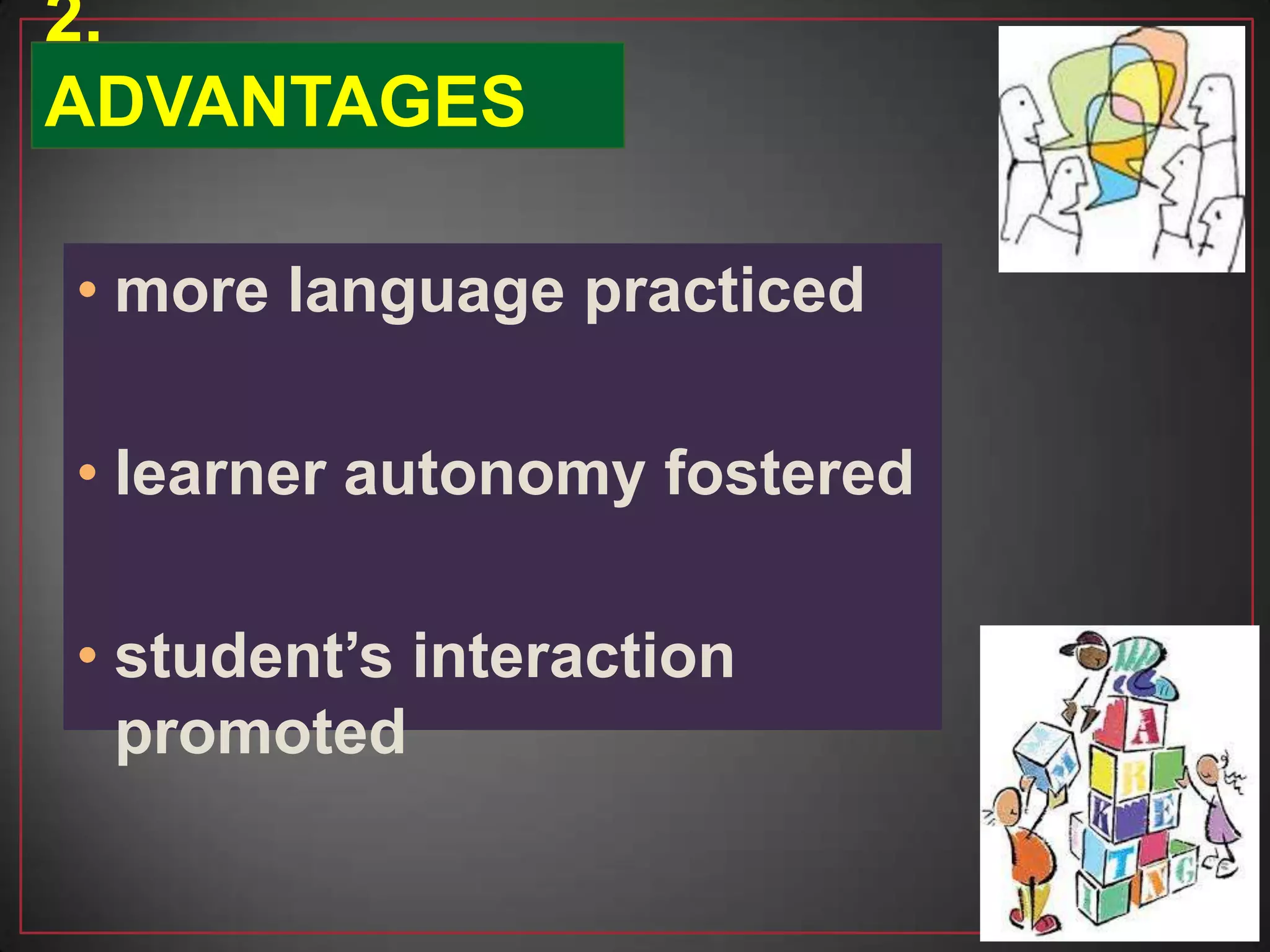
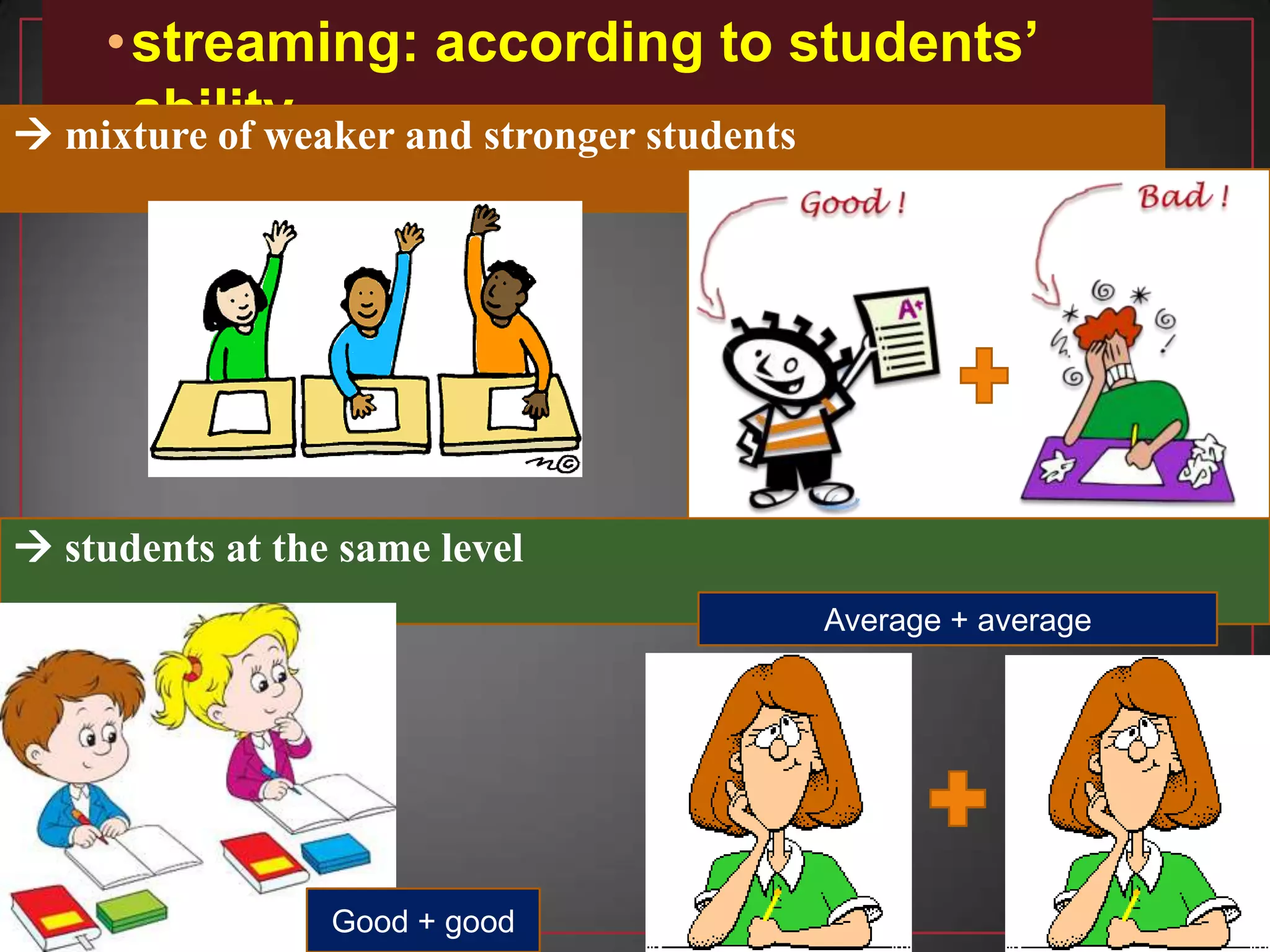
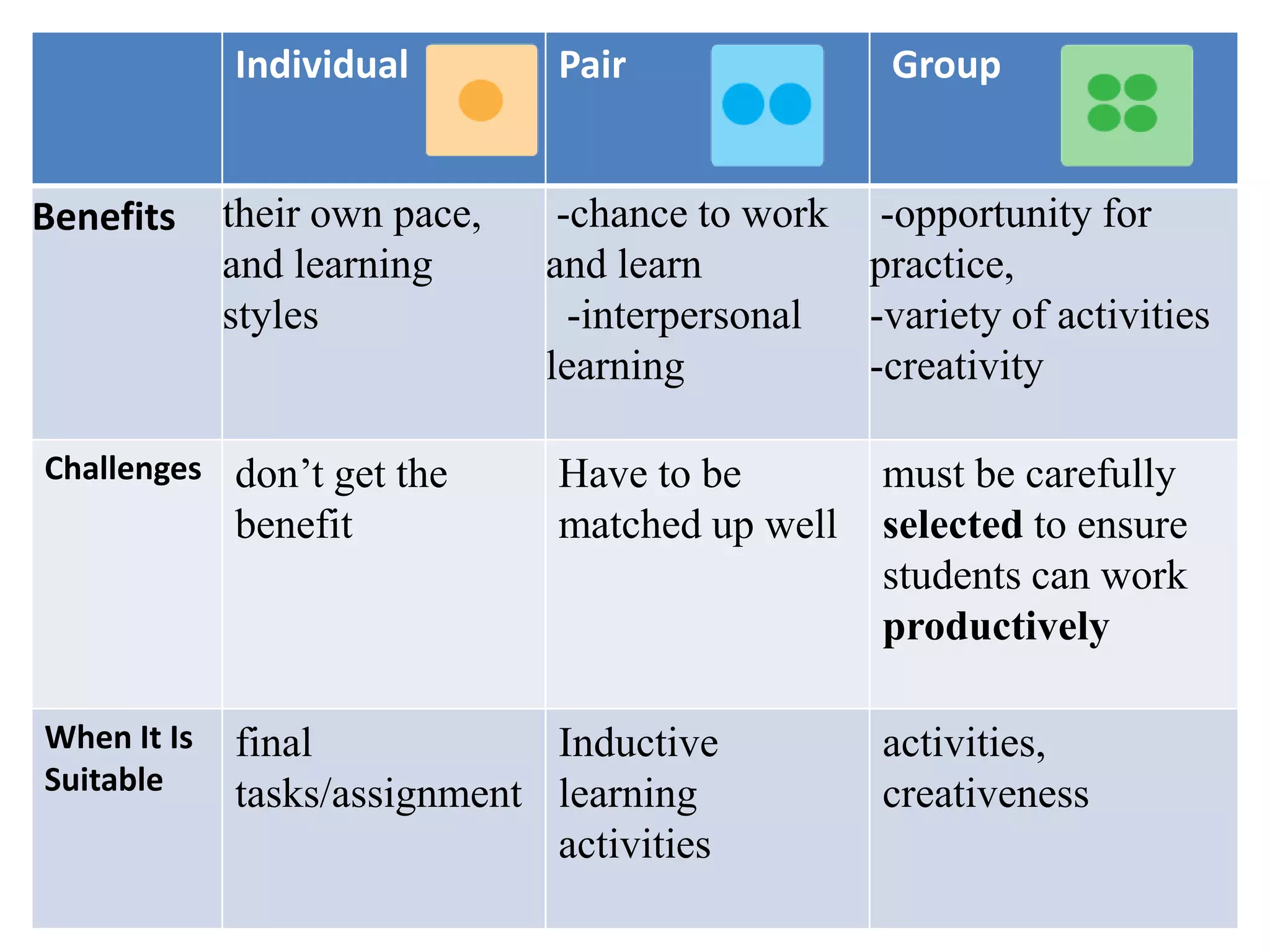
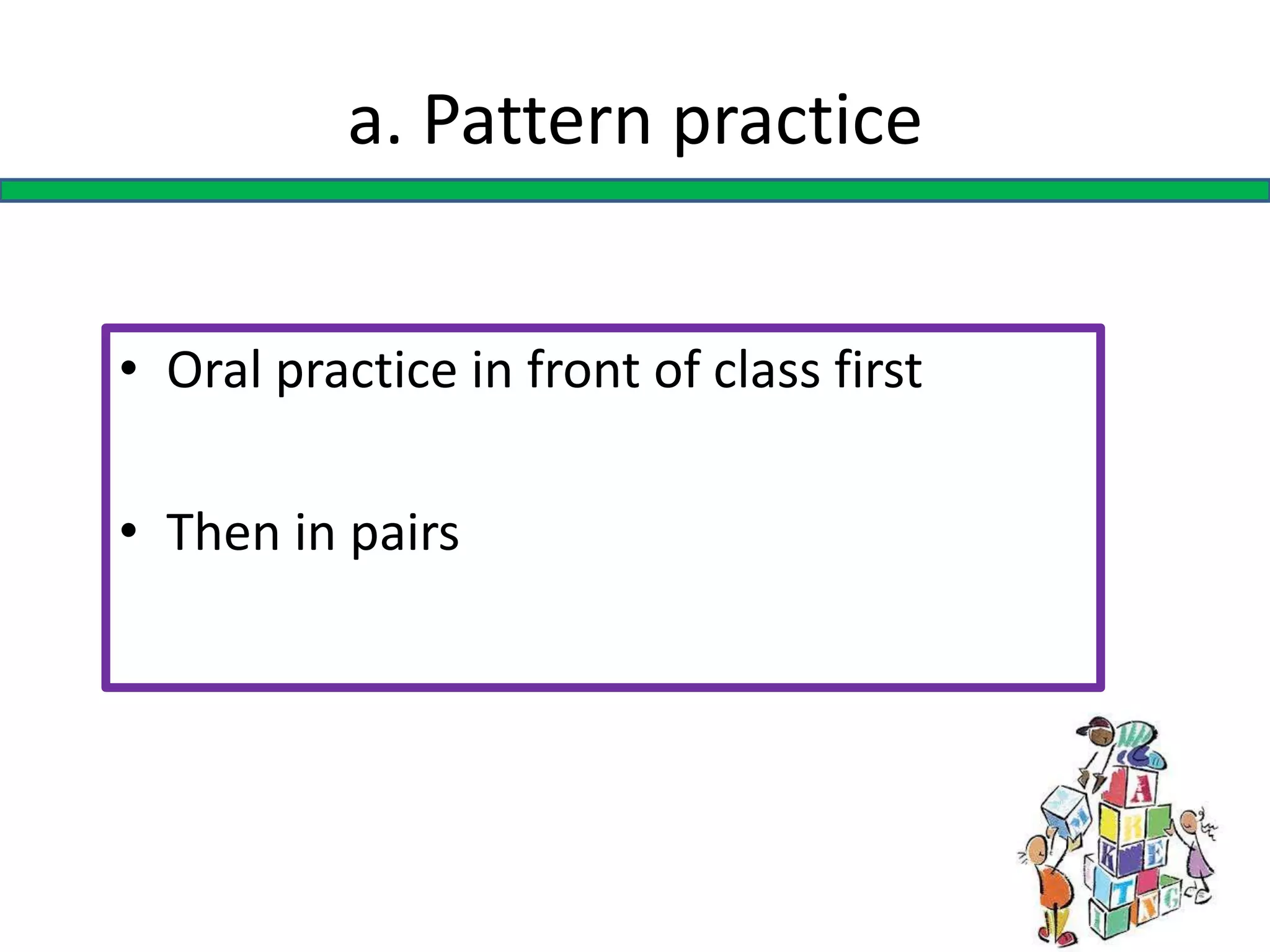
This document discusses the benefits and organization of pair and group work in language learning. It notes that pair and group work allows for more language practice, fosters learner autonomy, and promotes student interaction. When organizing activities, teachers should provide clear instructions, monitor for fluency versus accuracy, and give feedback. The document also addresses potential disadvantages like students going off-task and provides suggestions for formation, such as pairing students of similar ability or randomly.