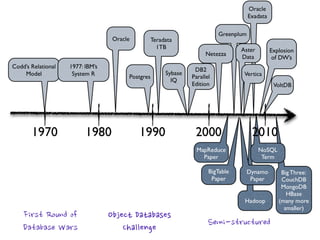
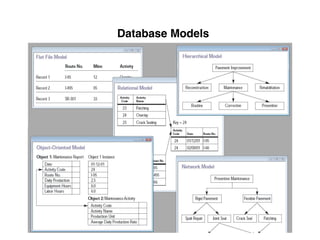
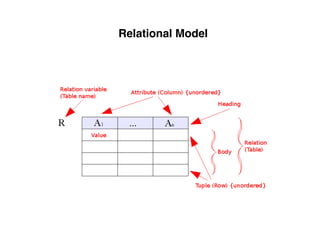
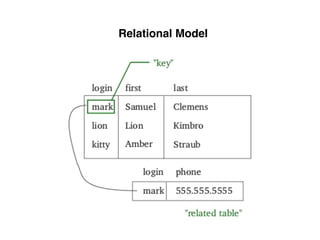
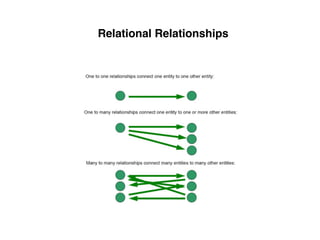
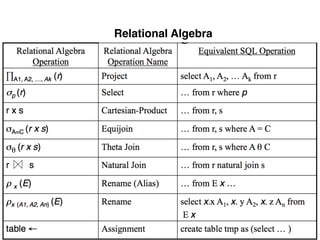
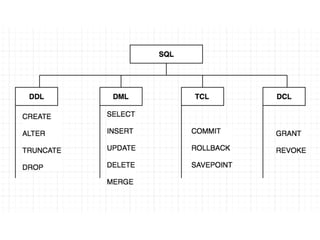
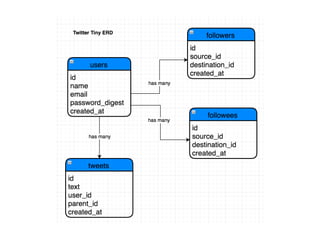
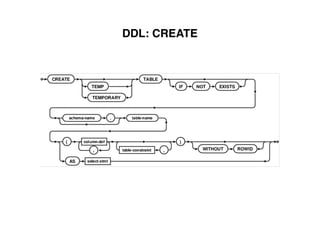
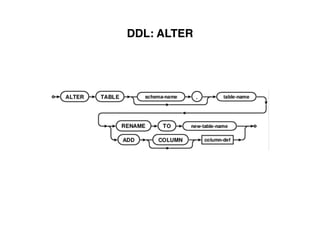
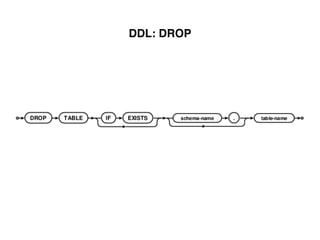
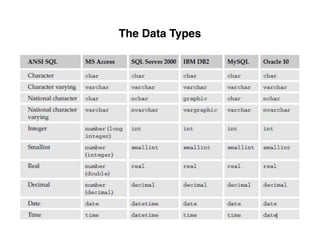
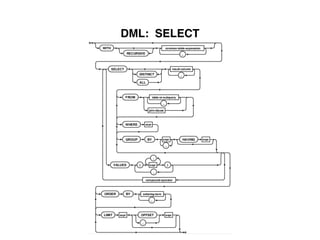
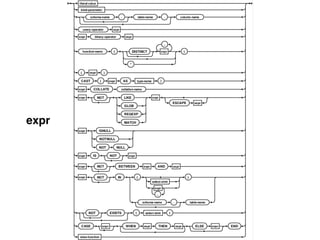
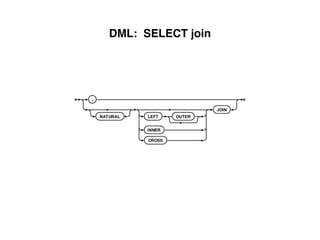
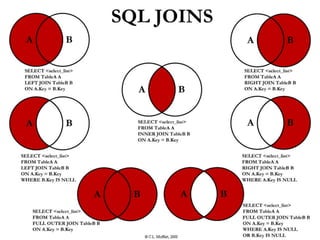
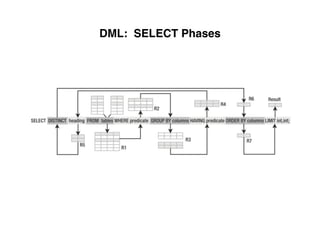
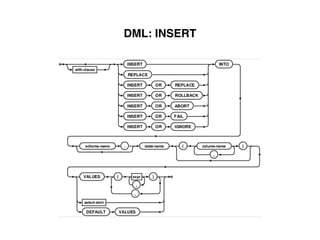
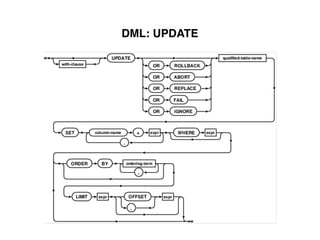
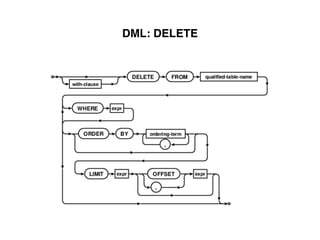
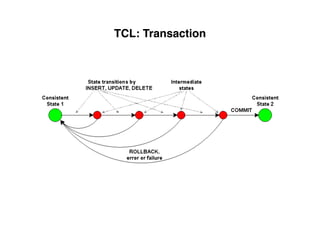
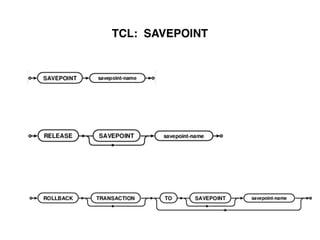
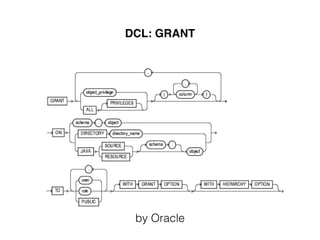
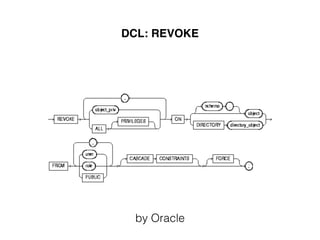
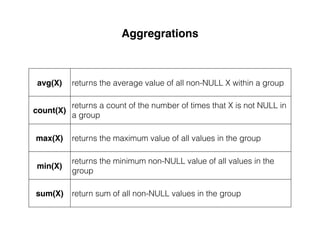
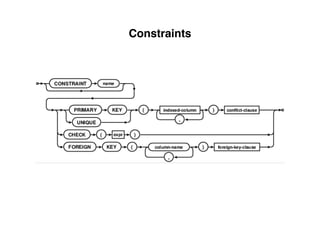
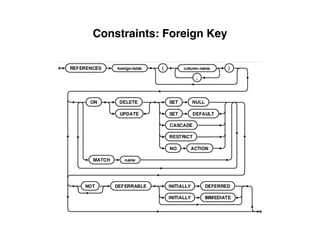
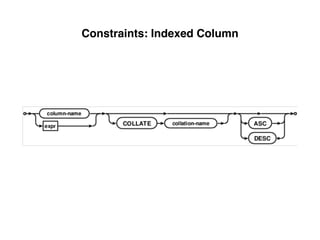
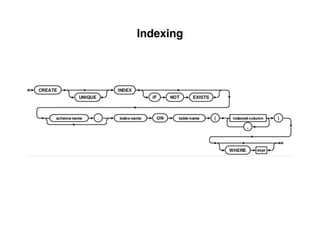
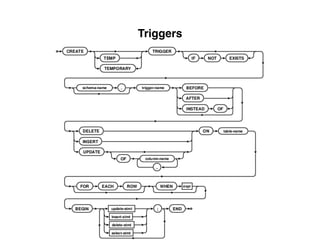
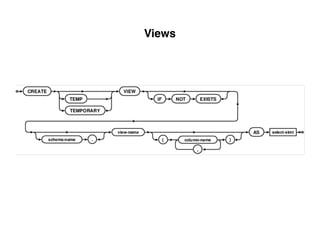
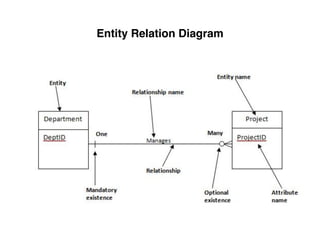
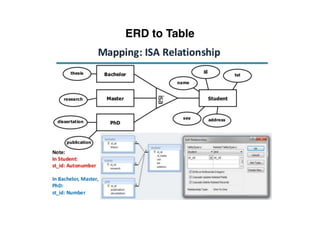
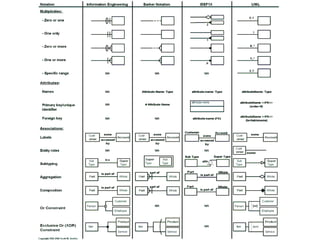
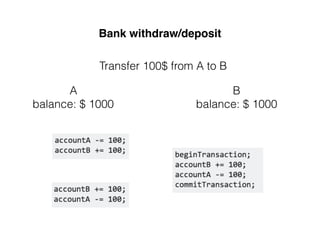
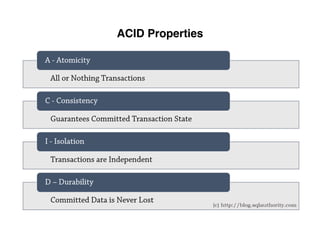
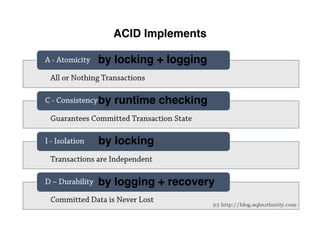
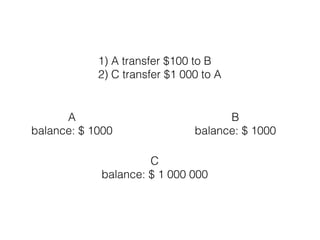
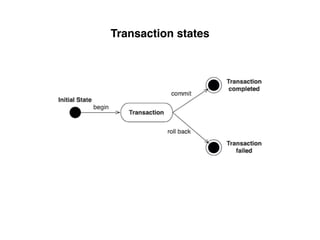
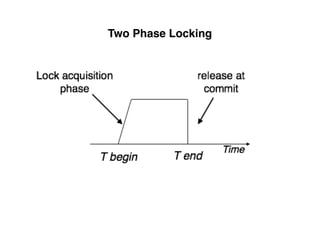
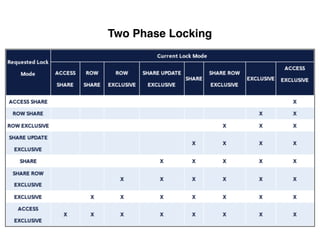
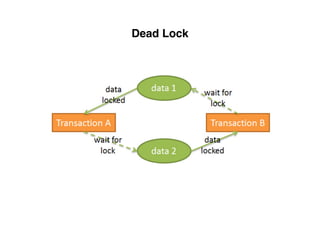
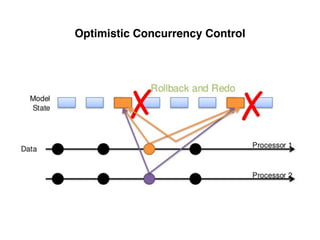
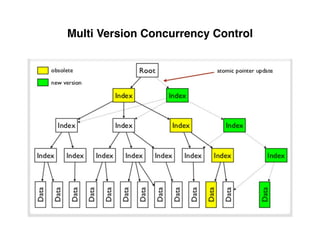
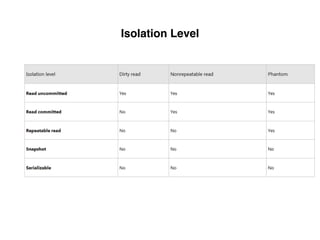
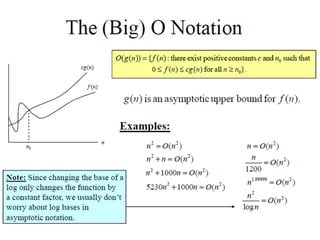
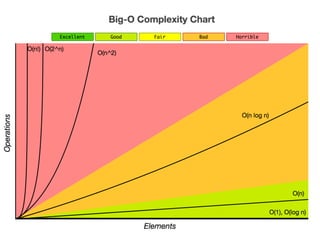
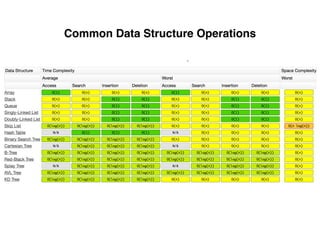
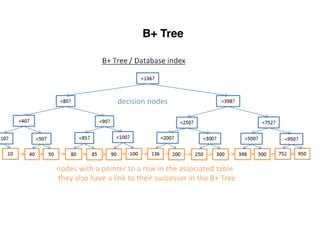
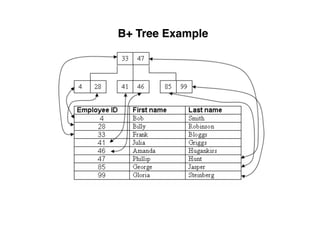
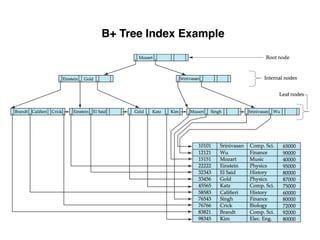
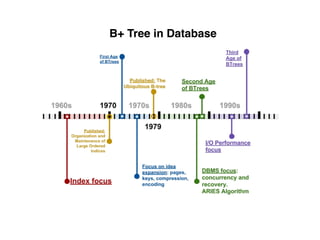
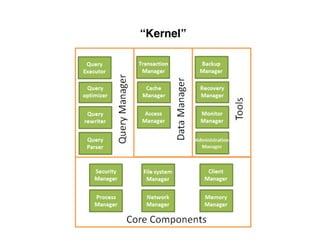
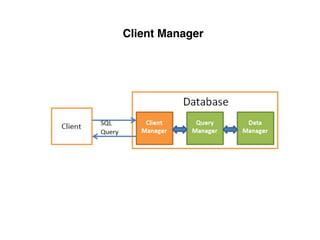
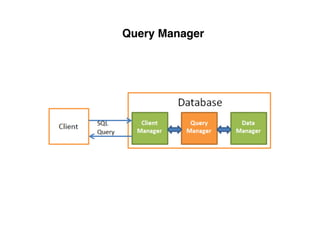
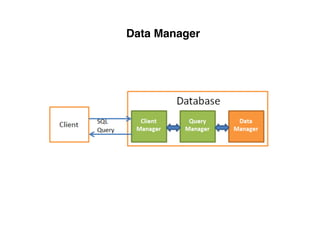
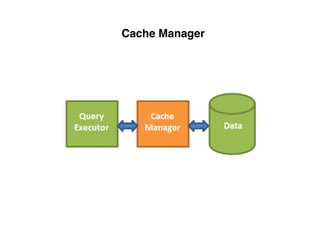
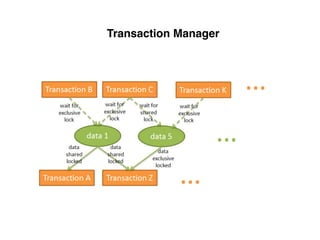
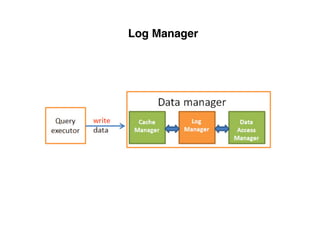
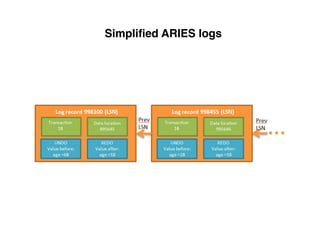
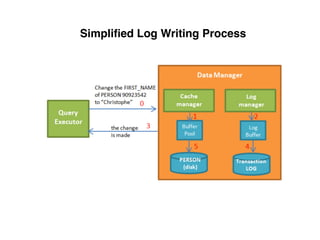
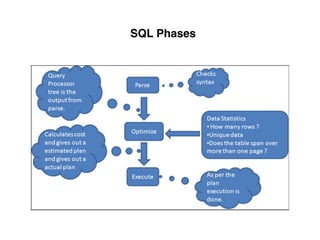
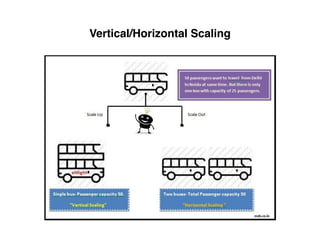
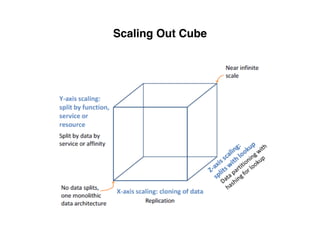
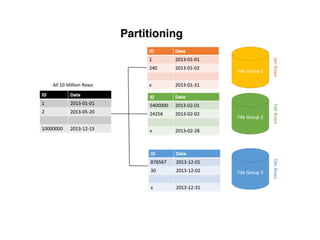
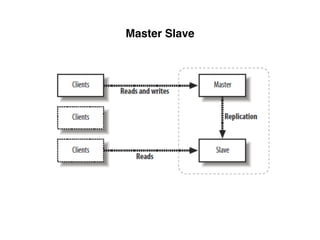
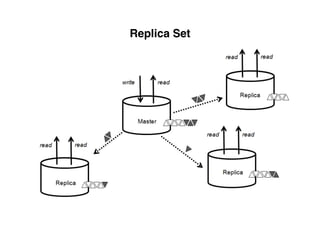
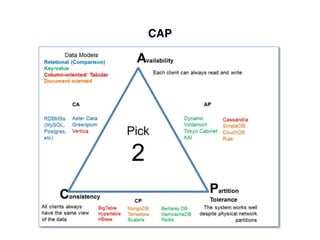
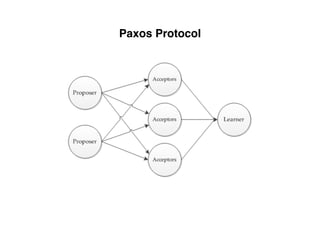
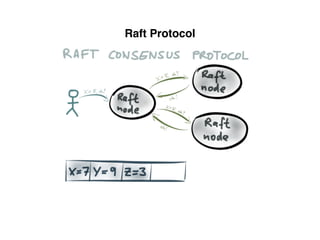
The document provides an overview of database fundamentals, including definitions of databases and Database Management Systems (DBMS), as well as details on various models like the relational model, SQL components (DDL, DML, TCL, DCL), and transaction management. It discusses functions, aggregations, constraints, and advanced topics such as ACID properties, concurrency control, and scaling strategies. Additionally, the document mentions key structures and algorithms used in databases and offers references for further reading.