practical examples of HTTP and gRPC service implementations, showcases endpoint and transport designs, and discusses the challenges and solutions in microservice architecture. Additional resources and links are provided for readers to explore the Go Kit framework and service mesh concepts further.














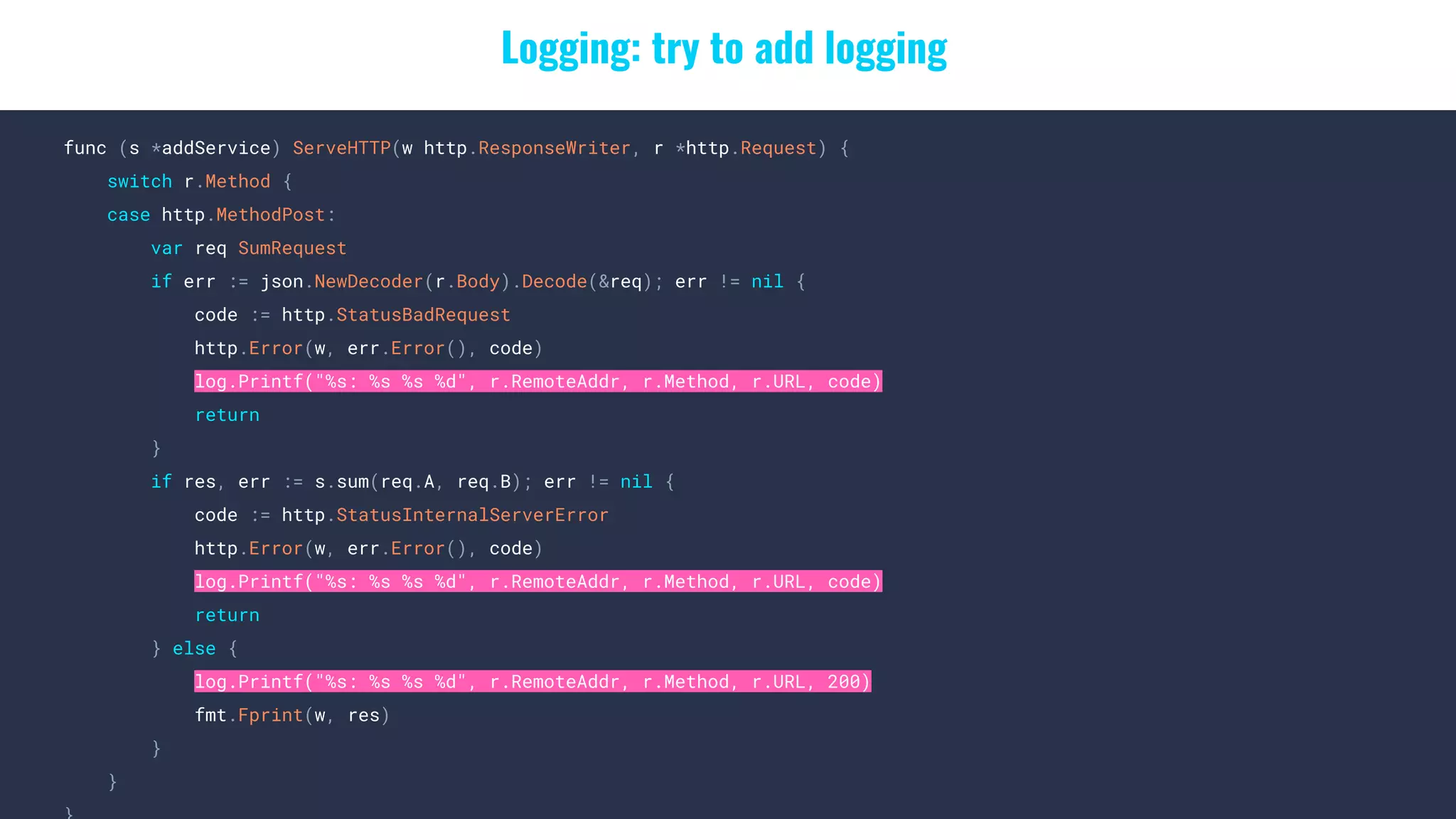
![Logging
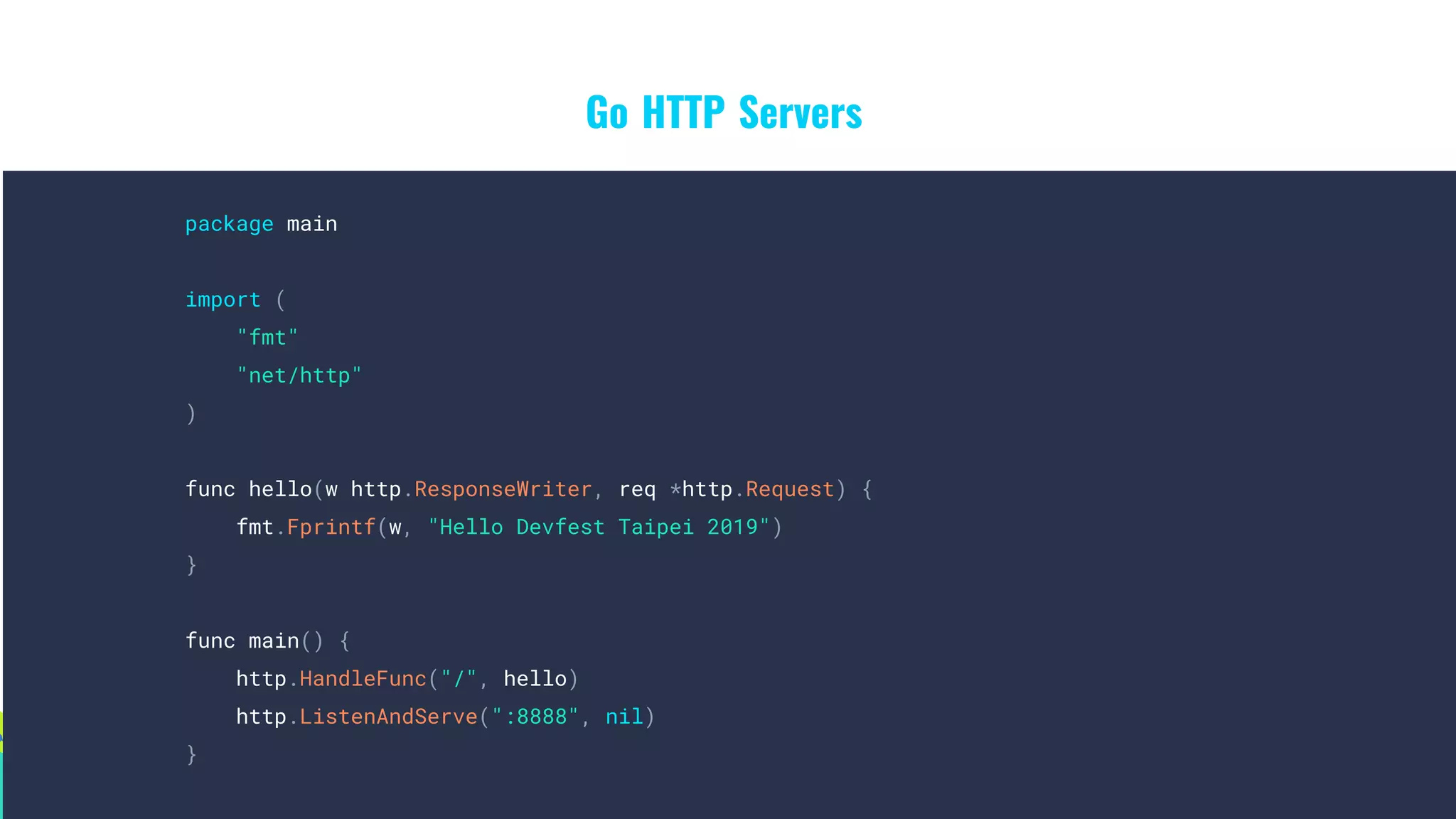
func main() {
log.Printf("listening on :8888")
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8888", &addService{}))
}
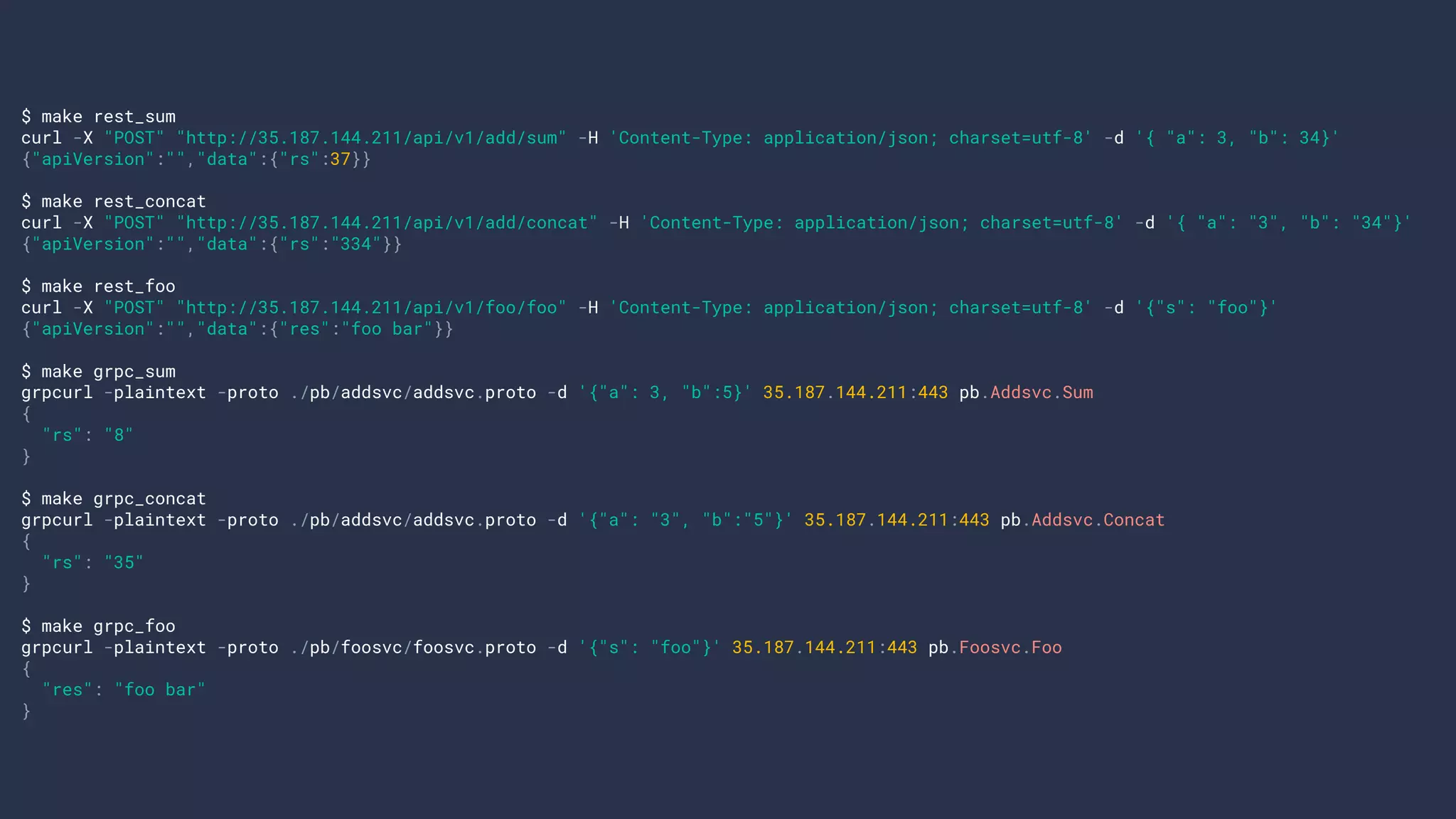
$ go run main.go
2019/11/29 15:24:29 listening on :8888
2019/11/29 15:24:32 [::1]:52200: POST / 200
$ curl -X "POST" "http://localhost:8888" -d '{ "a": 3, "b": 34}'
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gdgcloudtaipeimeetup50-buildgokitmicroservicesatkuberneteswithease-191216074128/75/GDG-Cloud-Taipei-meetup-50-Build-go-kit-microservices-at-kubernetes-with-ease-23-2048.jpg)










![Reference
1. Go + Microservices = Go Kit [I] - Peter Bourgon, Go Kit
2. Go kit
3. https://gokit.io/faq/
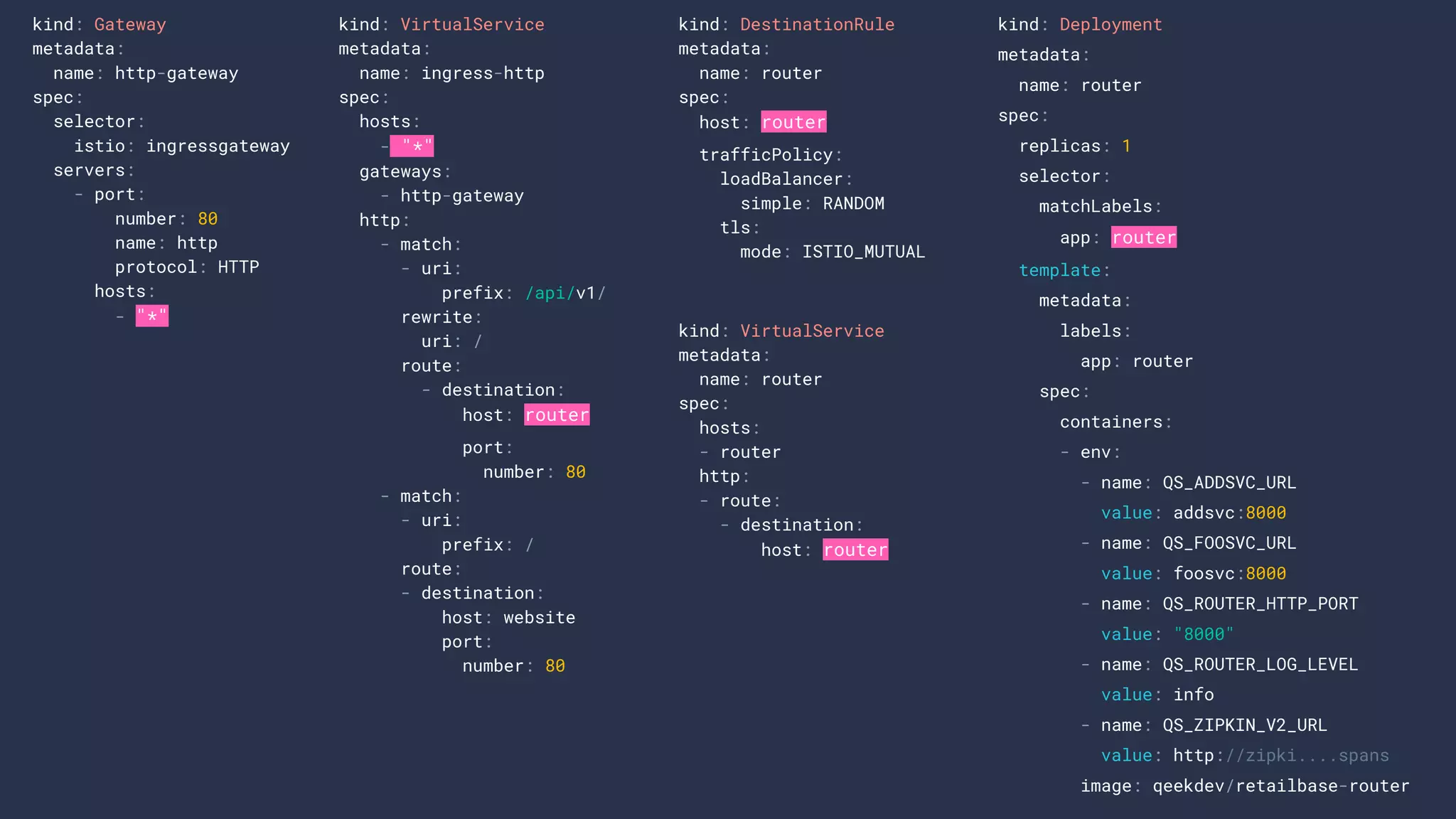
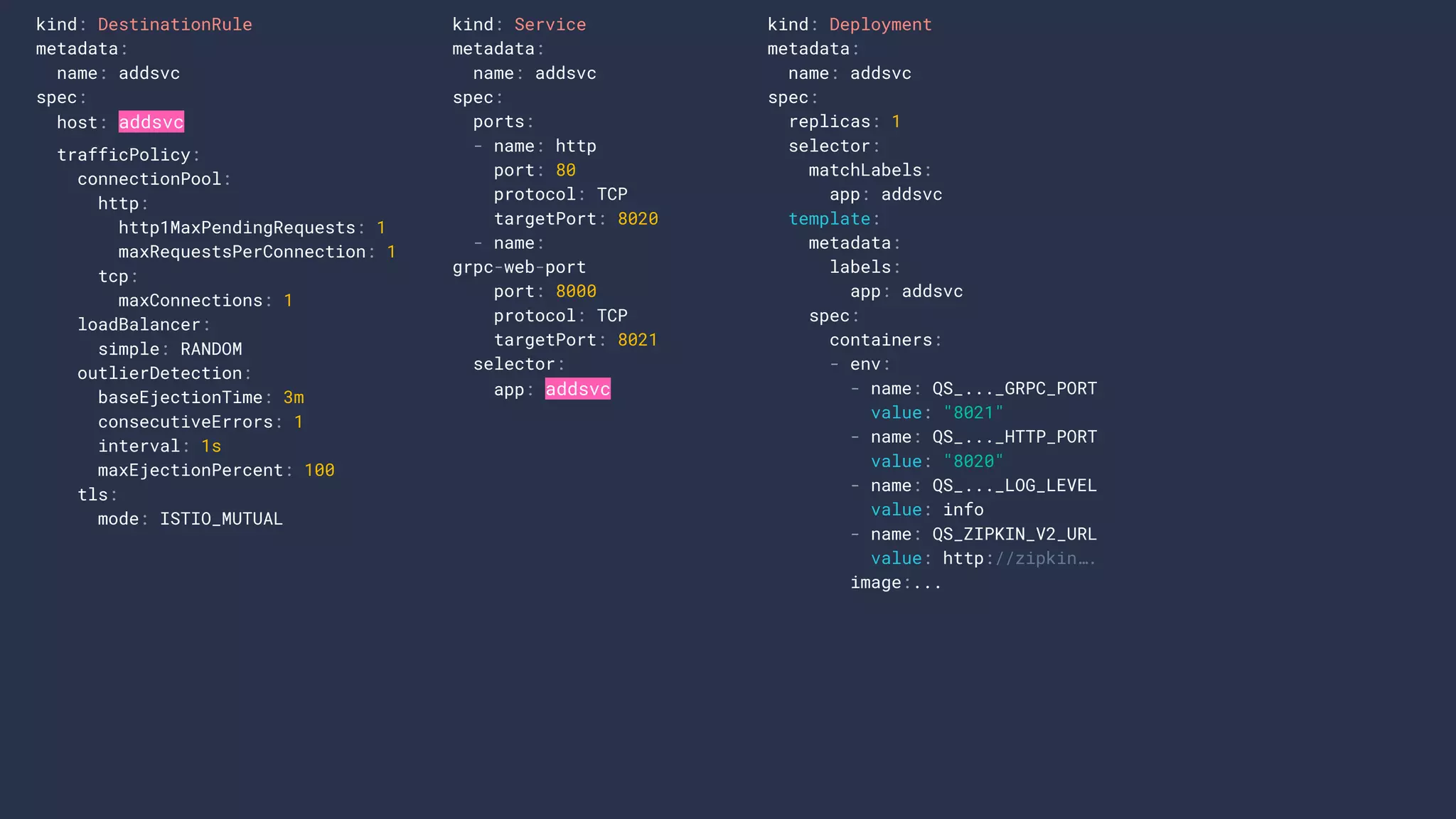
4. cage1016/gokitistio8s
5. cage1016/gk
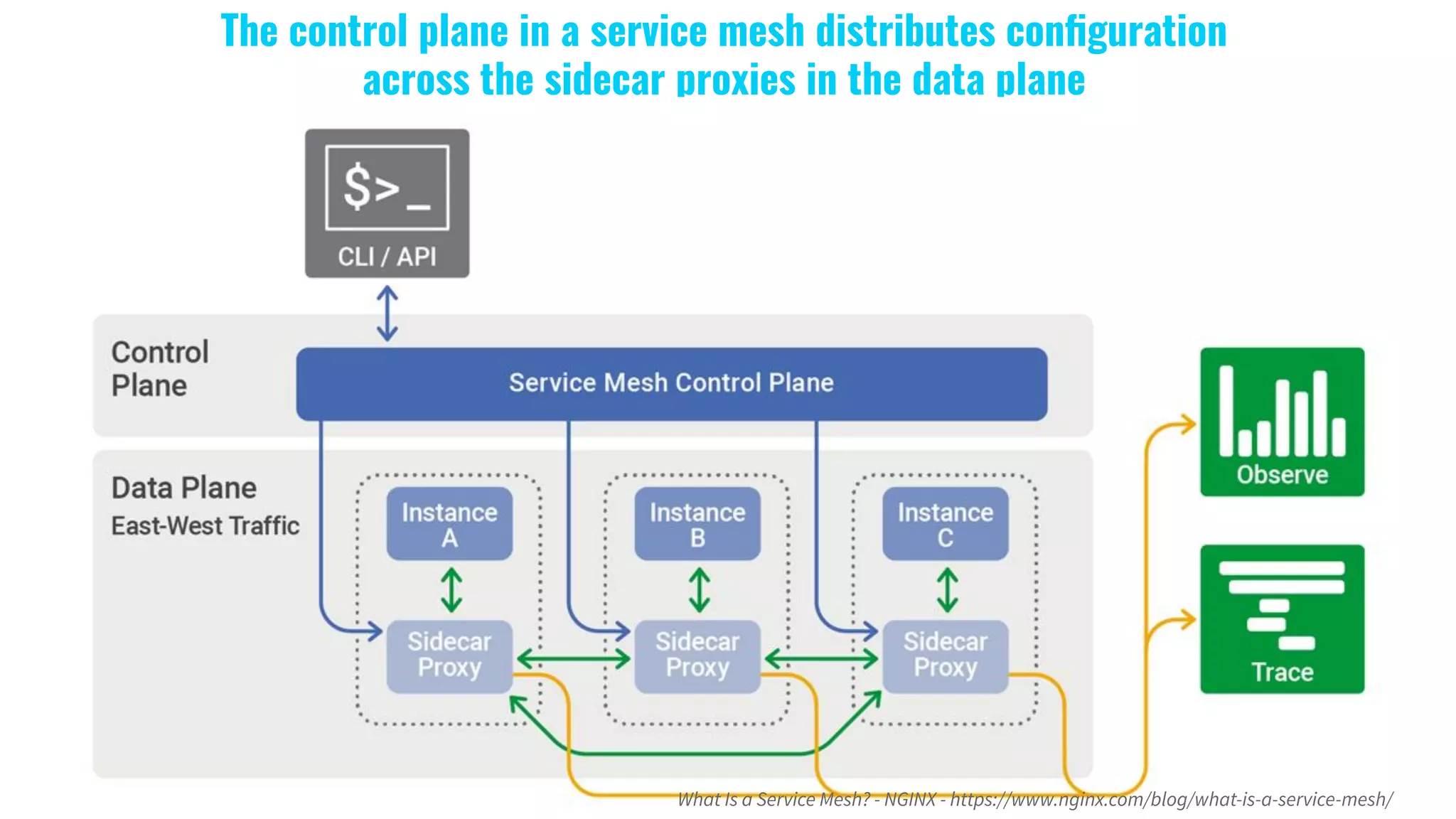
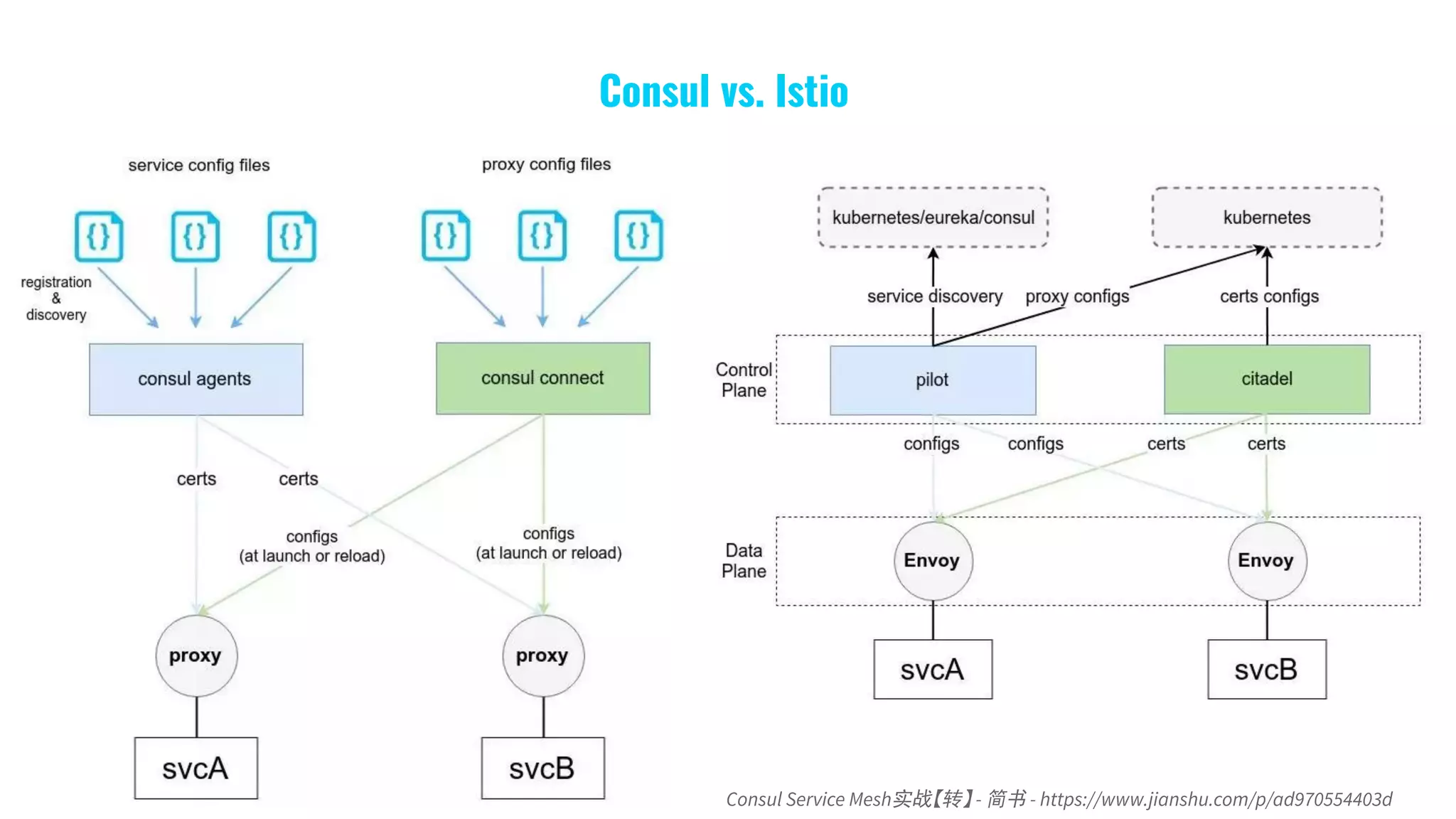
6. What Is a Service Mesh?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gdgcloudtaipeimeetup50-buildgokitmicroservicesatkuberneteswithease-191216074128/75/GDG-Cloud-Taipei-meetup-50-Build-go-kit-microservices-at-kubernetes-with-ease-42-2048.jpg)
