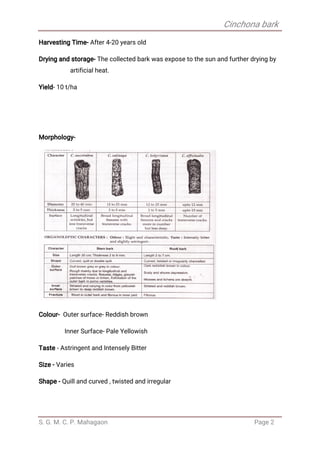
Cinchona bark comes from several species of Cinchona trees native to South America. It contains alkaloids such as quinine and quinidine that have antimalarial properties. The document describes the biological source, geographical source, cultivation methods, morphology, microscopic characteristics, chemical tests, chemical constituents, uses and allied drugs of Cinchona bark.