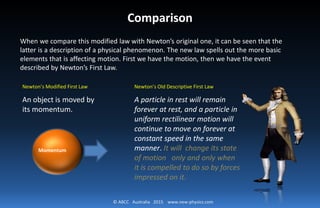
Newton established three laws of motion that described the relationship between forces and motion. The first law stated that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Galileo established through experiments that acceleration increases the speed of falling objects at a steady rate, with distance traveled being proportional to the square of time. The document discusses reexamining Newton's laws and modifying the first law to state that an object is carried by its momentum rather than being motivated by forces. It also explores the relationship between force, changes in motion, and acceleration.





![© ABCC Australia 2015 www.new-physics.com
[and] a particle in uniform rectilinear motion will
continue to move on forever at constant speed in
the same manner.
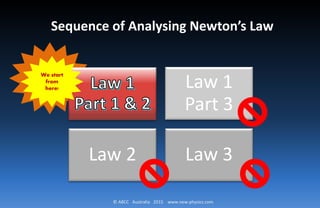
Newton’s First Law in 3 Parts
A particle in rest will remain forever at rest
It will change its state of motion only and only
when it is compelled to do so by forces impressed
on it.
Law No. 1 can be more conveniently studied in three parts I , II, & III.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/part3-150710081459-lva1-app6892/85/Part-3-newton-s-principia-6-320.jpg)

![© ABCC Australia 2015 www.new-physics.com
[and] a particle in uniform rectilinear motion will continue
to move on forever at constant speed in the same manner.
Newton’s First Law : Part 2
This is the old description
of impetus and
conservation familiar to
John Philoponus, Jean
Buridan, Descartes and
Galileo Galilee. This will be
studied in the coming
sections.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/part3-150710081459-lva1-app6892/85/Part-3-newton-s-principia-8-320.jpg)


![© ABCC Australia 2015 www.new-physics.com
[and] a particle in uniform rectilinear motion will continue
to move on forever at constant speed in the same manner.
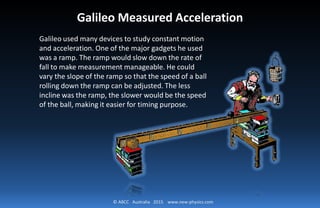
Newton’s First Law : Part 2
This phenomenon had been
demonstrated by Galileo before in
his ramp experiment. When there is
no friction and air resistance, the ball
will move on forever.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/part3-150710081459-lva1-app6892/85/Part-3-newton-s-principia-12-320.jpg)




![© ABCC Australia 2015 www.new-physics.com
. . . it will change its state of motion only and only when
it is compelled to do so by forces impressed on it.
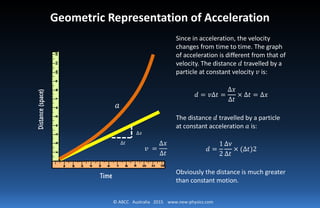
Part 3 of Newton’s First Law
Part 3 of Newton’s First Law spells the relation between state of motion and
force:
The right place for this part should be a part of the second law where it would
probably read:
Force changes the state of motion [of a particle].
However, this is enough for us to start to discuss on a new state of motion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/part3-150710081459-lva1-app6892/85/Part-3-newton-s-principia-18-320.jpg)