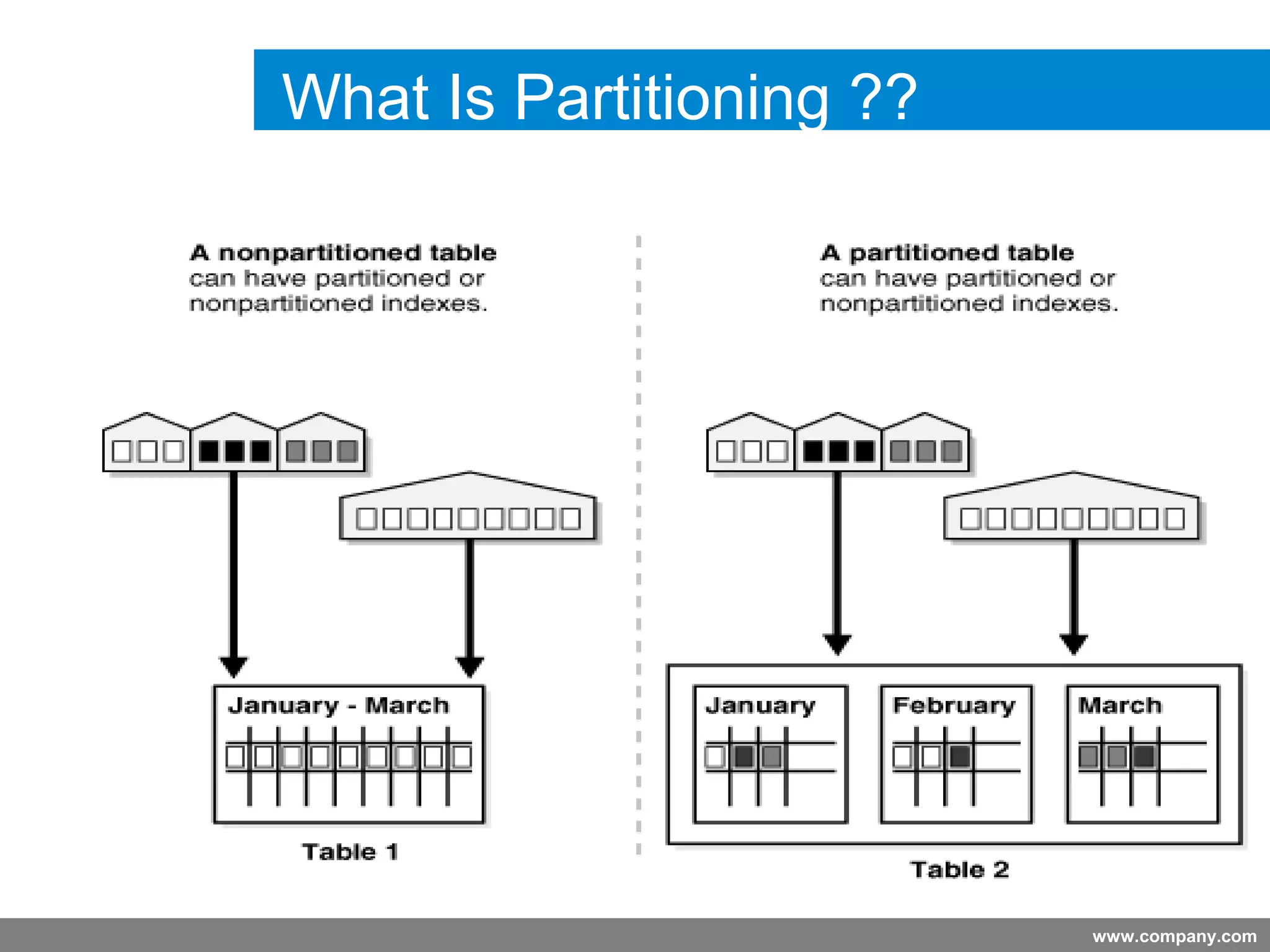
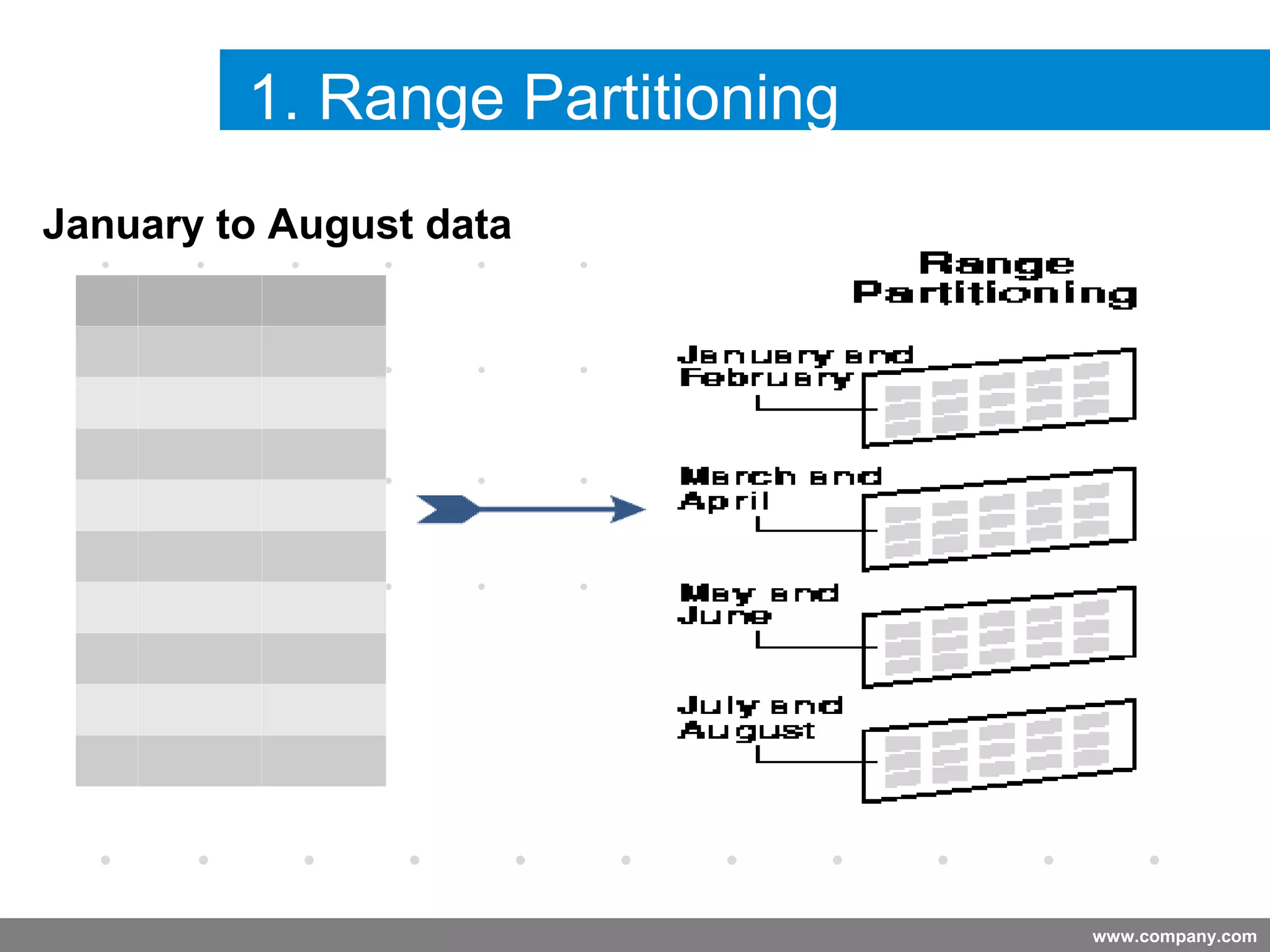
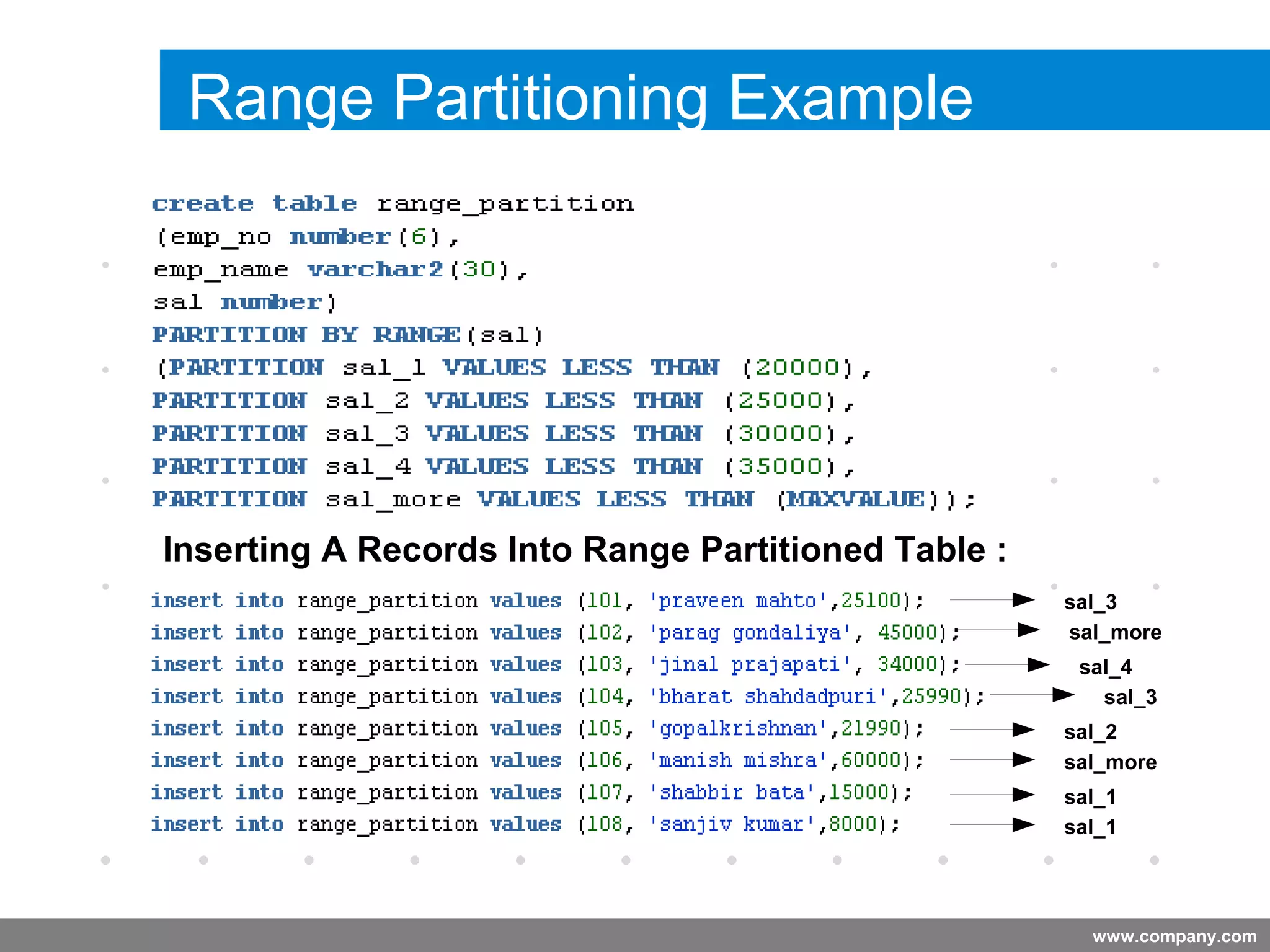
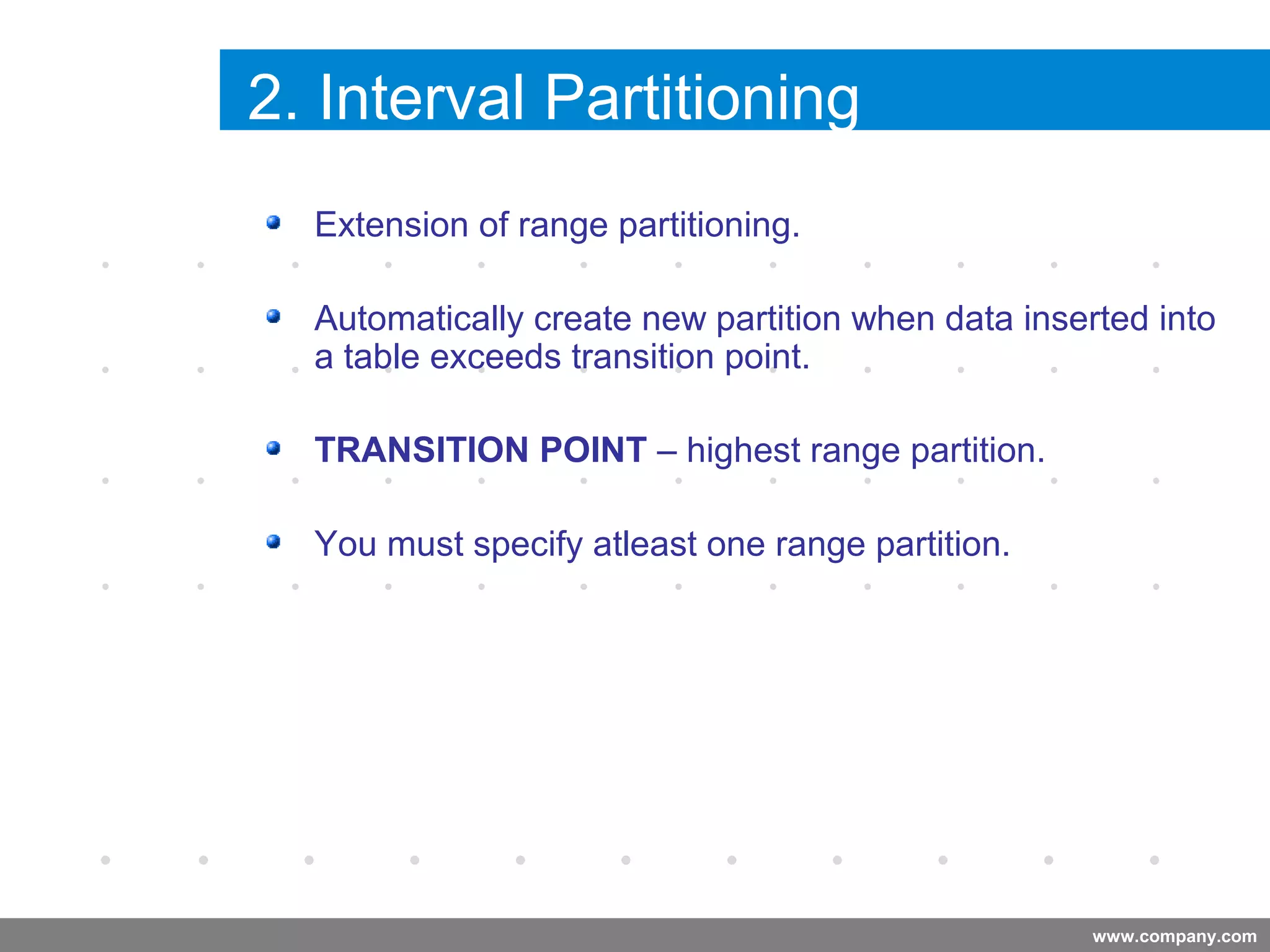
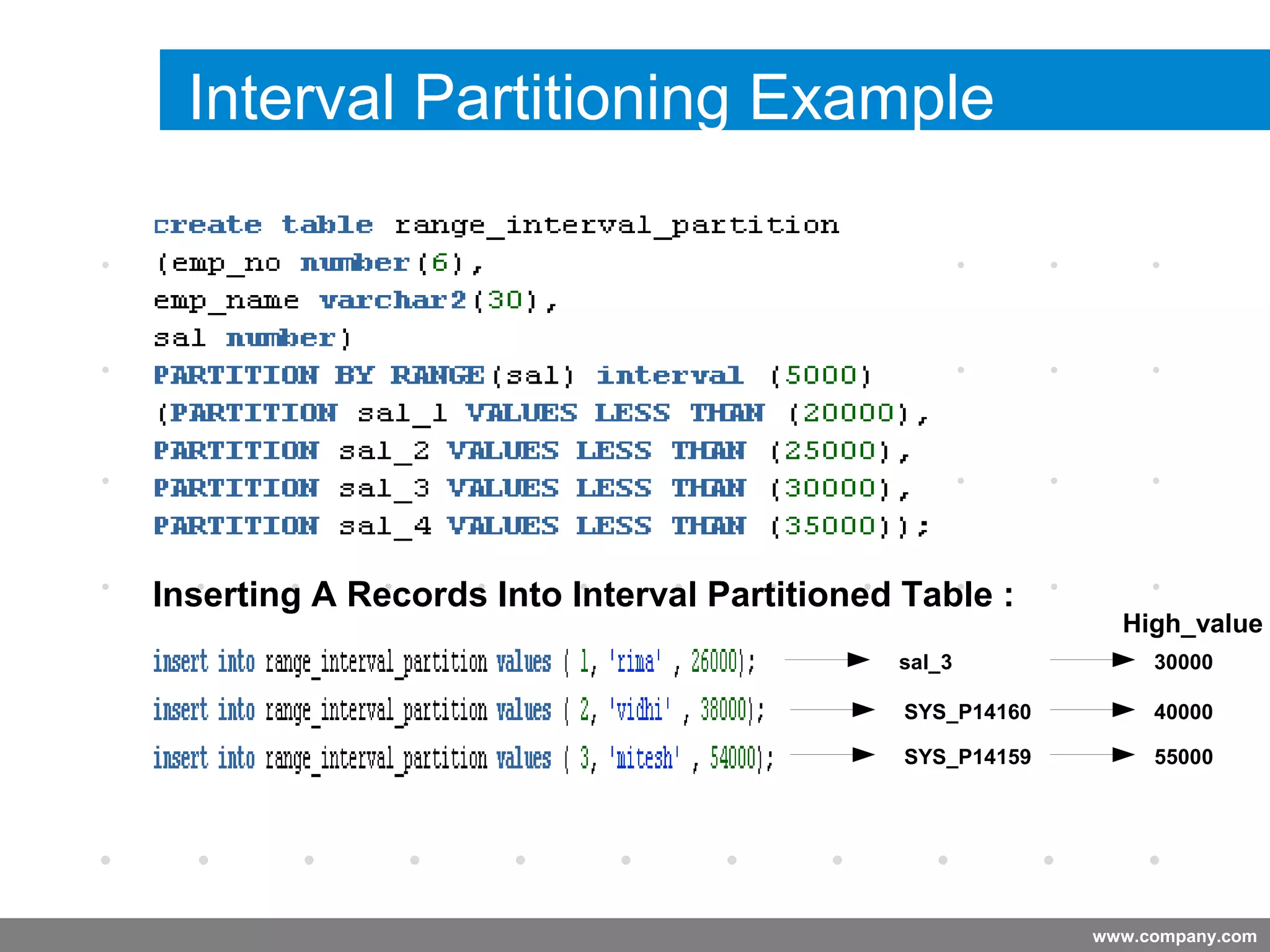
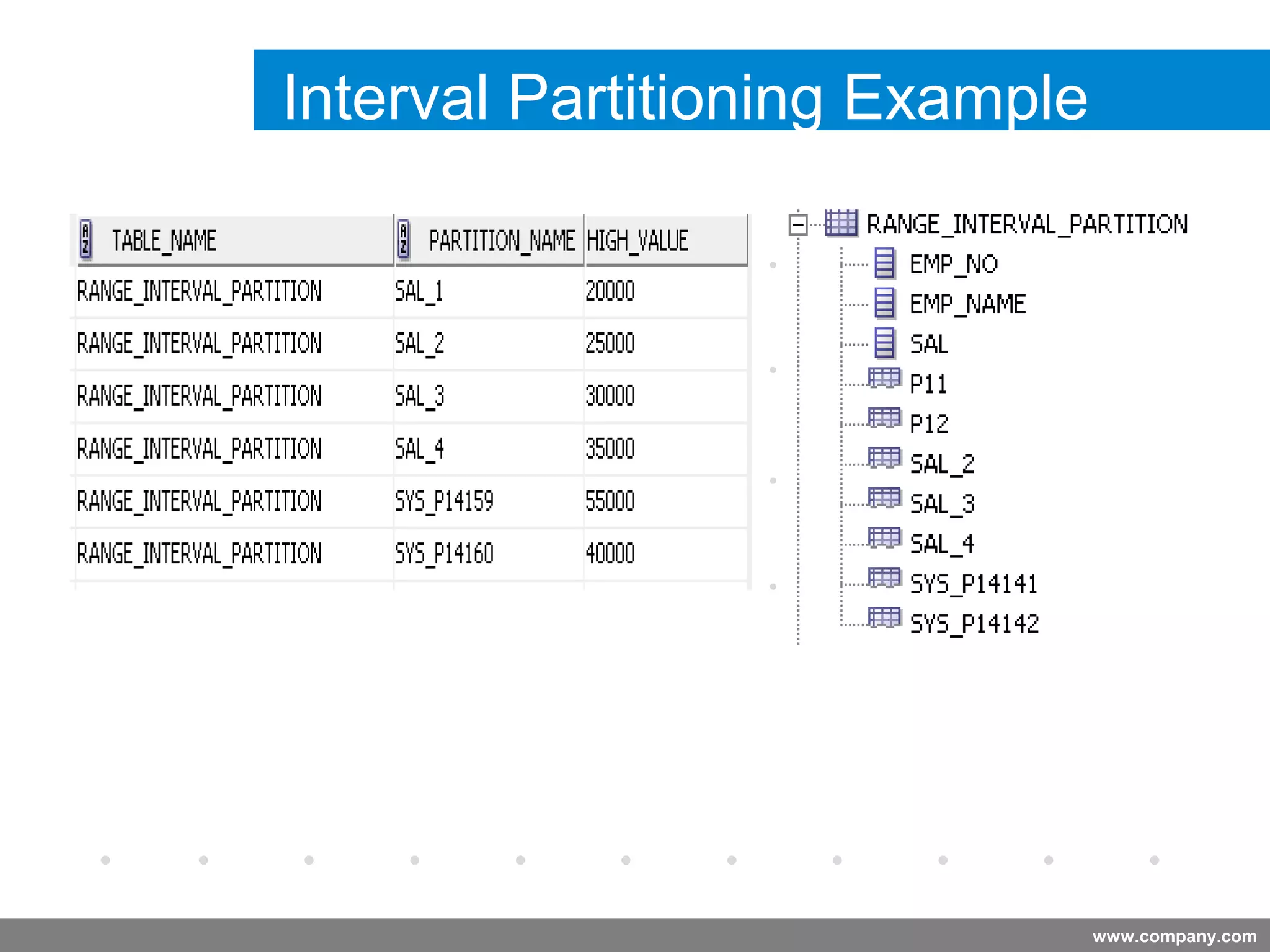
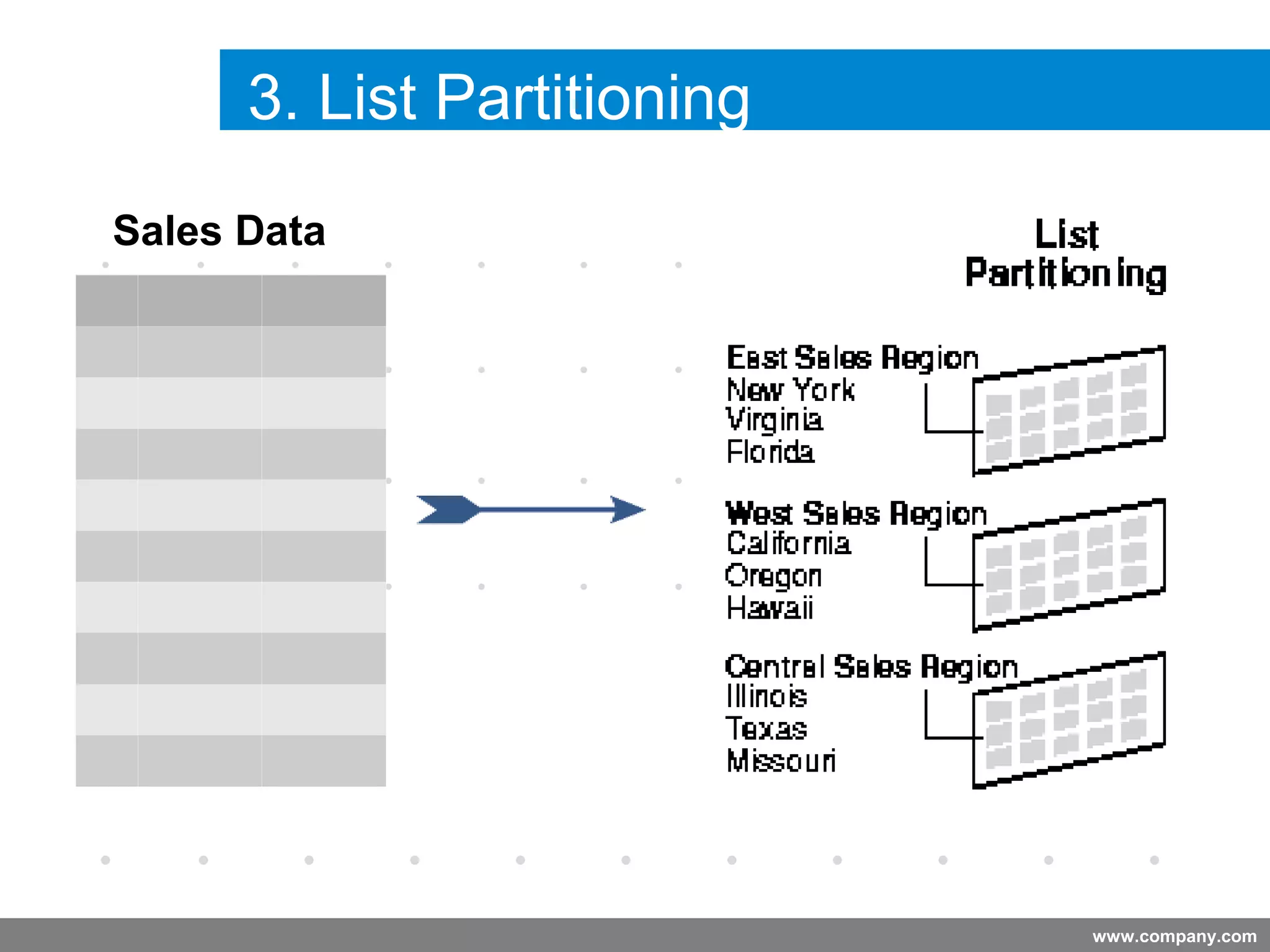
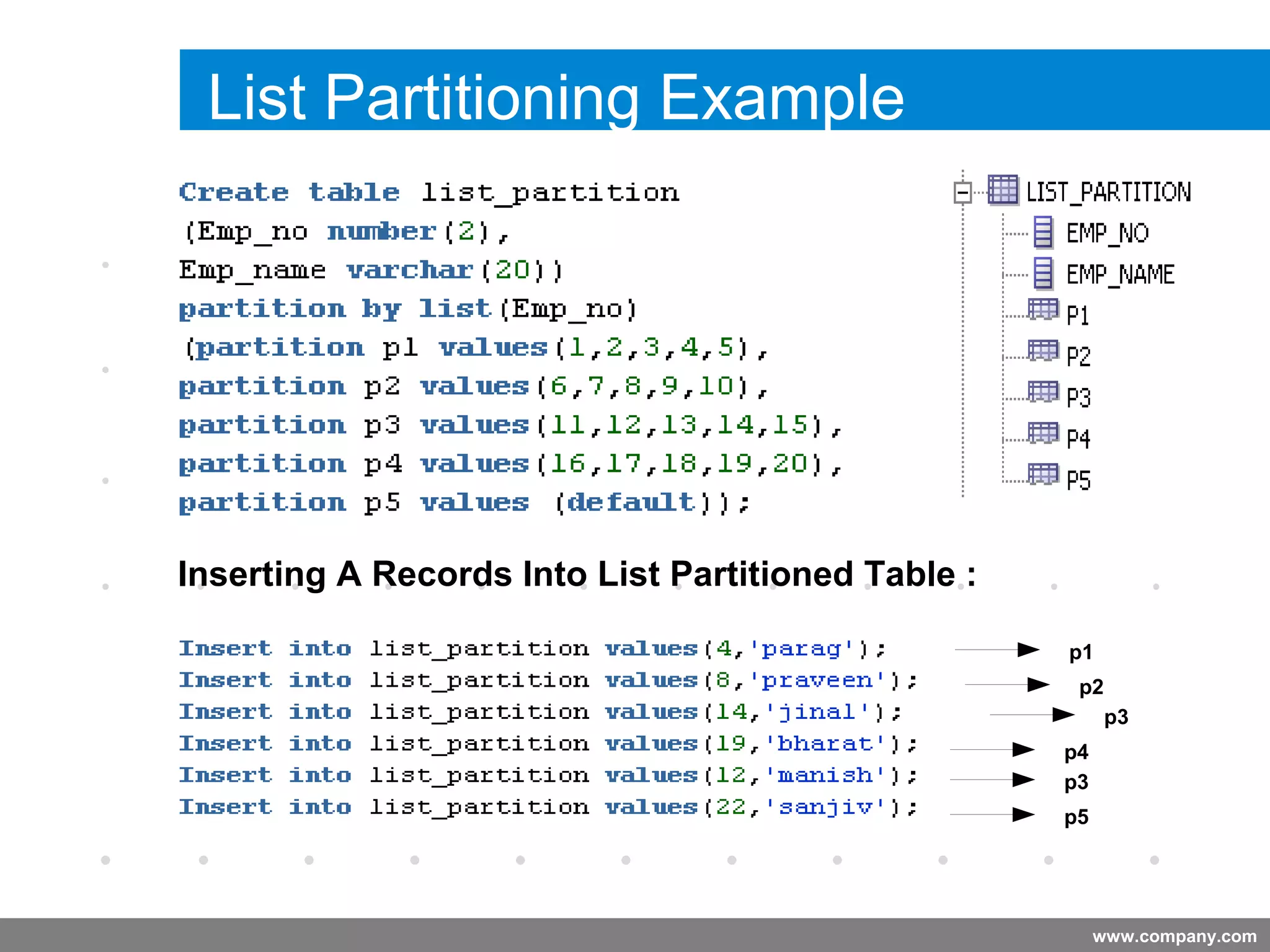
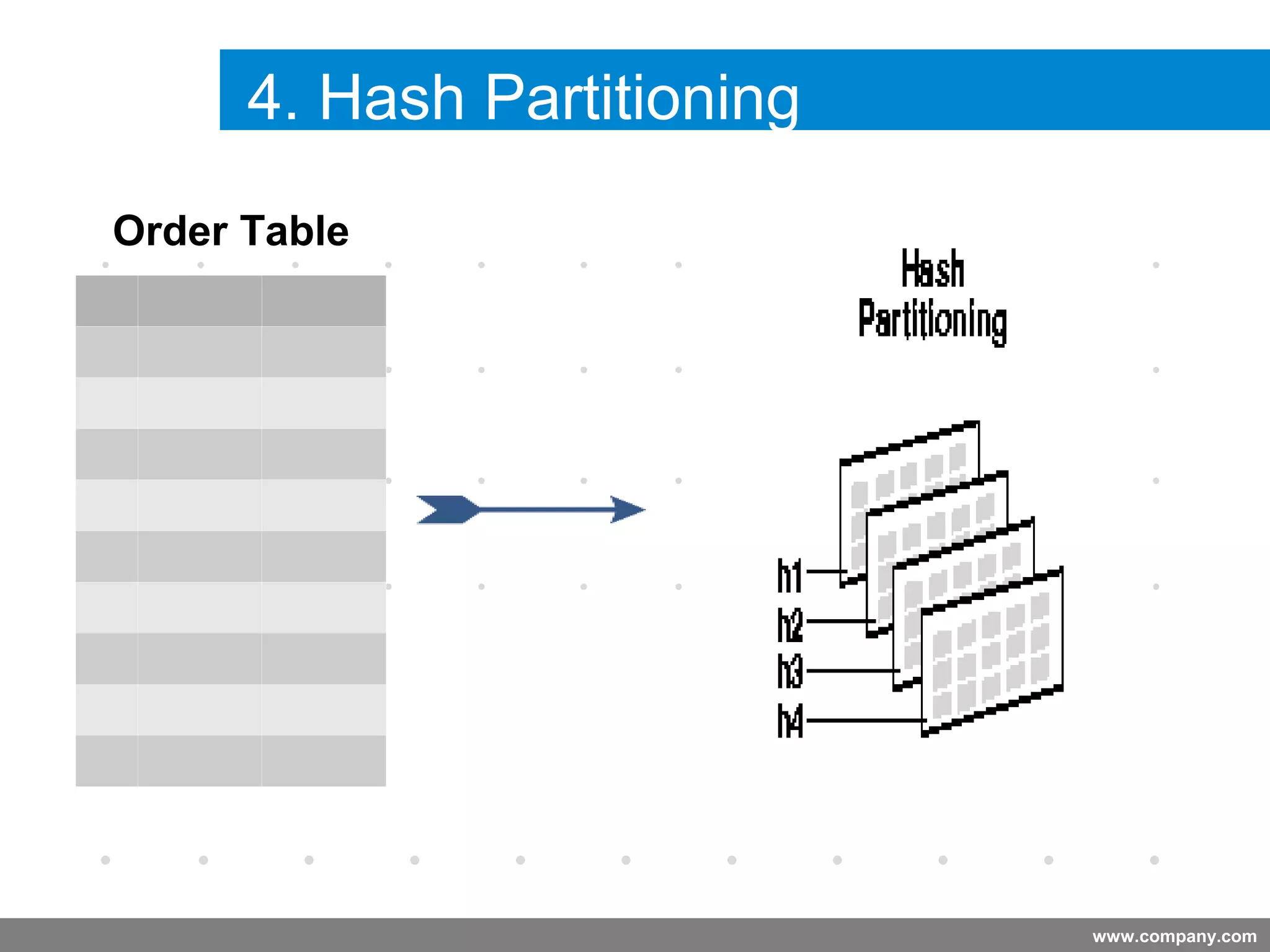
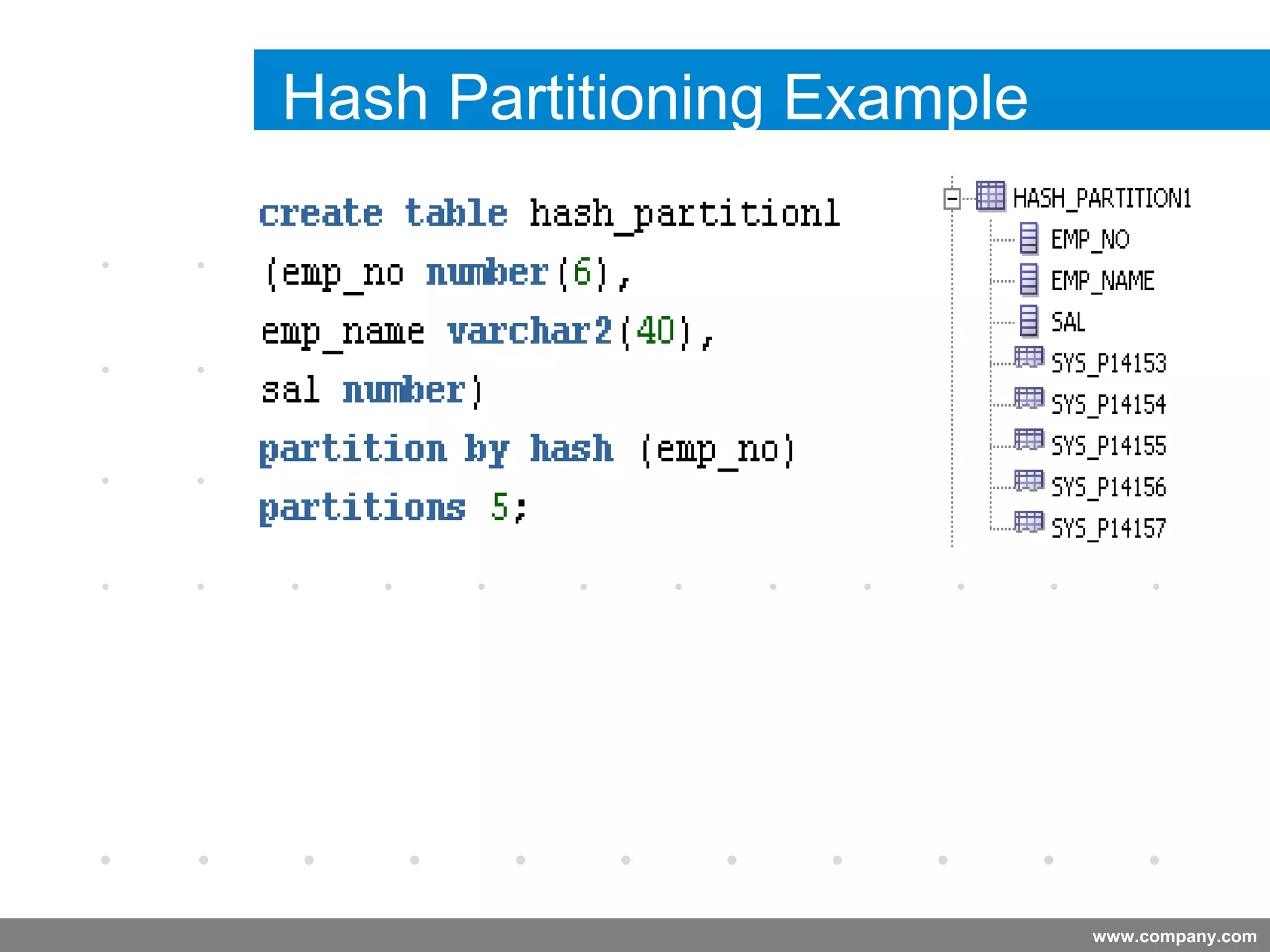
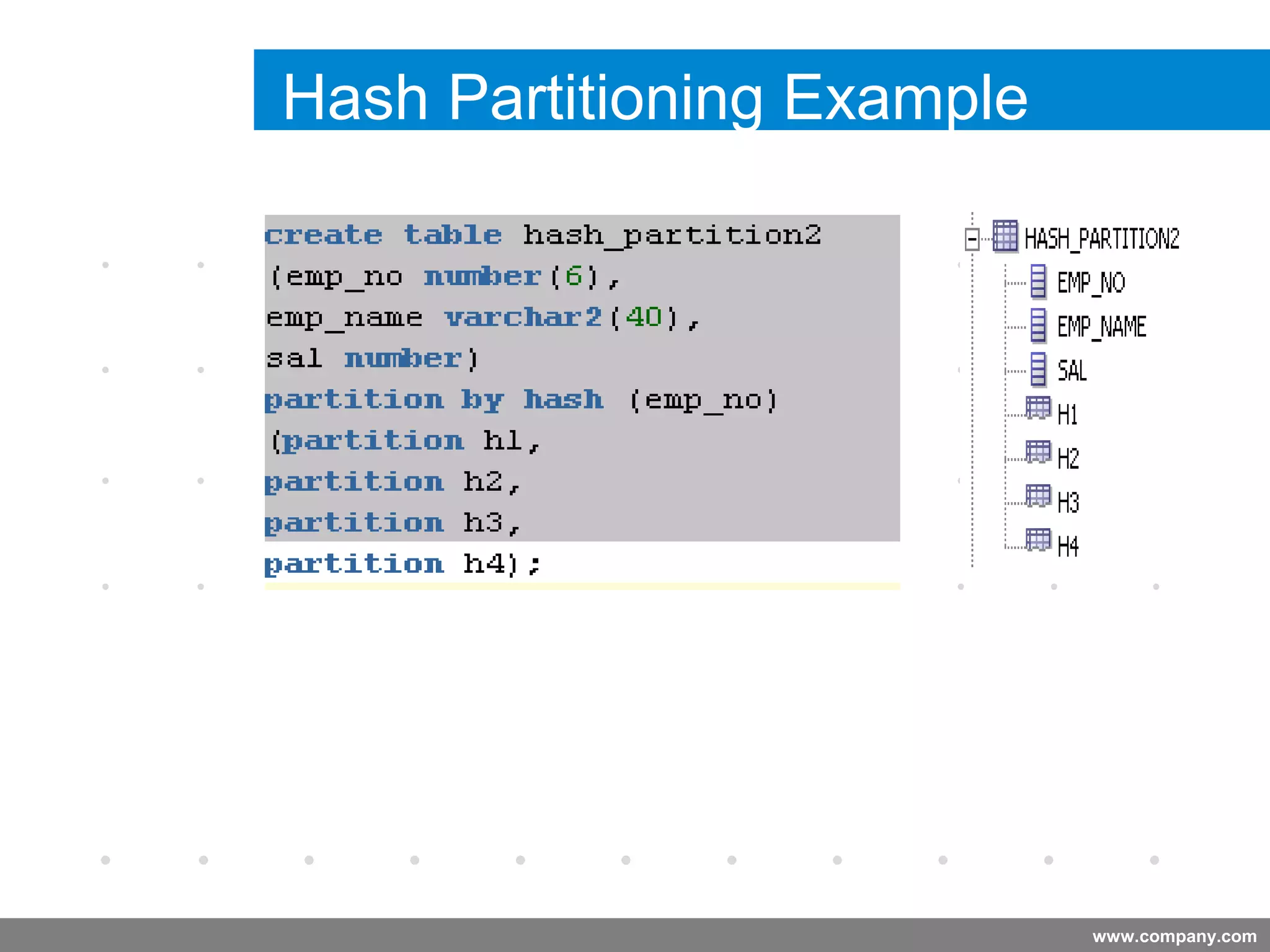
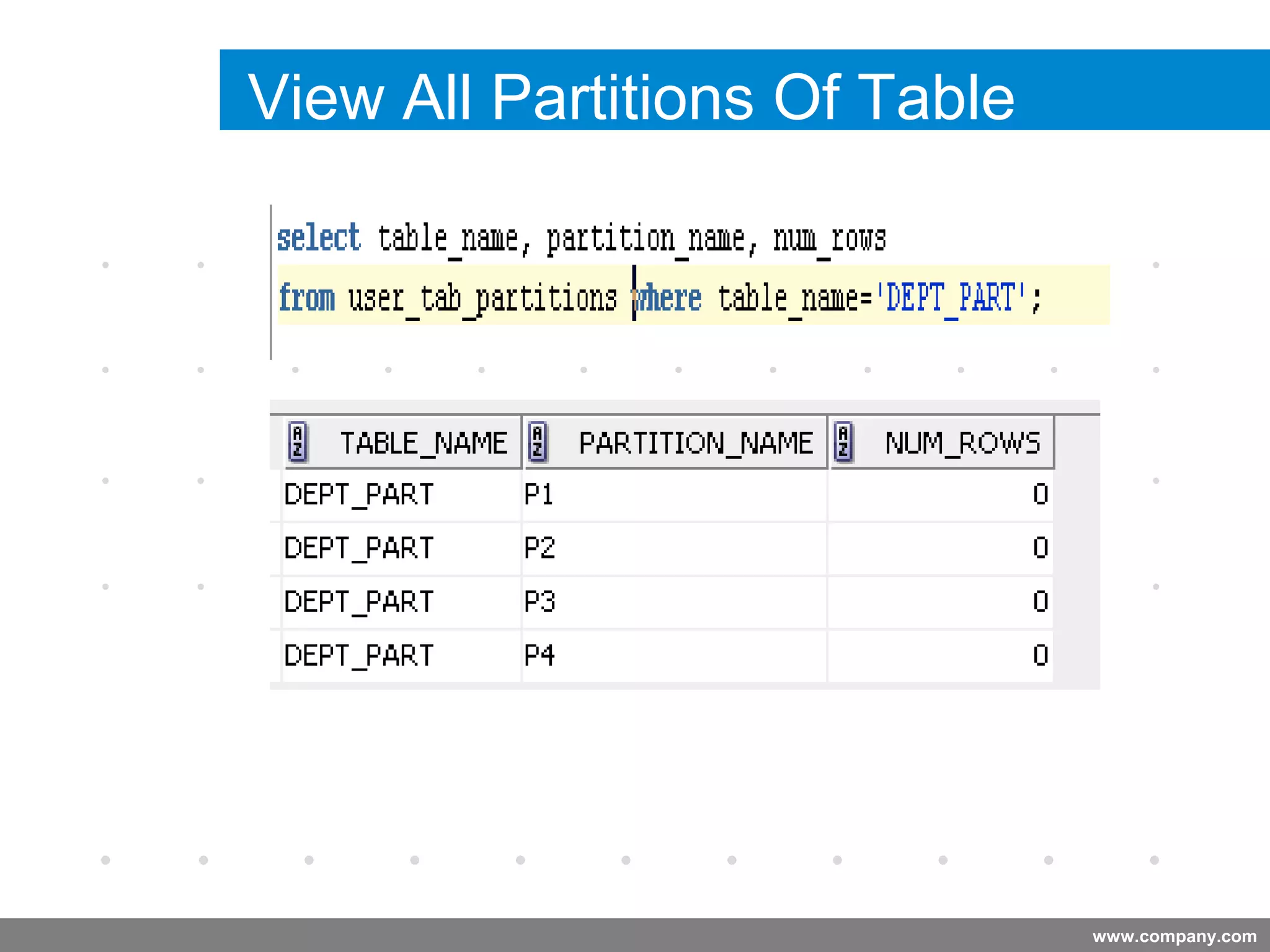
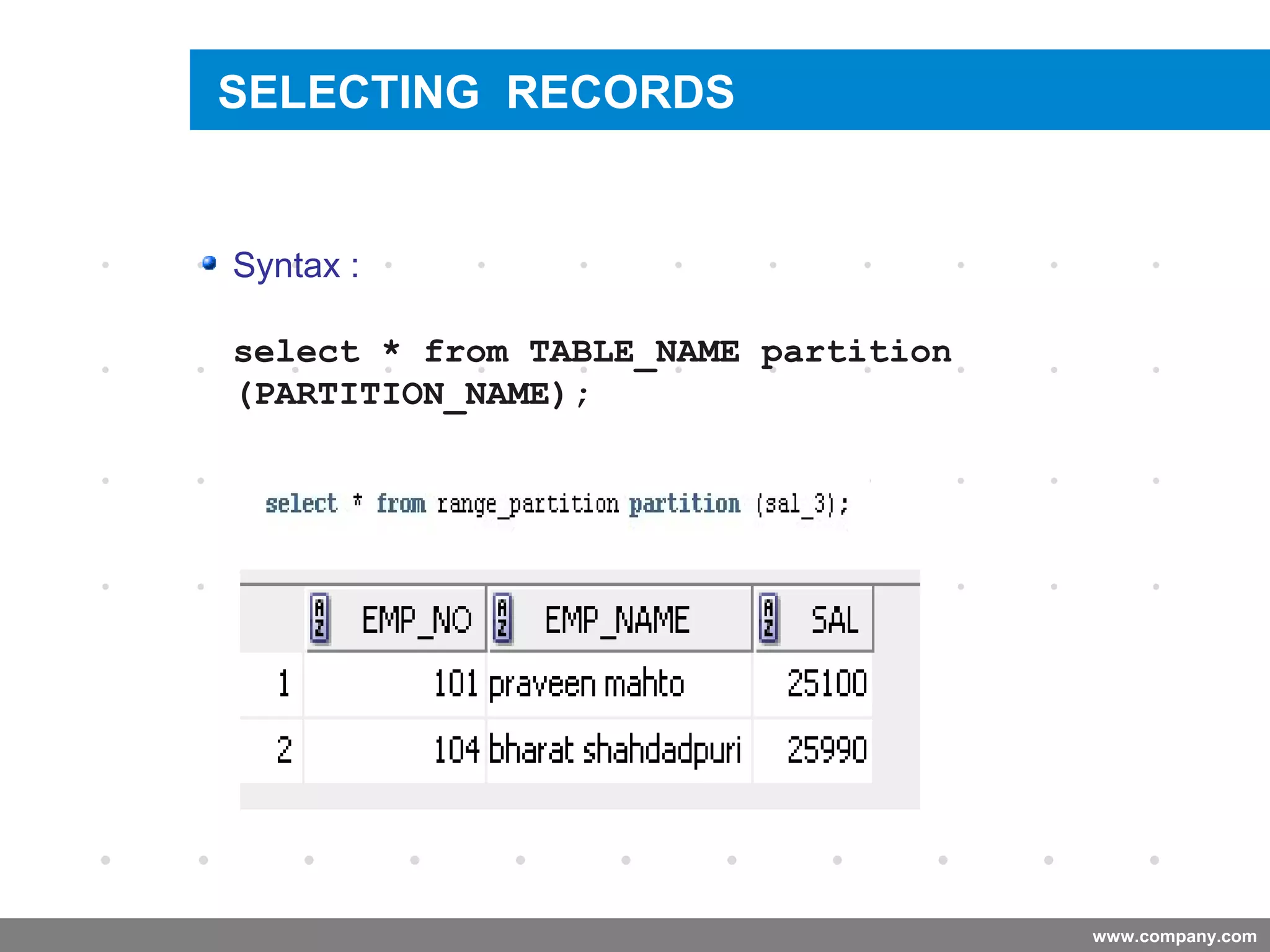
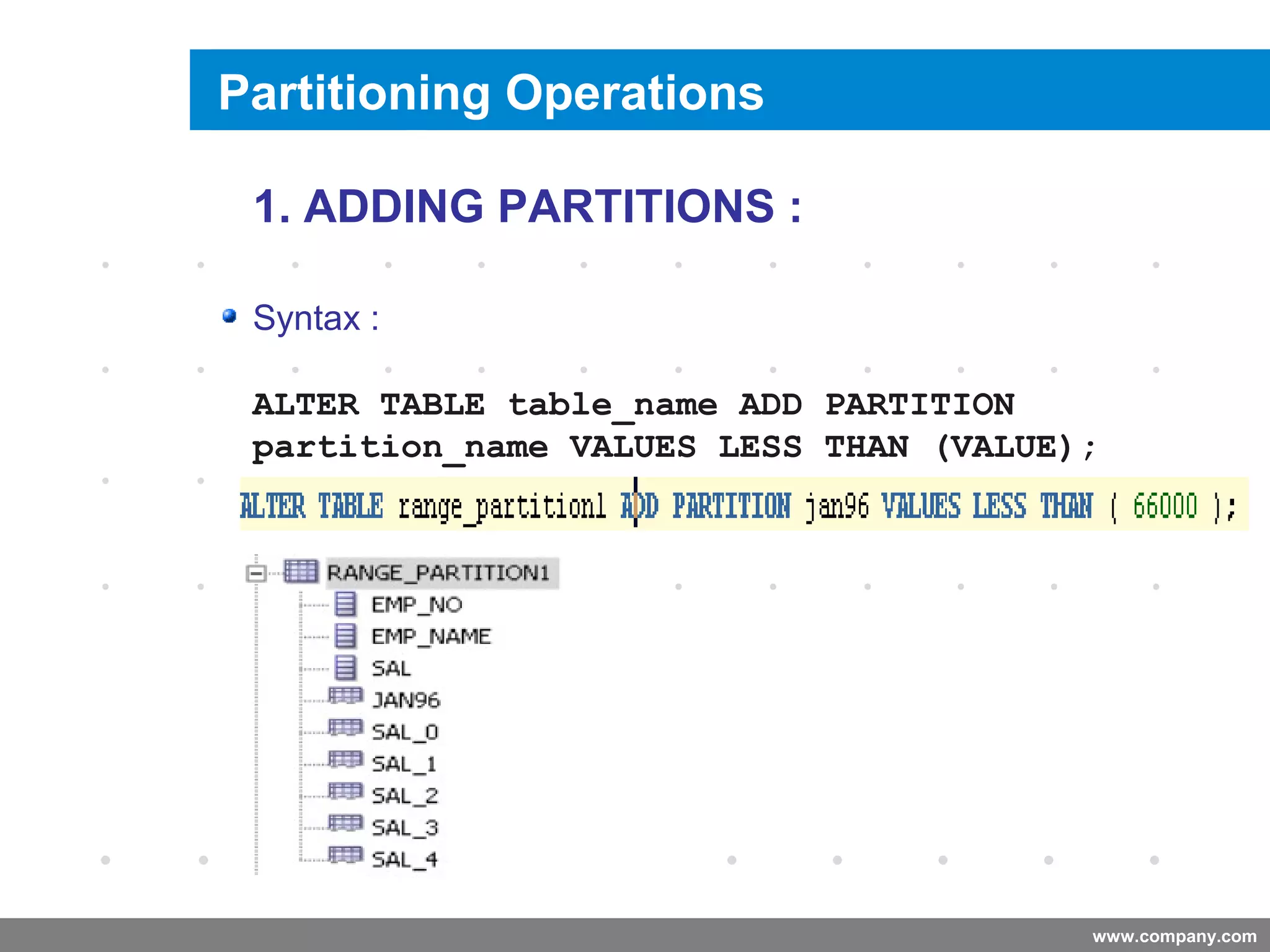
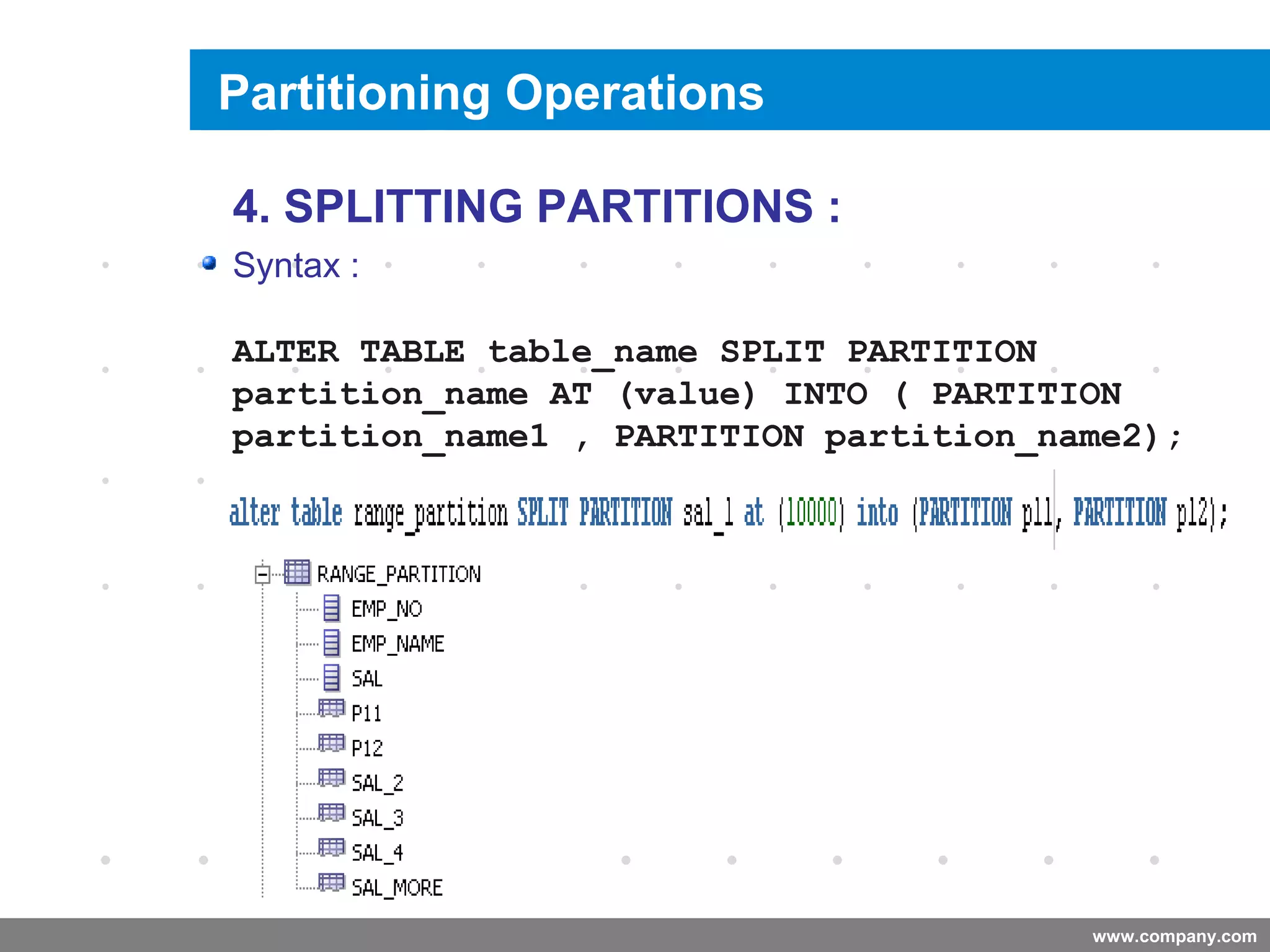
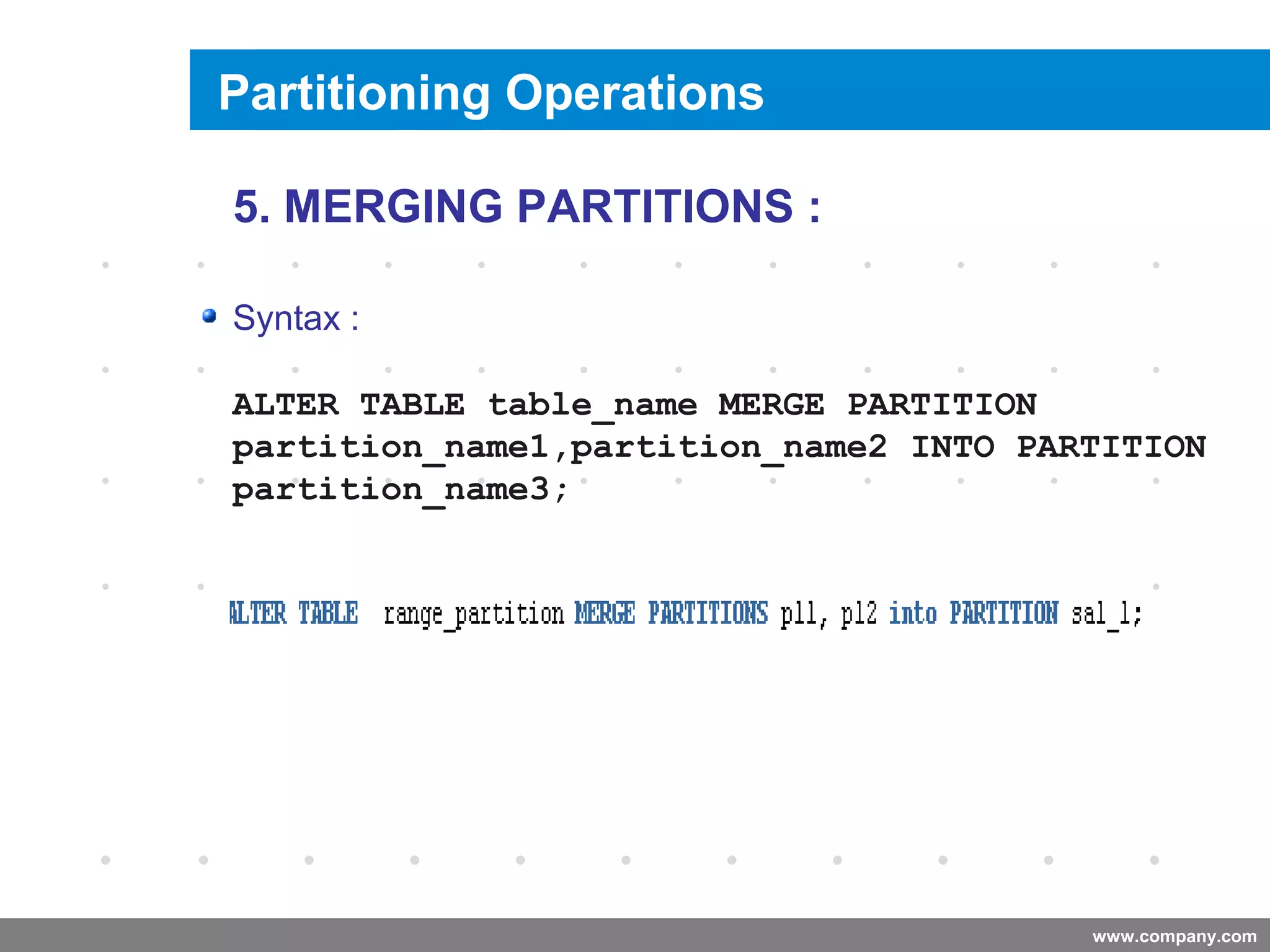
Partitioning allows tables and indexes to be subdivided into smaller pieces called partitions. Tables can be partitioned using a partition key which determines which partition each row belongs to. Partitioning provides benefits like improved query performance for large tables, easier management of historical data, and increased high availability. Some disadvantages include additional licensing costs, storage space usage, and administrative overhead to manage partitions. Common partitioning strategies include range, list, hash and interval which divide tables in different ways based on column values.