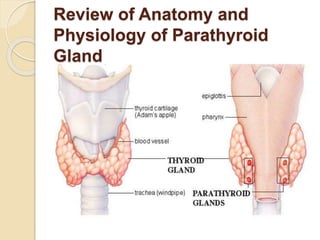
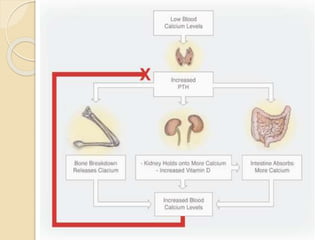
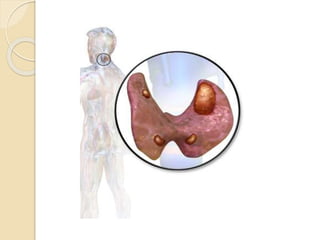
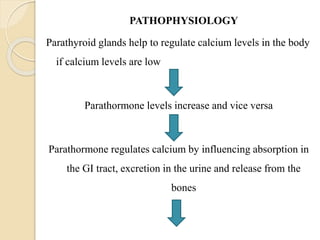
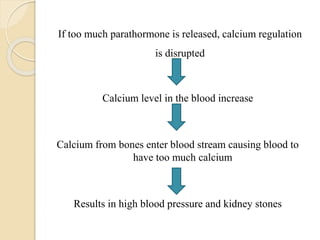
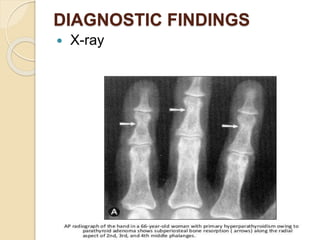
The document outlines a seminar on disorders of the parathyroid glands presented by Ms. Gautami S. Tirpude. It discusses the general and specific objectives of gaining knowledge about parathyroid gland disorders and their application in nursing practice. The seminar covers topics like hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism including their definition, etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic studies, and medical and surgical management. It also discusses the nursing role in managing related complications through various nursing interventions.