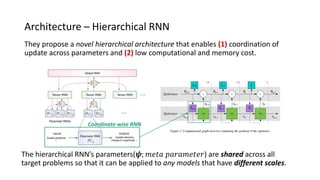
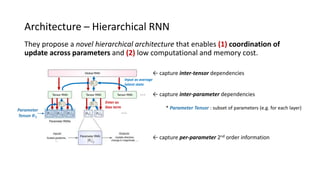
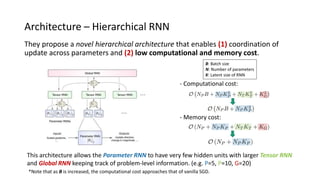
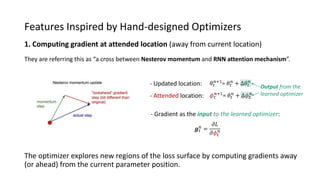
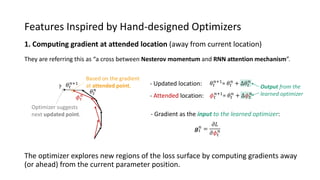
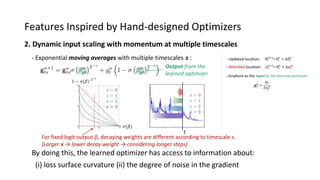
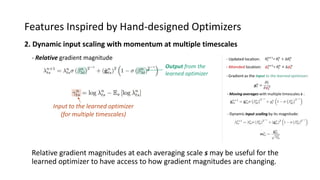
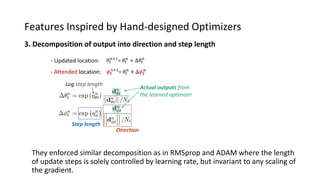
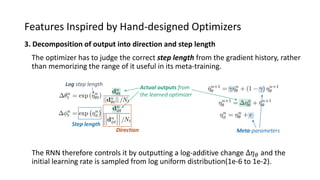
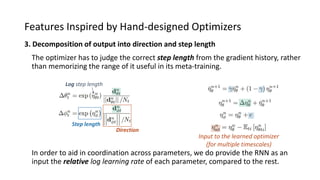
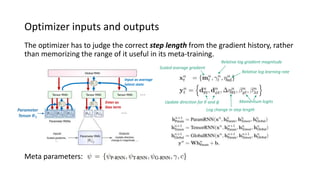
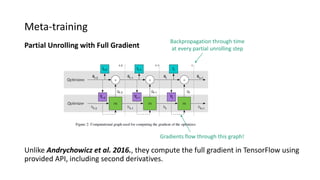
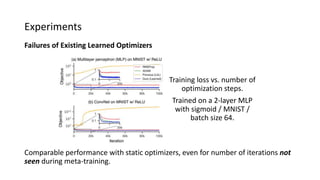
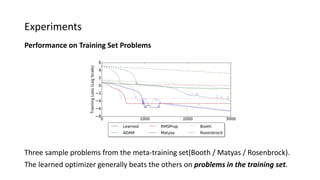
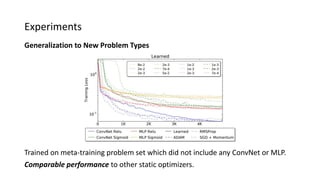
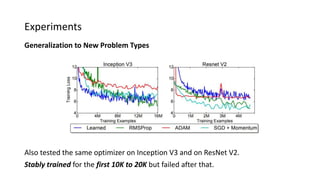
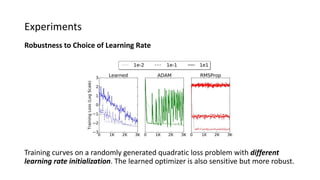
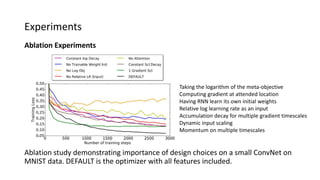
The paper proposes a novel hierarchical RNN architecture for a learned optimizer that aims to address scalability and generalization issues. The architecture uses a hierarchical structure of parameter, tensor, and global RNNs to enable coordination of updates across parameters with low memory and computation costs. It also incorporates features inspired by hand-designed optimizers like computing gradients at attended locations and dynamic input scaling to provide the learned optimizer with useful information. The optimizer is meta-trained on diverse small problems and can generalize to optimizing new problem types, though it struggles on very large models. Ablation studies show the importance of the paper's design choices for the learned optimizer's performance.