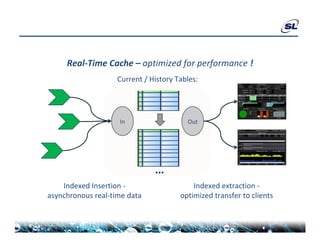
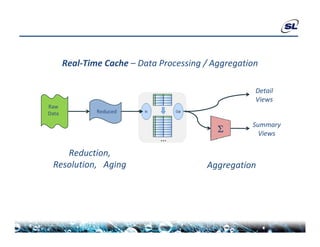
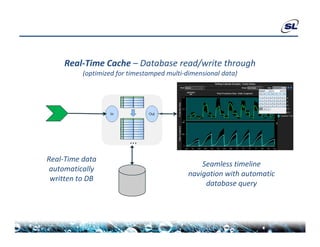
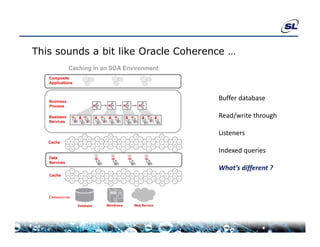
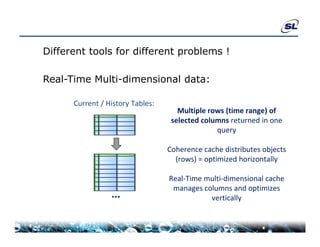
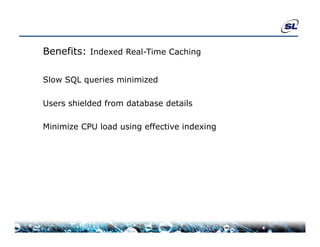
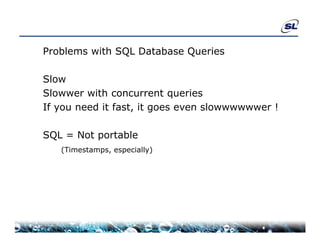
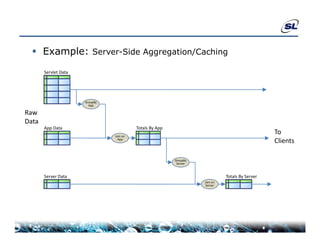
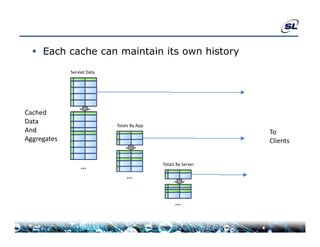
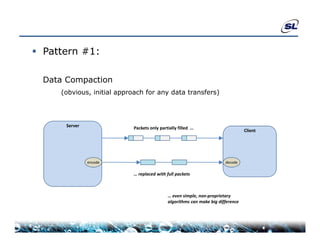
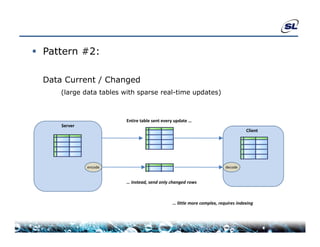
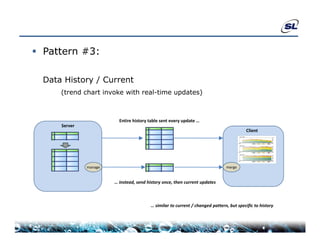
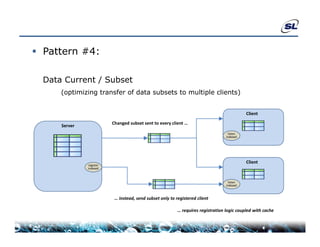
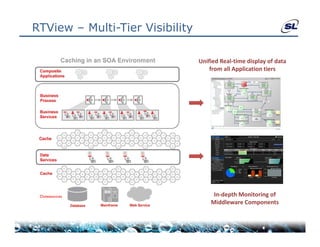
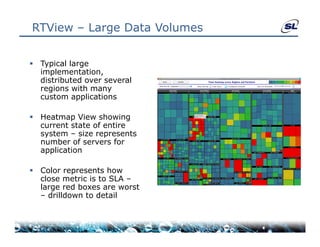
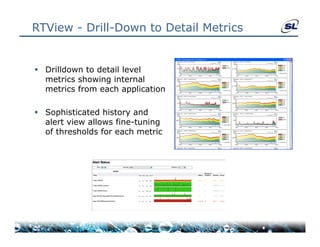
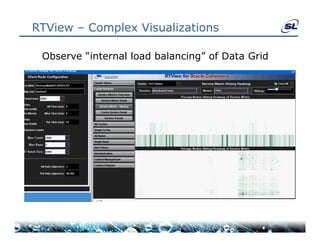
The document discusses the challenges of achieving real-time performance in large-scale data-centric applications, identifying key issues such as database performance, network bandwidth, processor efficiency, and unpredictability due to virtualization. It proposes solutions including proper data modeling, server-side aggregation, and efficient data transfer design patterns to optimize performance. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of understanding data and respecting established design patterns for effective application performance monitoring.