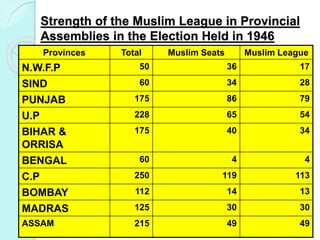
The document summarizes the key events of the Pakistan movement from 1940 to 1947, including the Lahore Resolution of 1940, the Cripps Mission of 1942, the Quit India Movement of 1942, the Gandhi-Jinnah talks of 1944, the Wavell Plan and Simla Conference of 1945, elections from 1945-1946, the Cabinet Mission Plan of 1946, the June 3rd Plan of 1947, the Radcliffe Award boundary demarcation, and finally the Indian Independence Act of 1947 which partitioned British India and led to the independence of Pakistan and India.