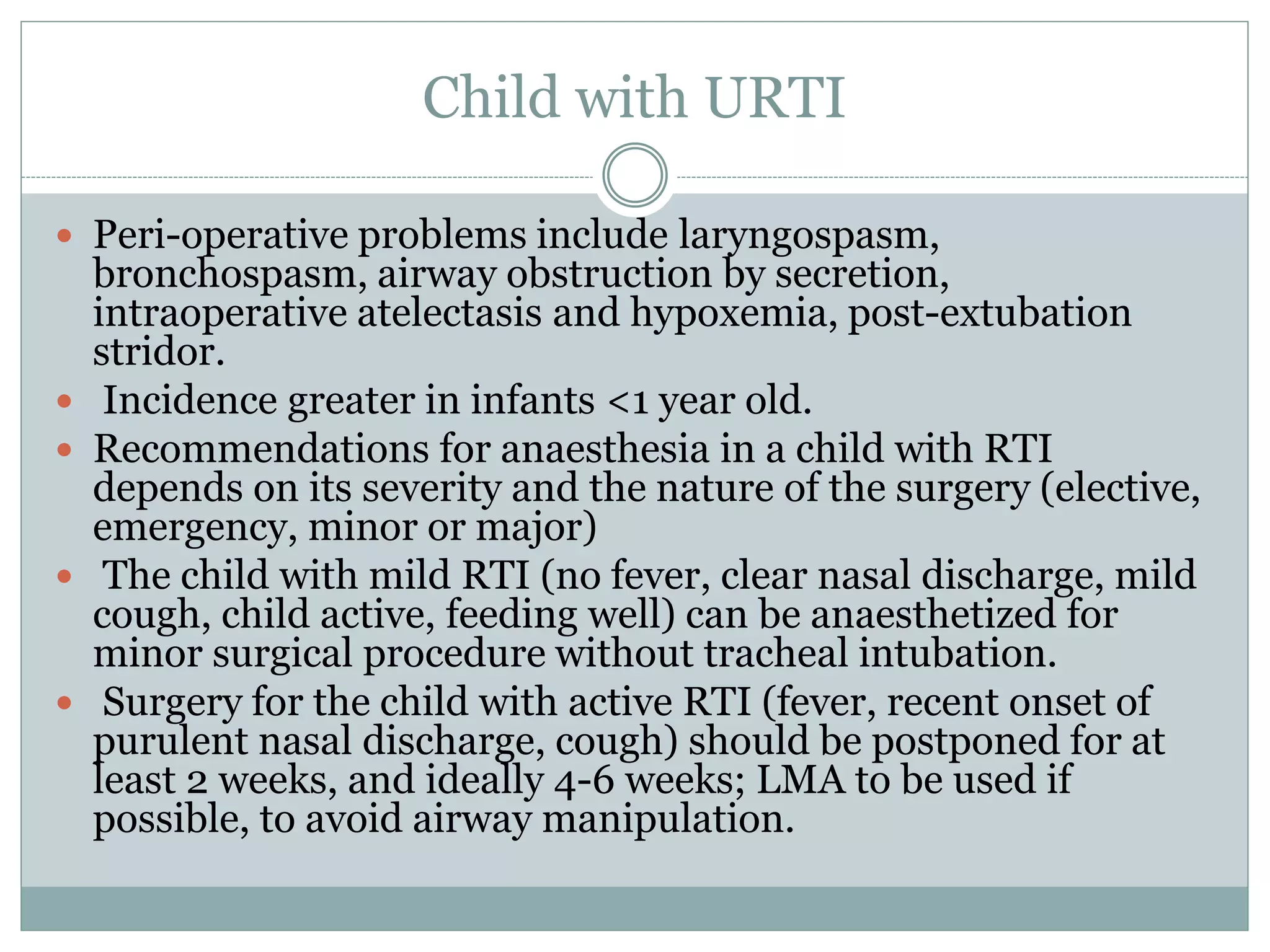
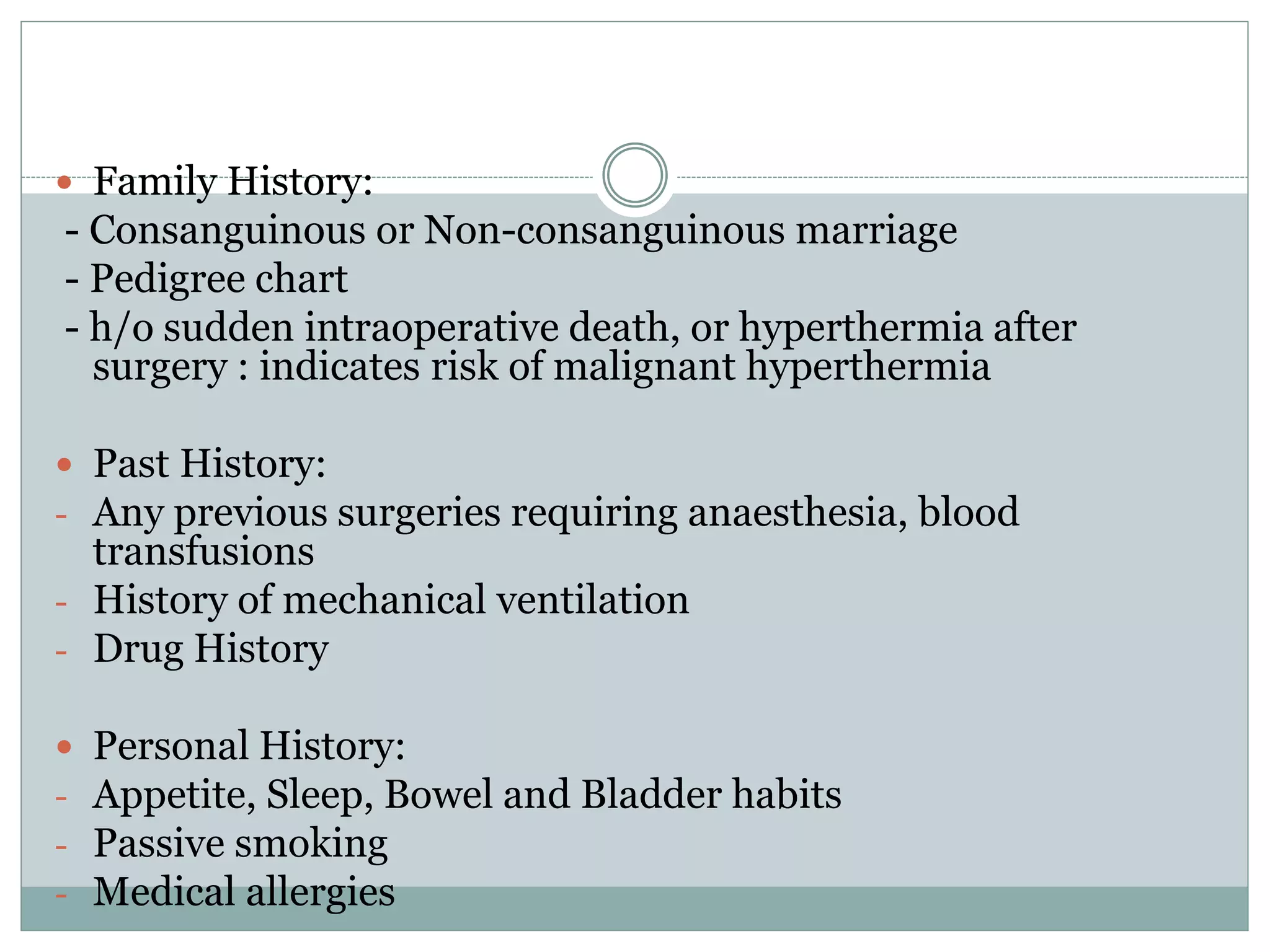
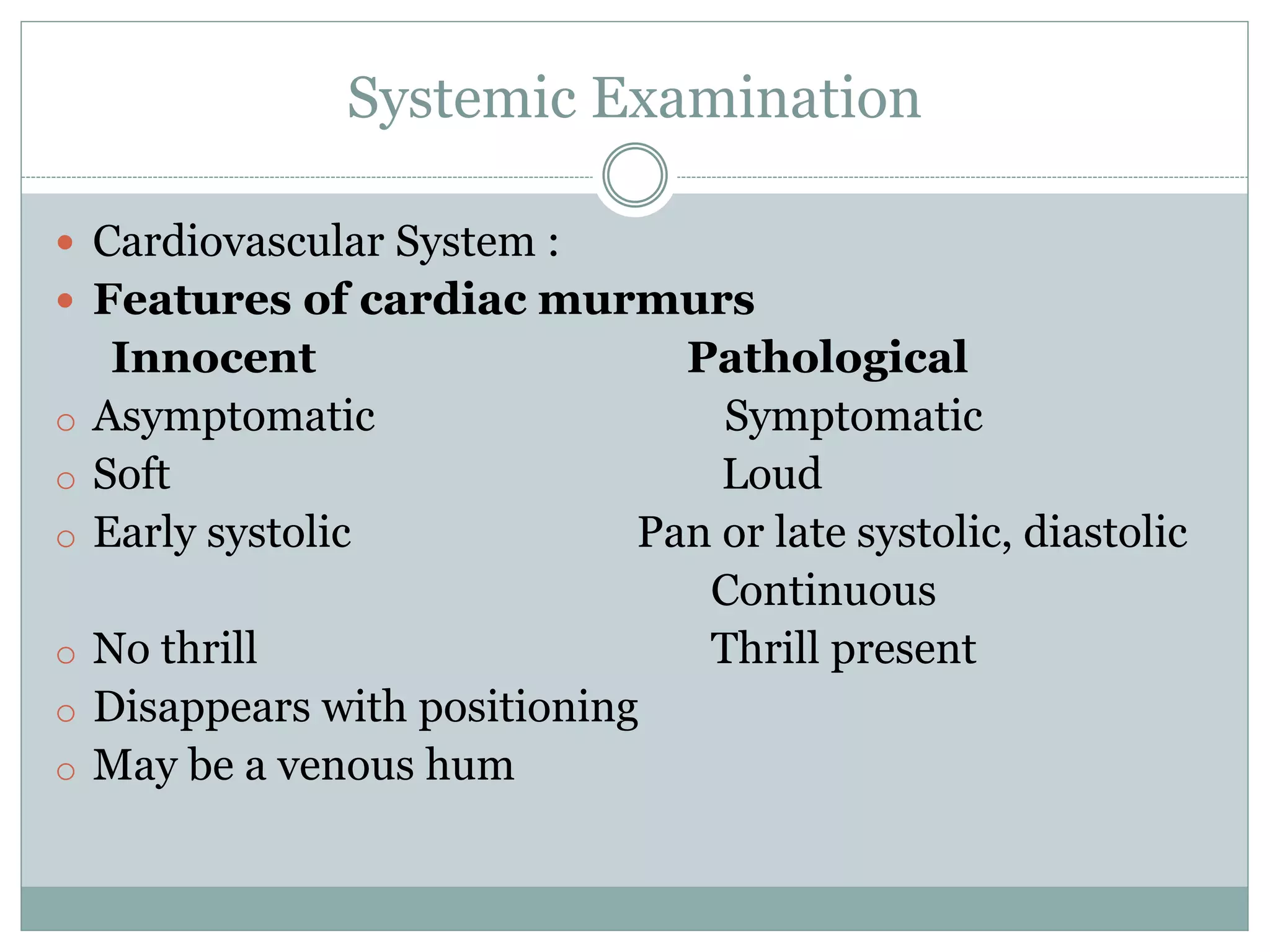
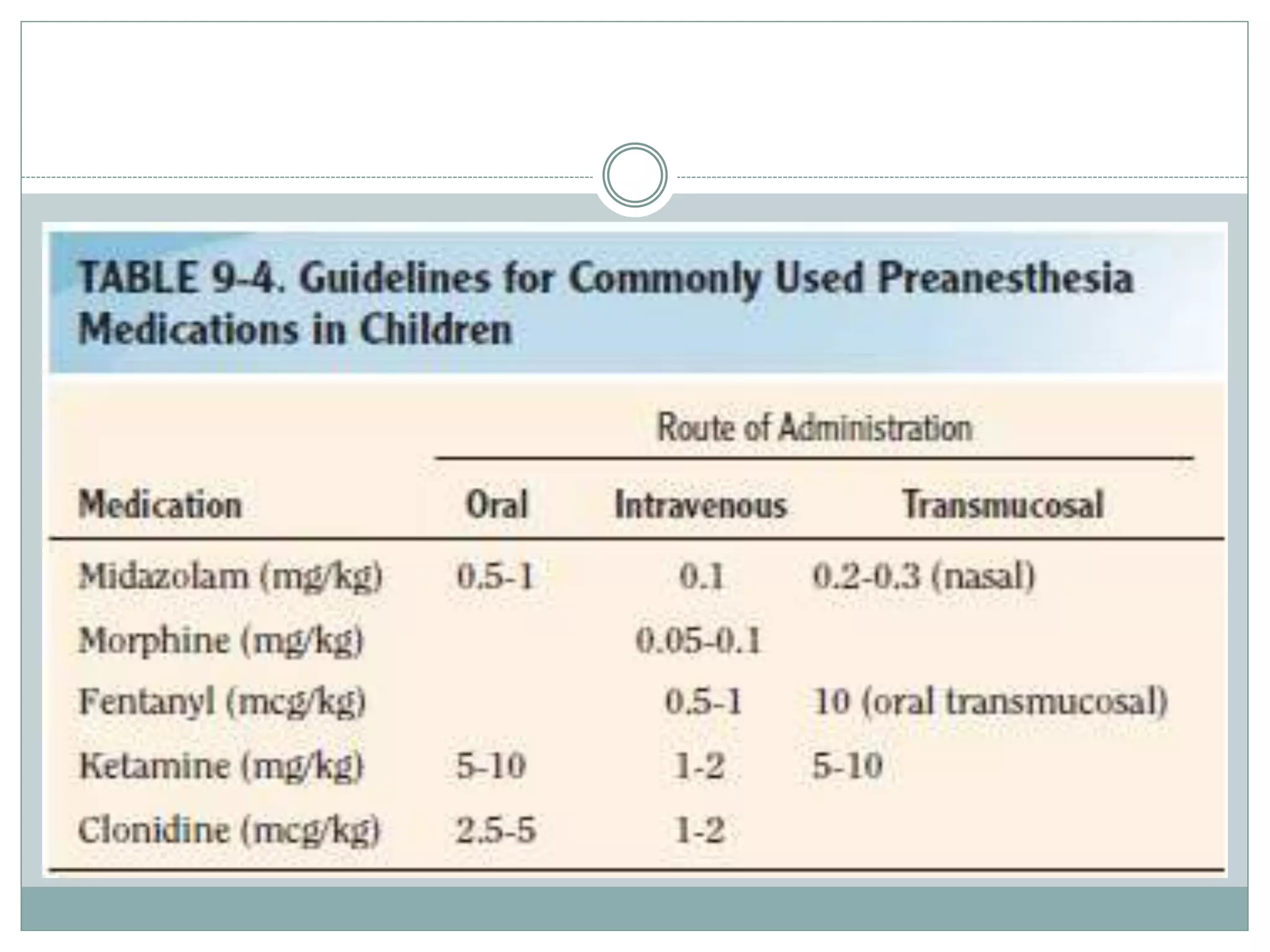
This document provides guidance on pre-anaesthetic evaluation for paediatric patients. It discusses the importance of a thorough history, physical exam, and assessment to plan safe anaesthesia and post-operative care. The key components of evaluation are outlined, including assessing medical history, performing a physical exam, reviewing investigations, determining ASA classification, obtaining consent, and preparing the patient. Factors like temperature control, fluid management, and psychological preparation are also addressed to optimize patient safety and outcomes.