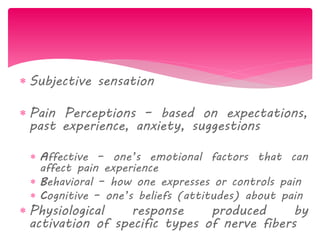
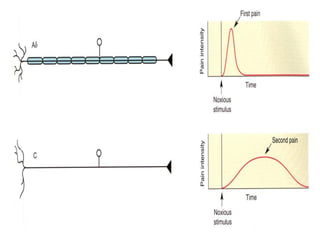
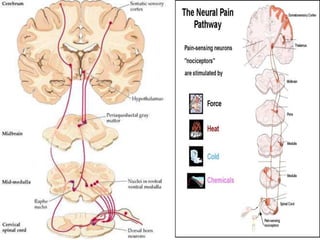
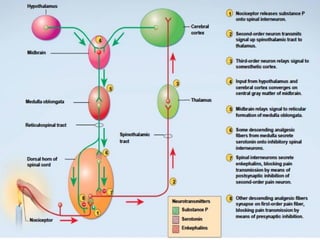
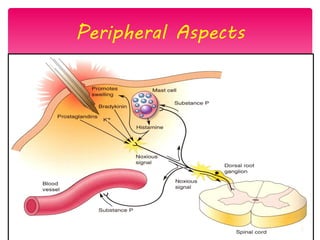
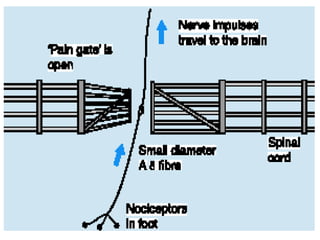
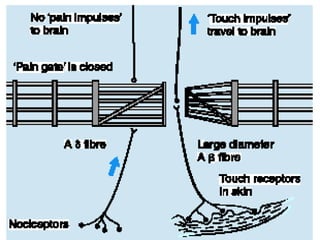
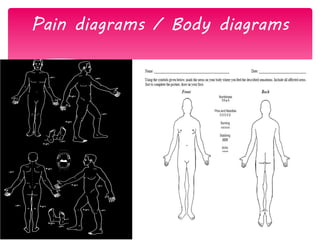
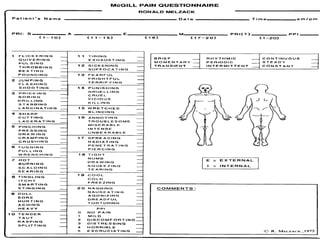
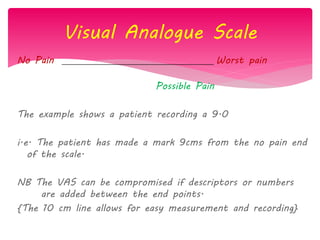
The document discusses the definition, theories, and types of pain, explaining it as an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience related to potential tissue damage. It covers various pain pathways, physiological responses, and the gate control theory, highlighting how pain is perceived and assessed subjectively. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of accurate assessment in understanding pain and notes various tools for pain measurement.