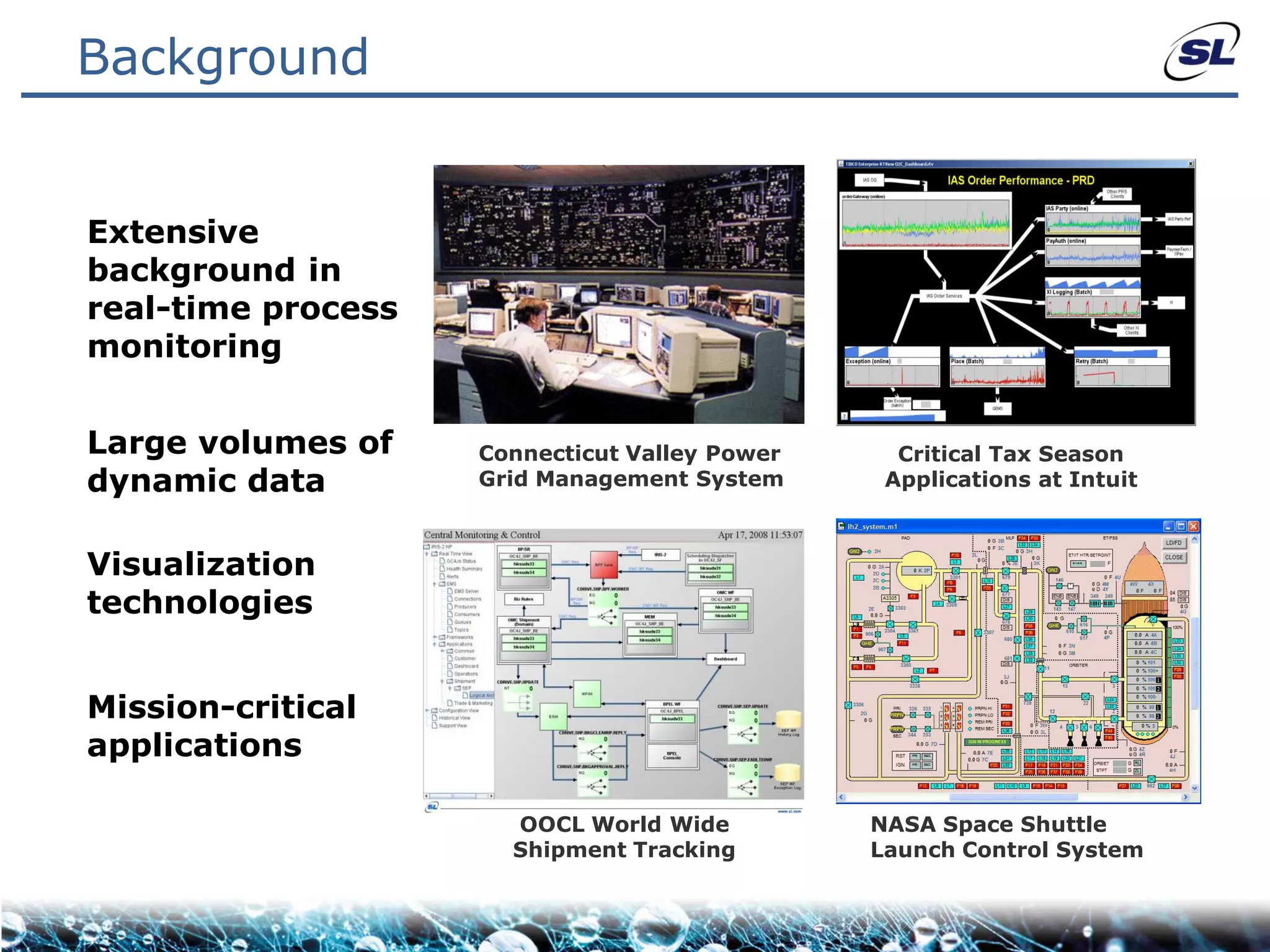
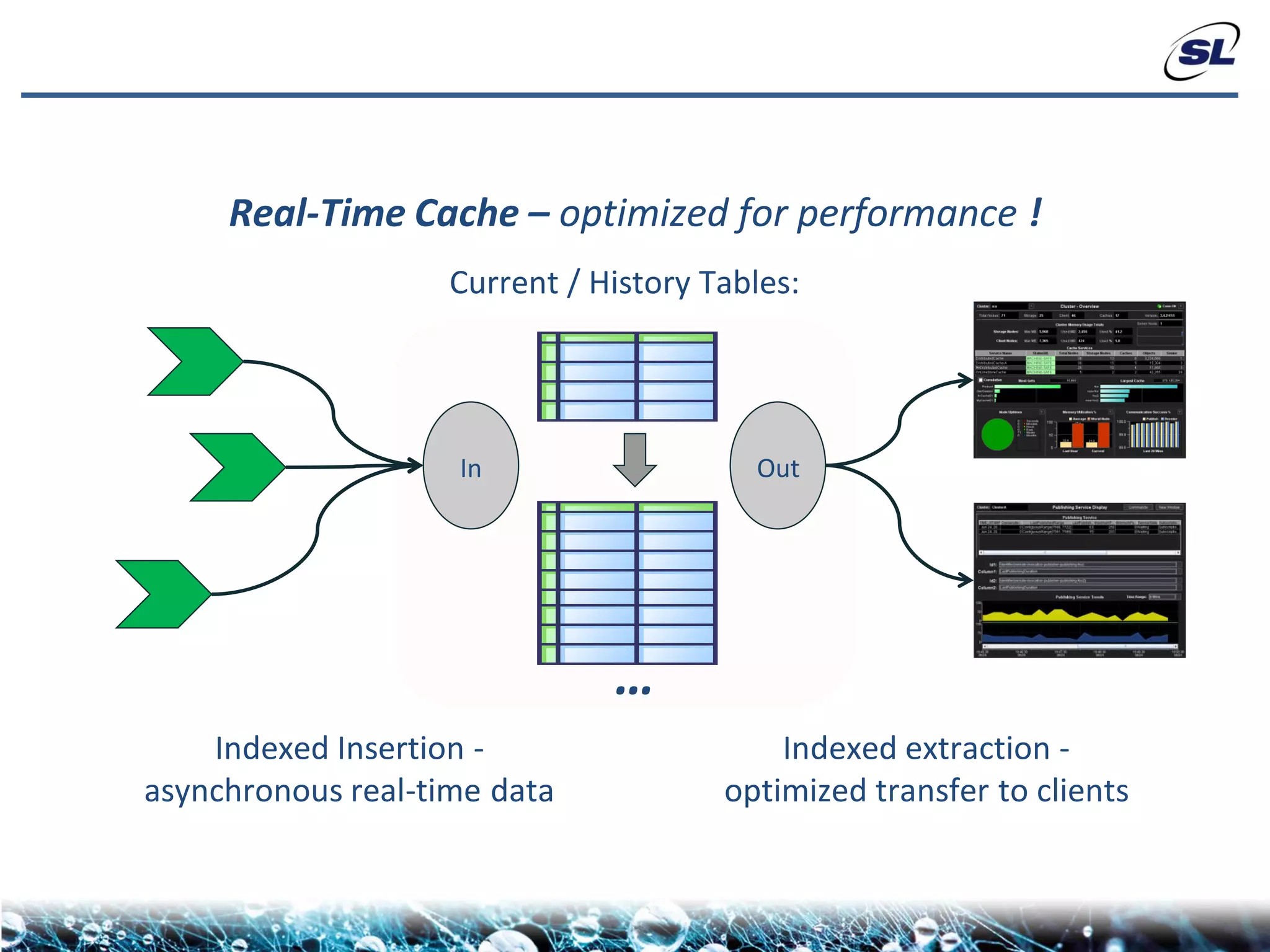
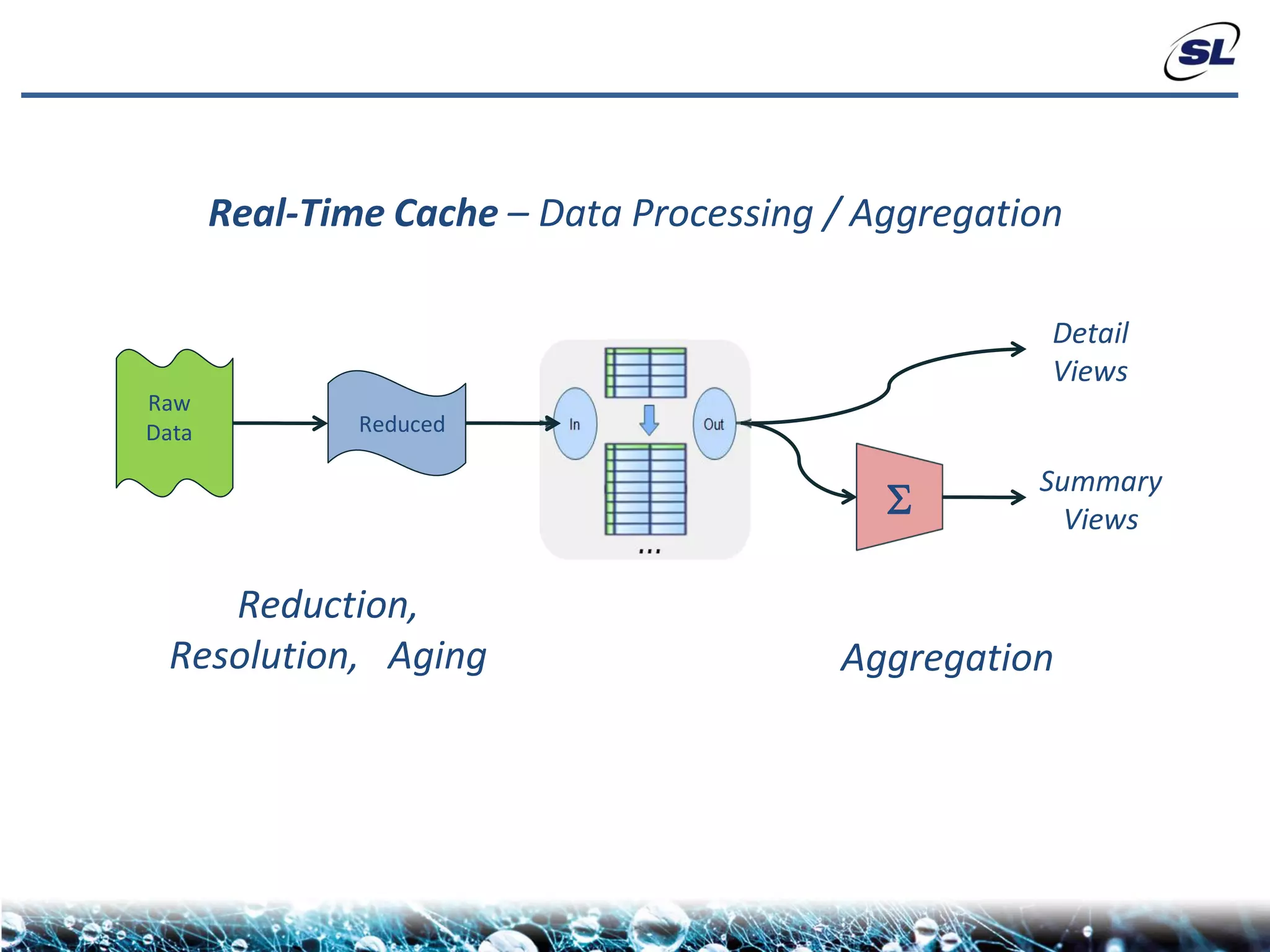
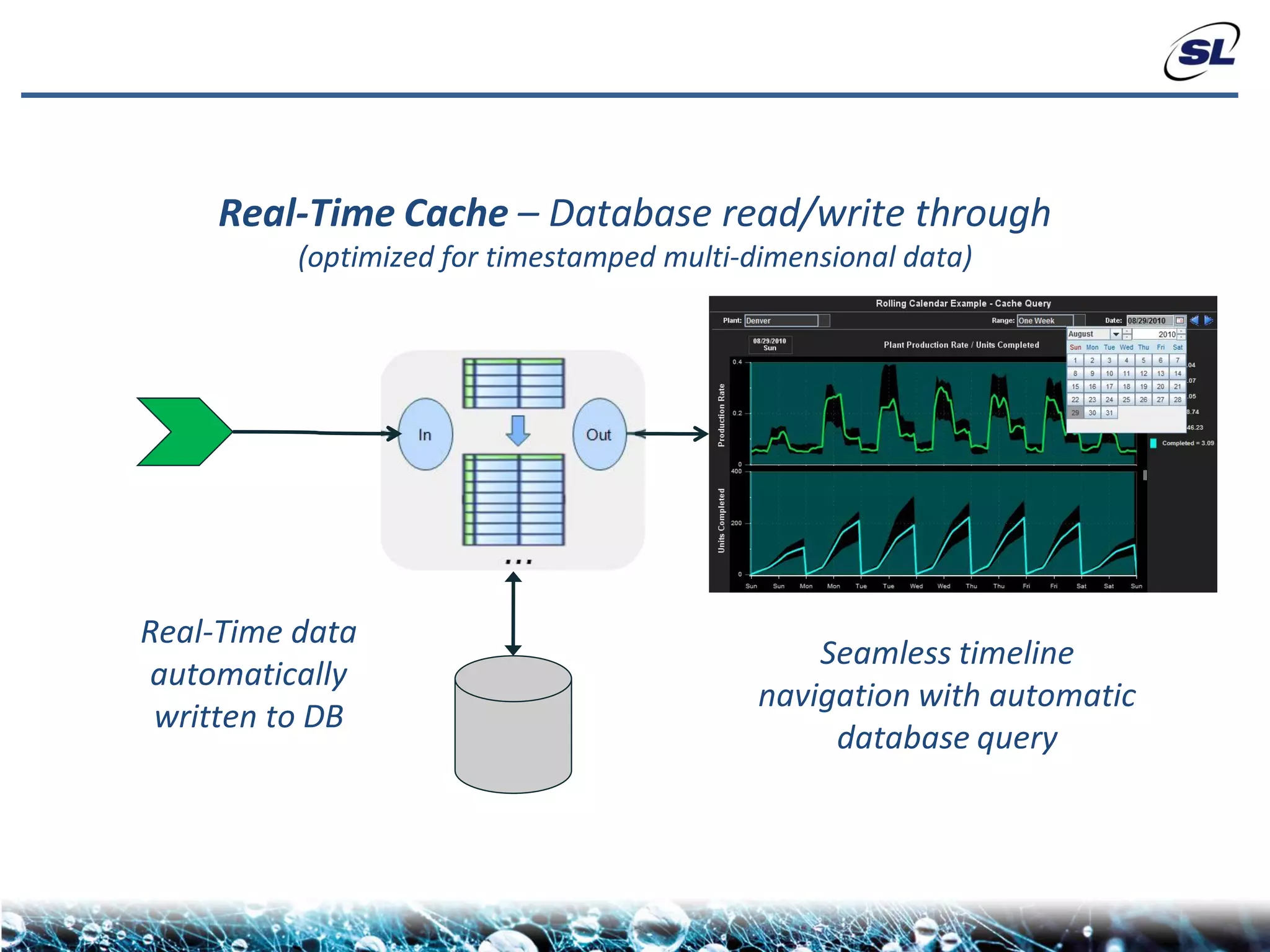
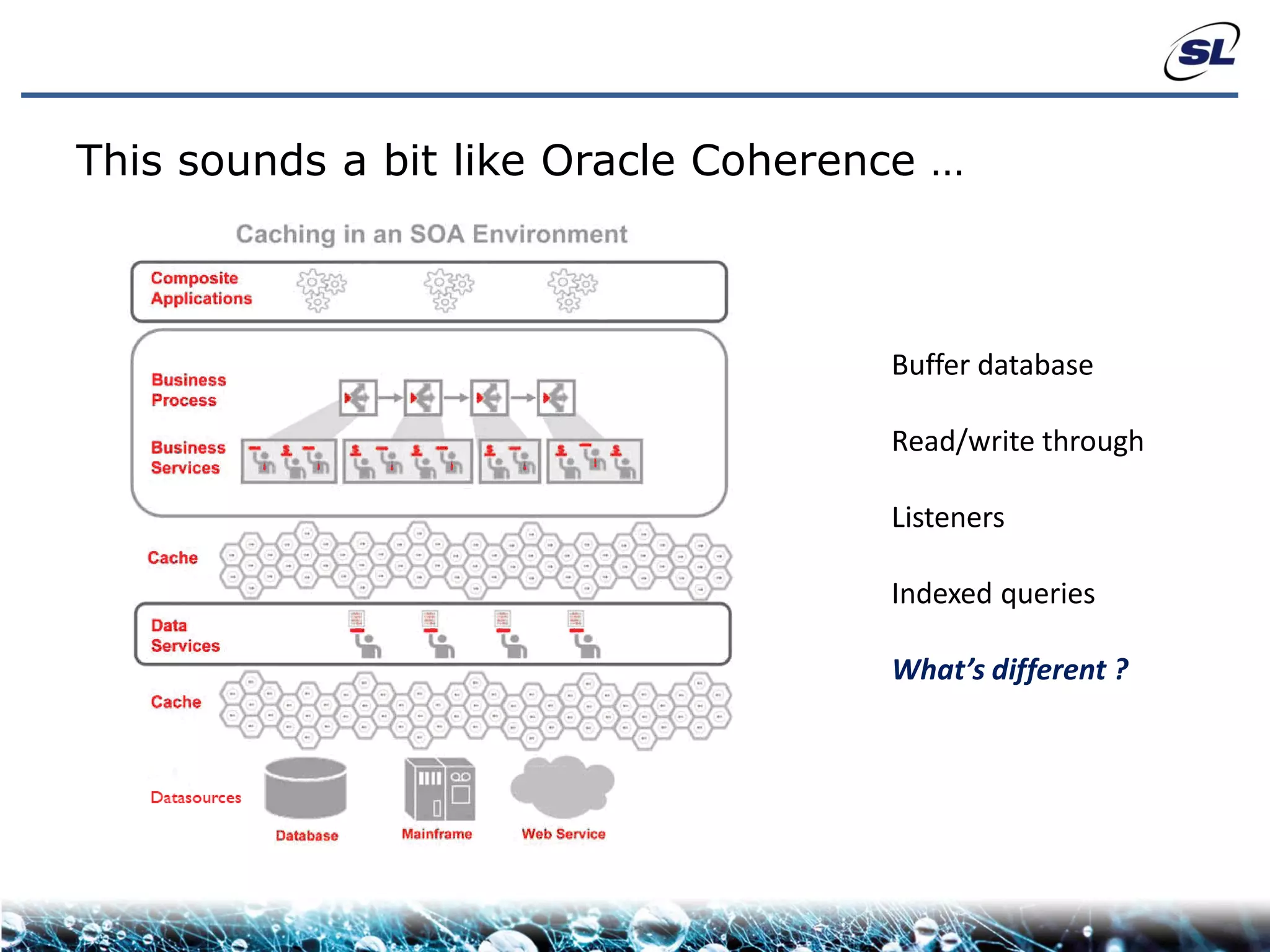
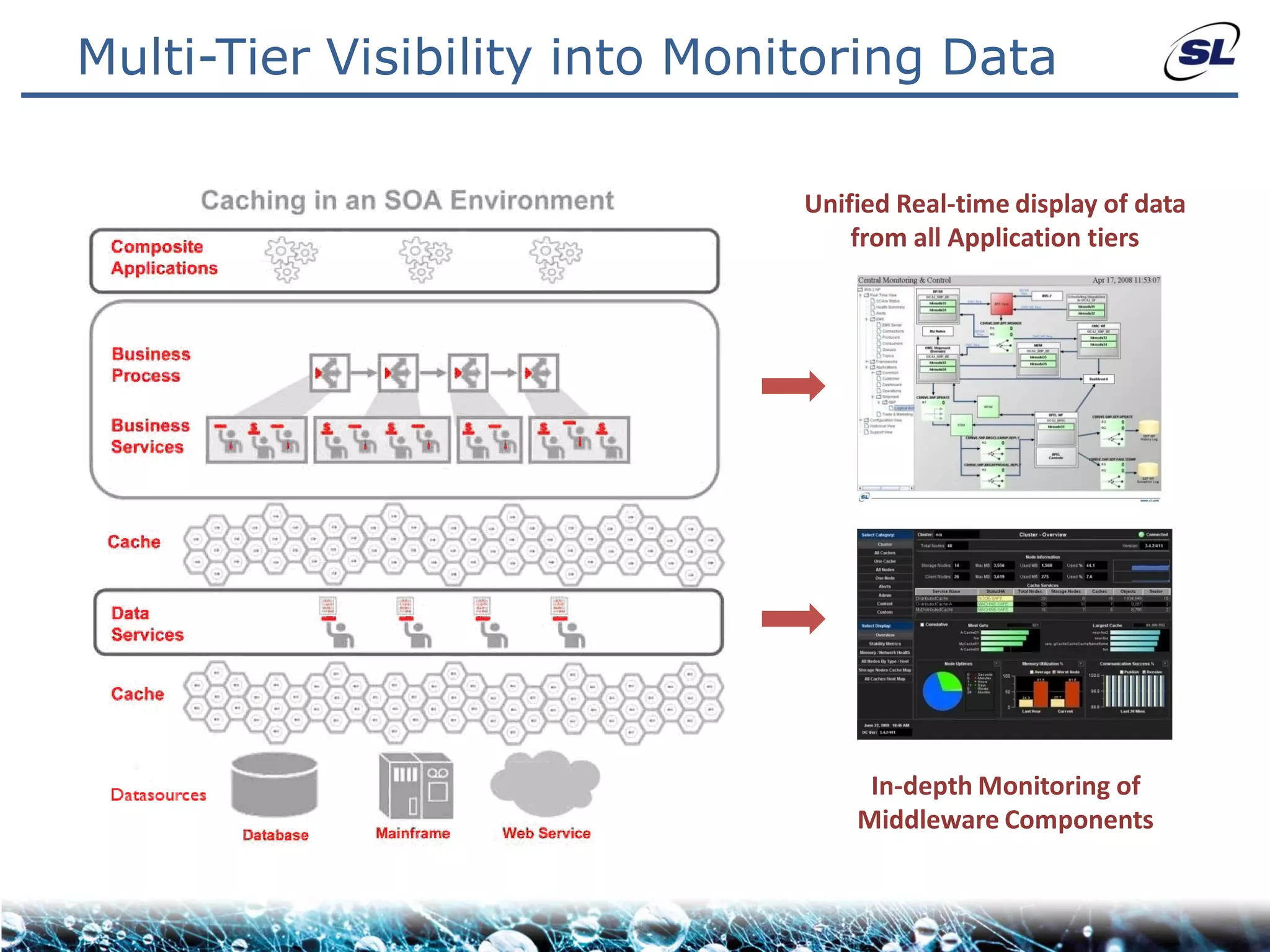
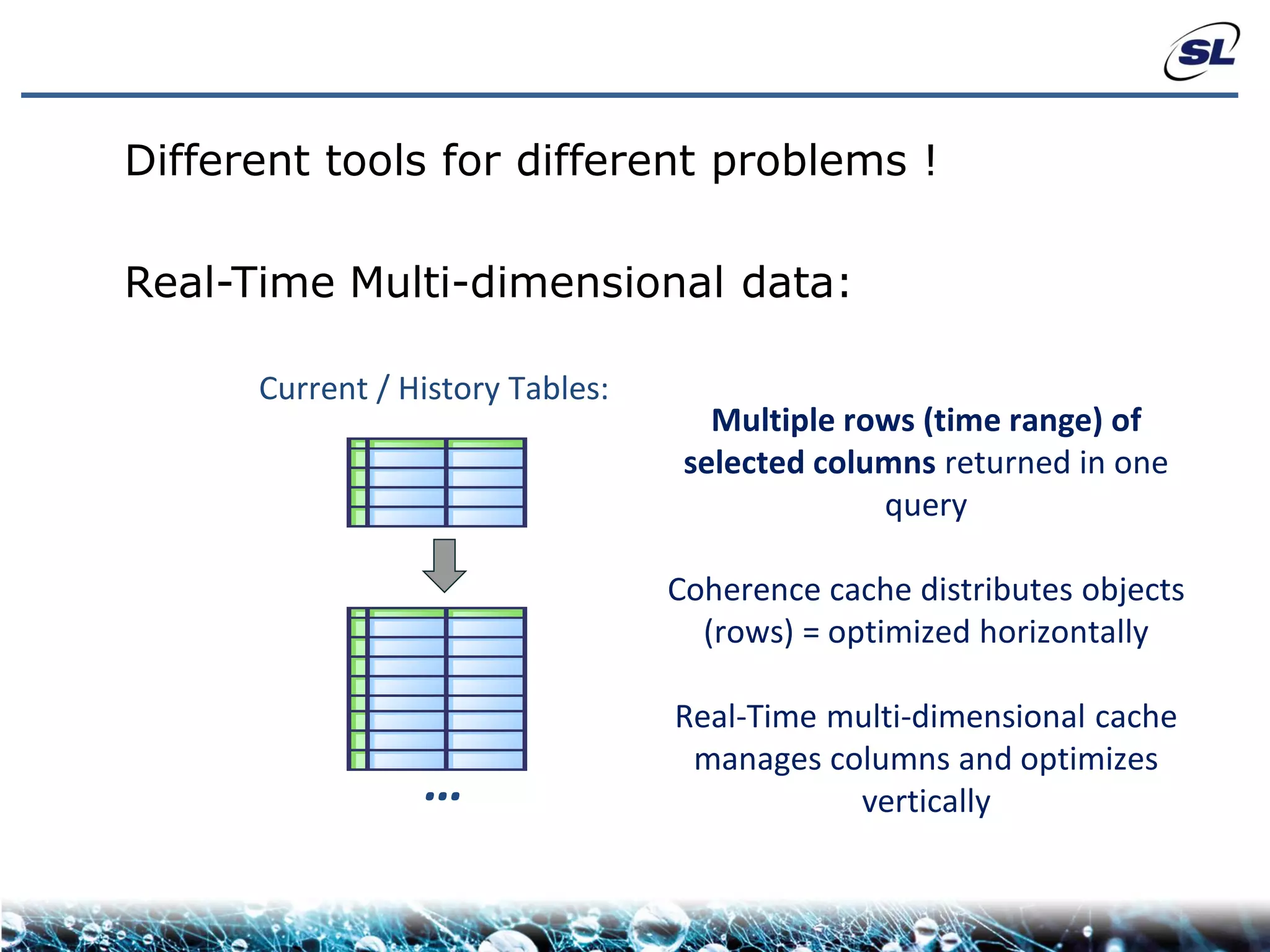
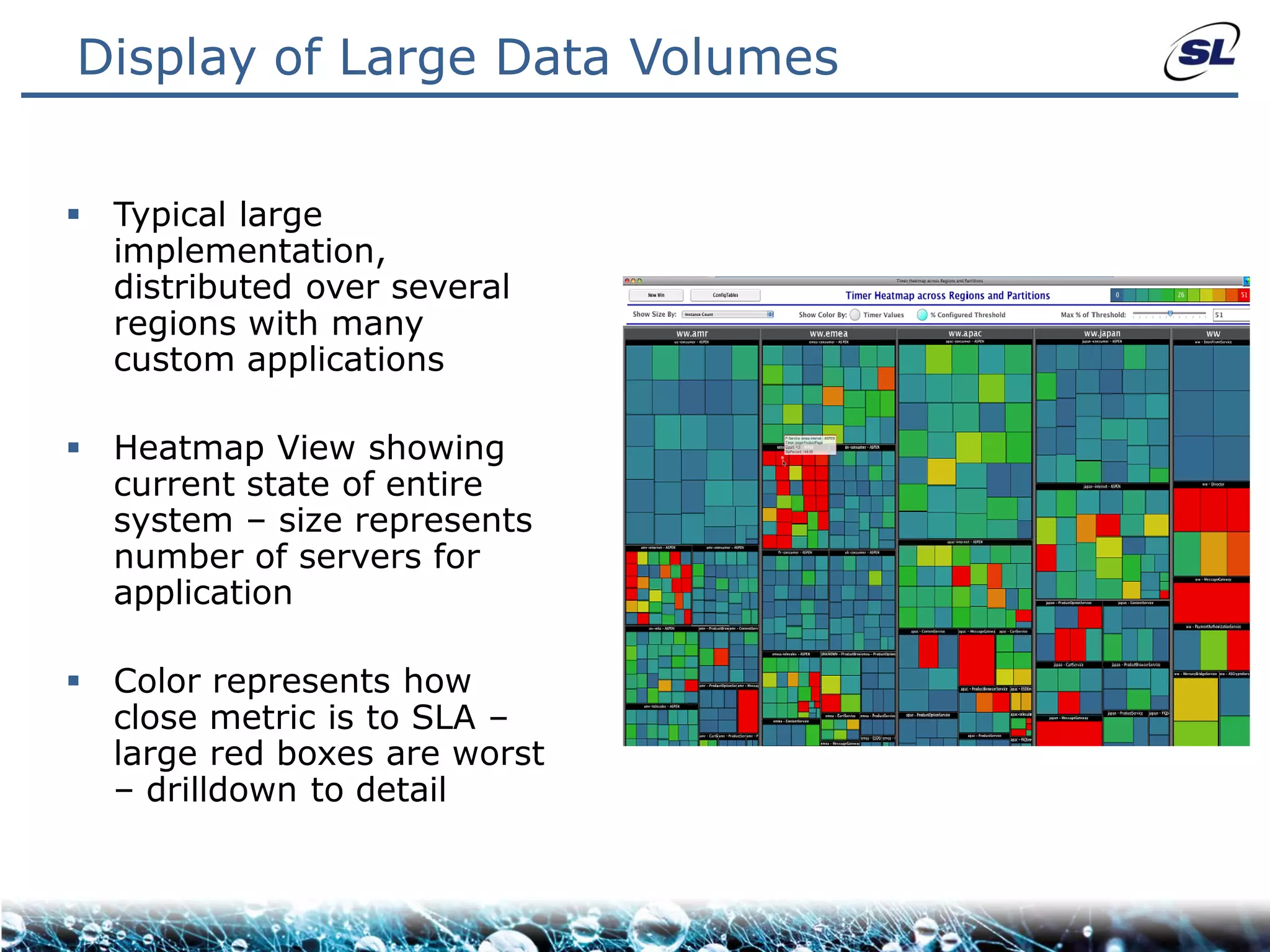
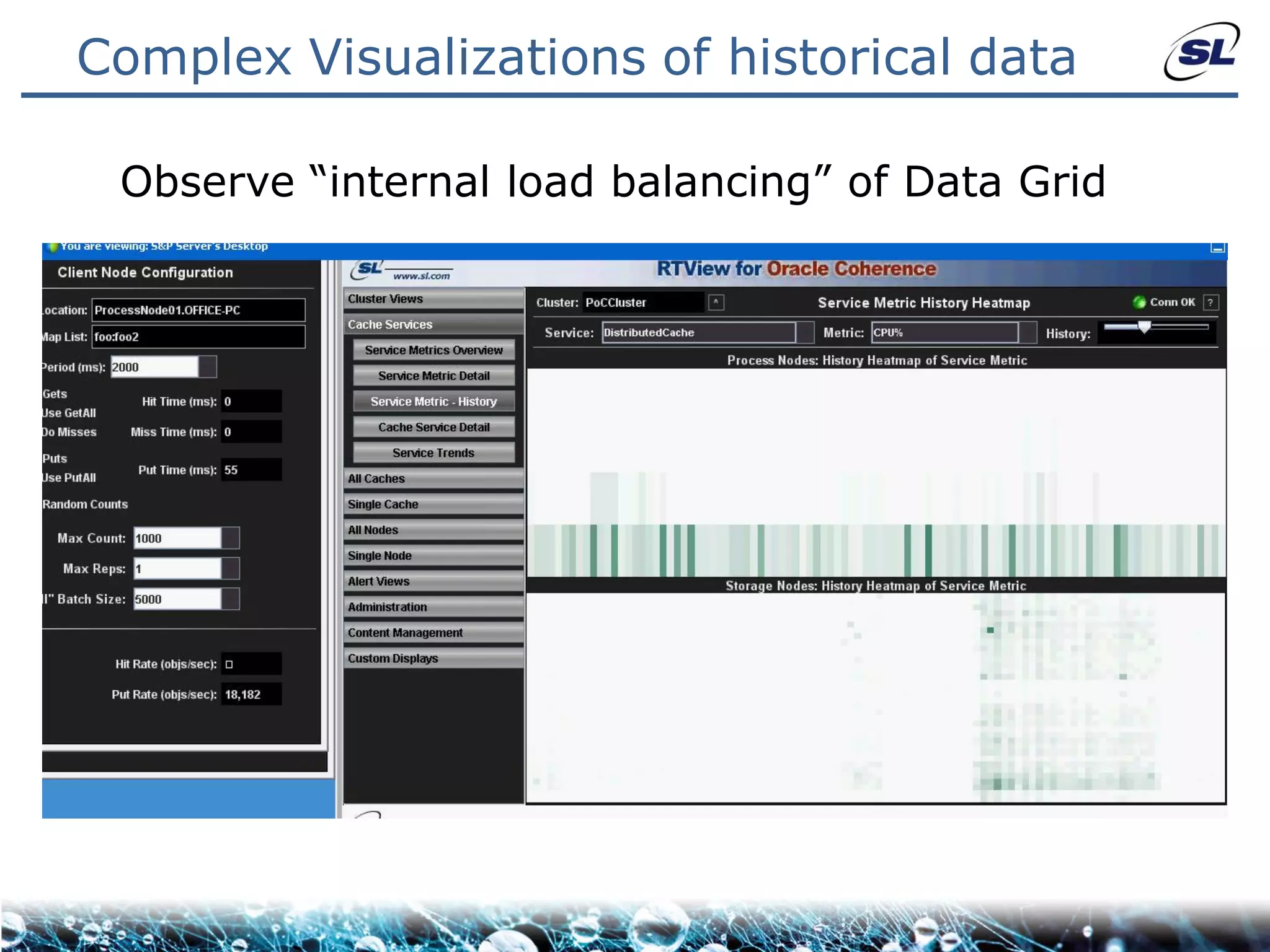
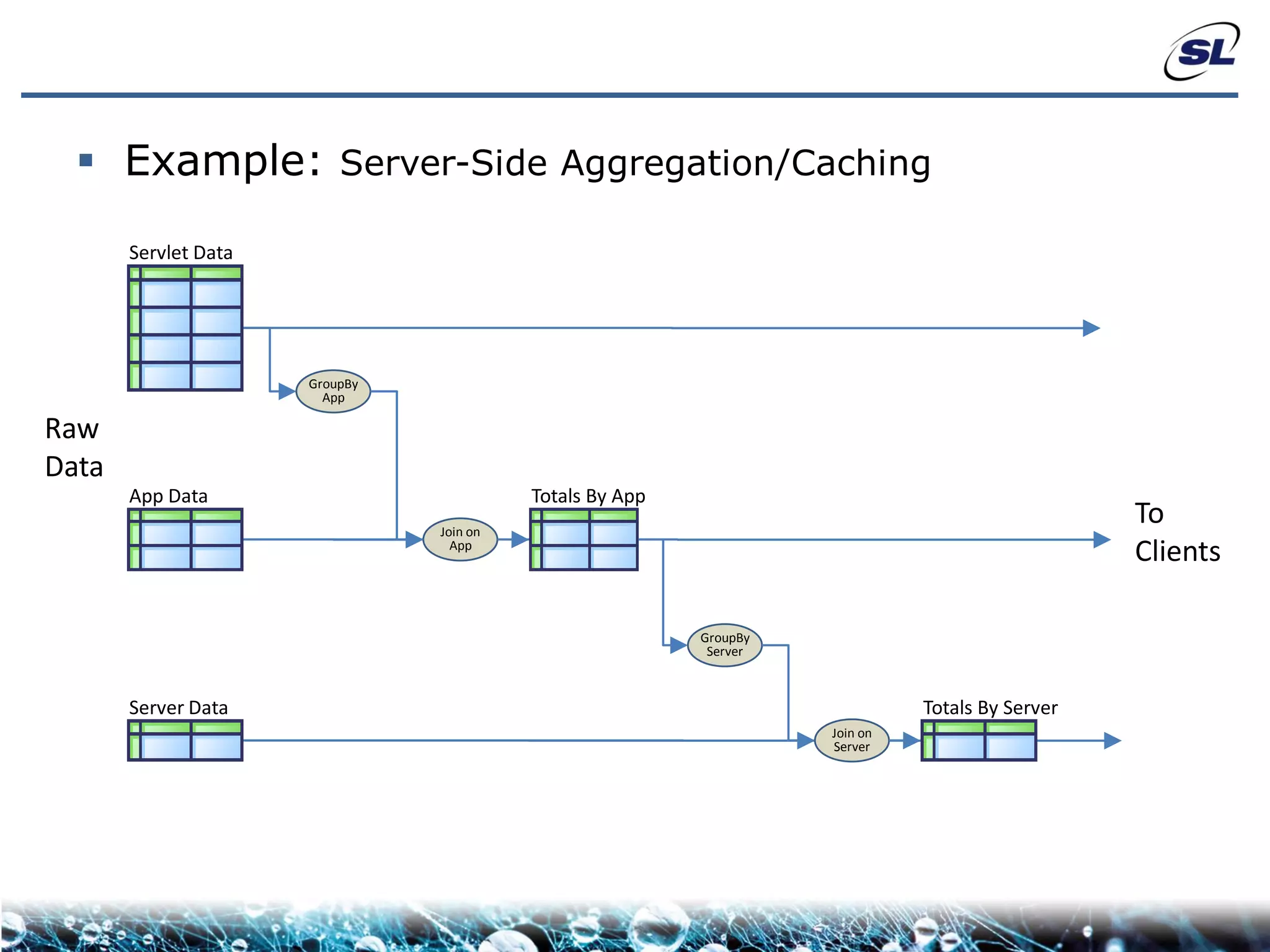
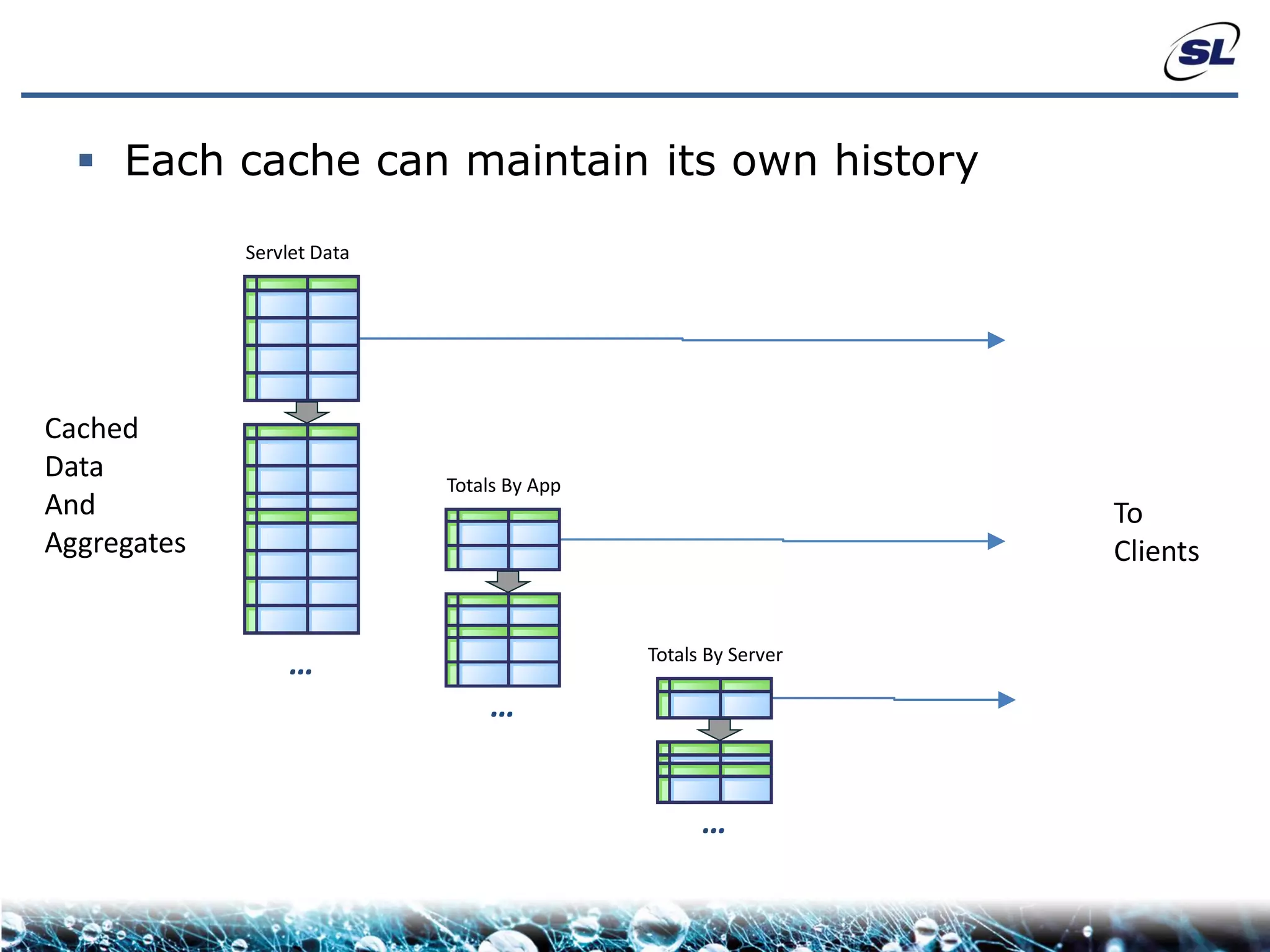
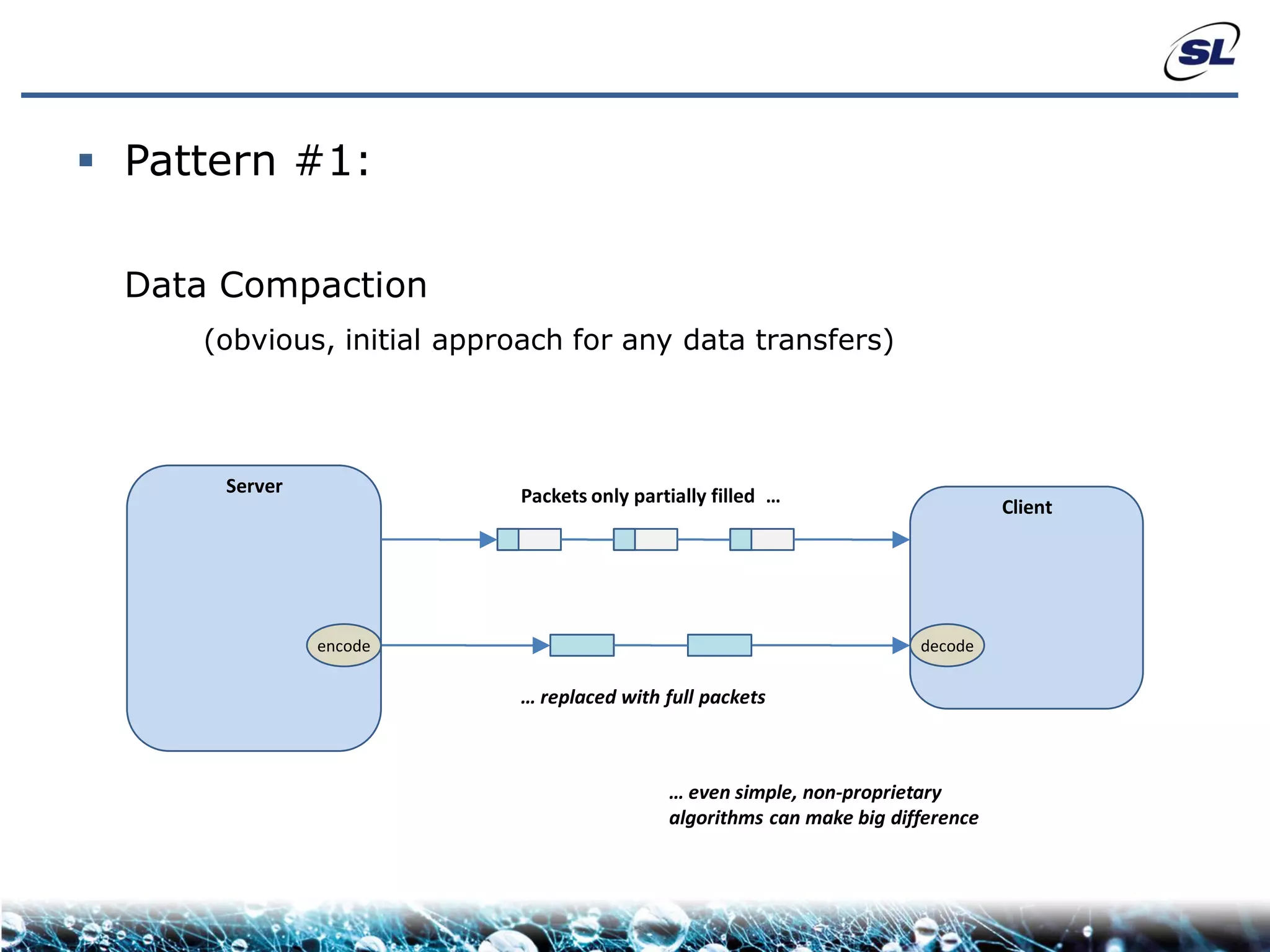
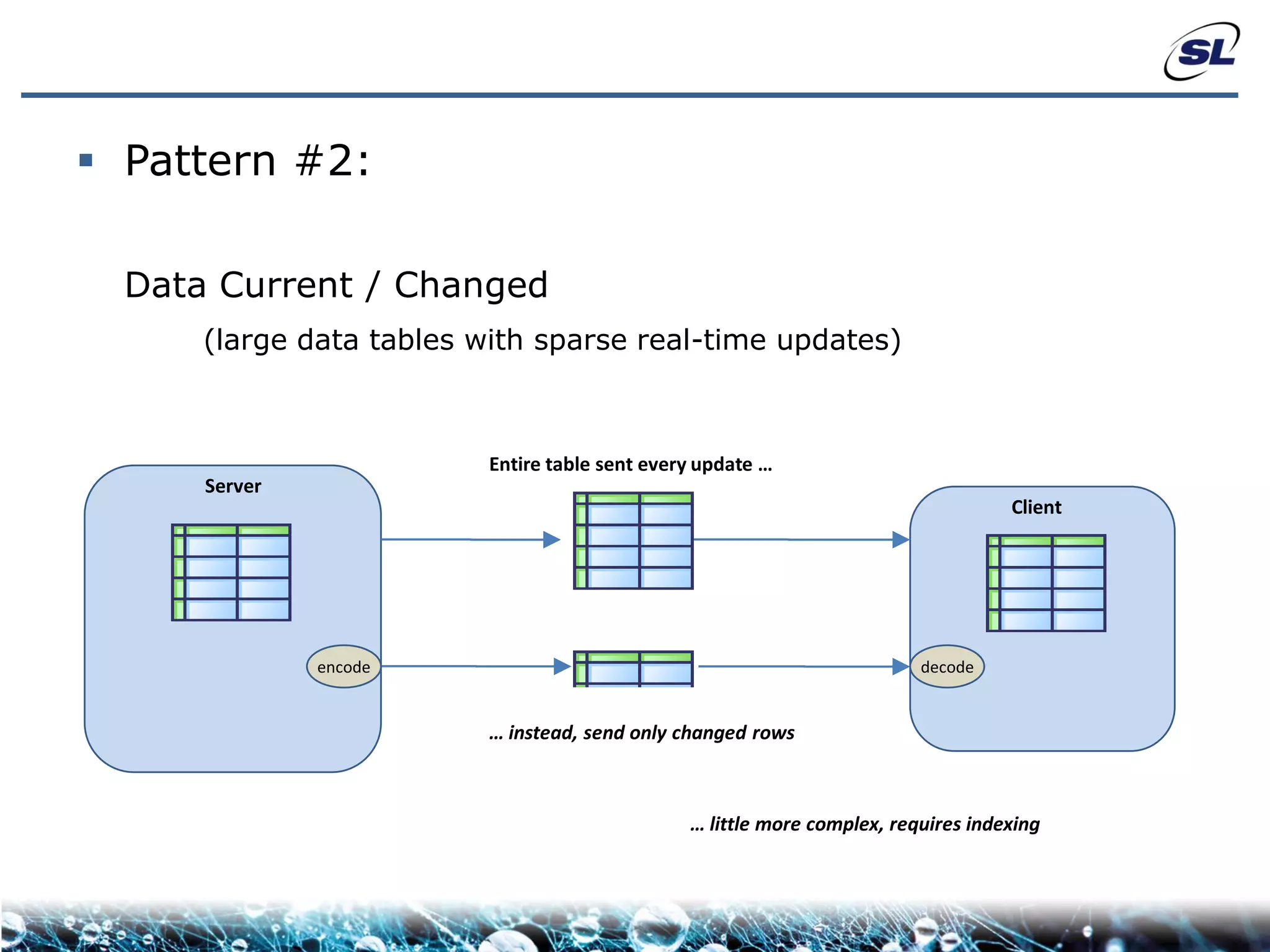
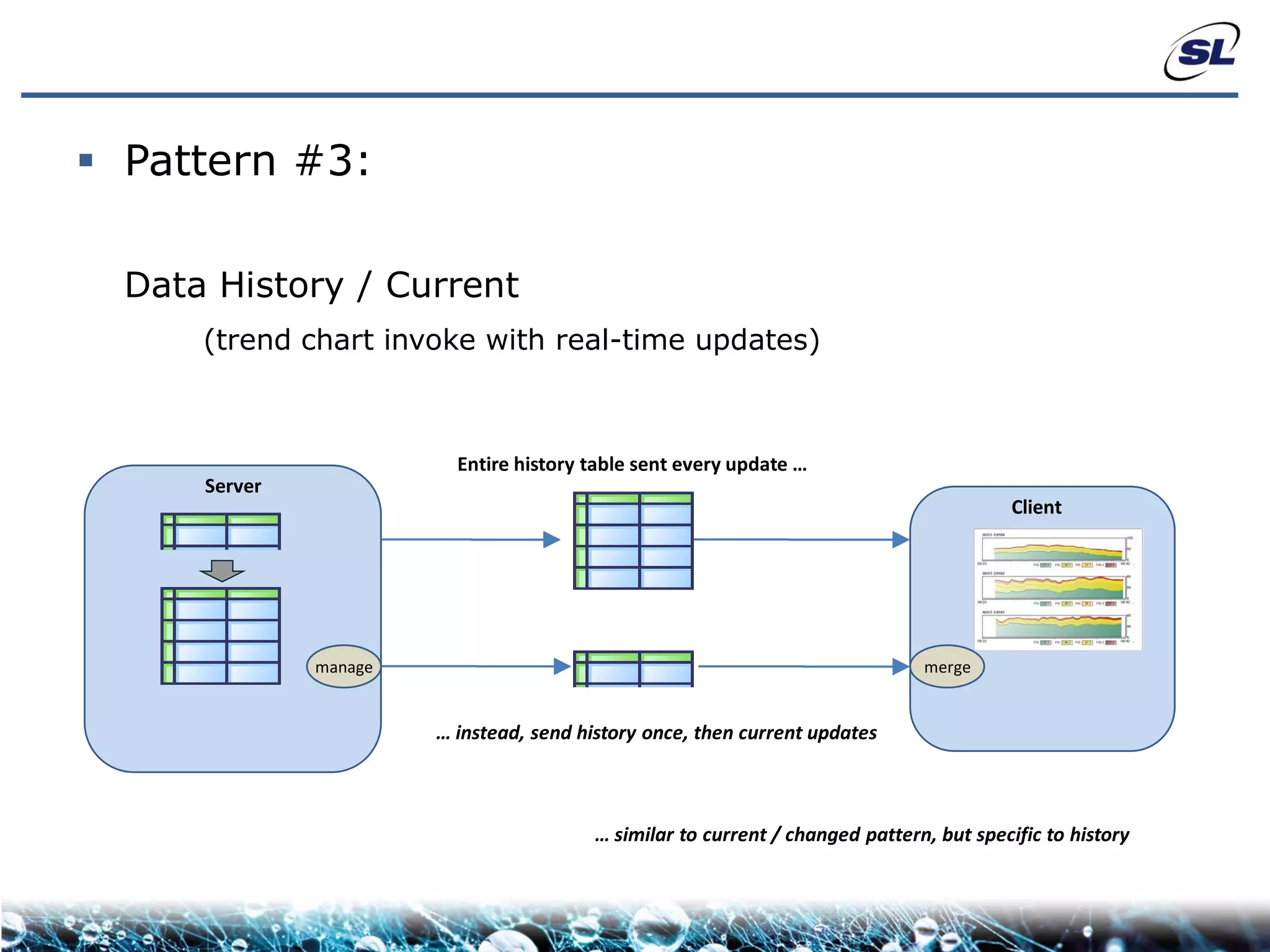
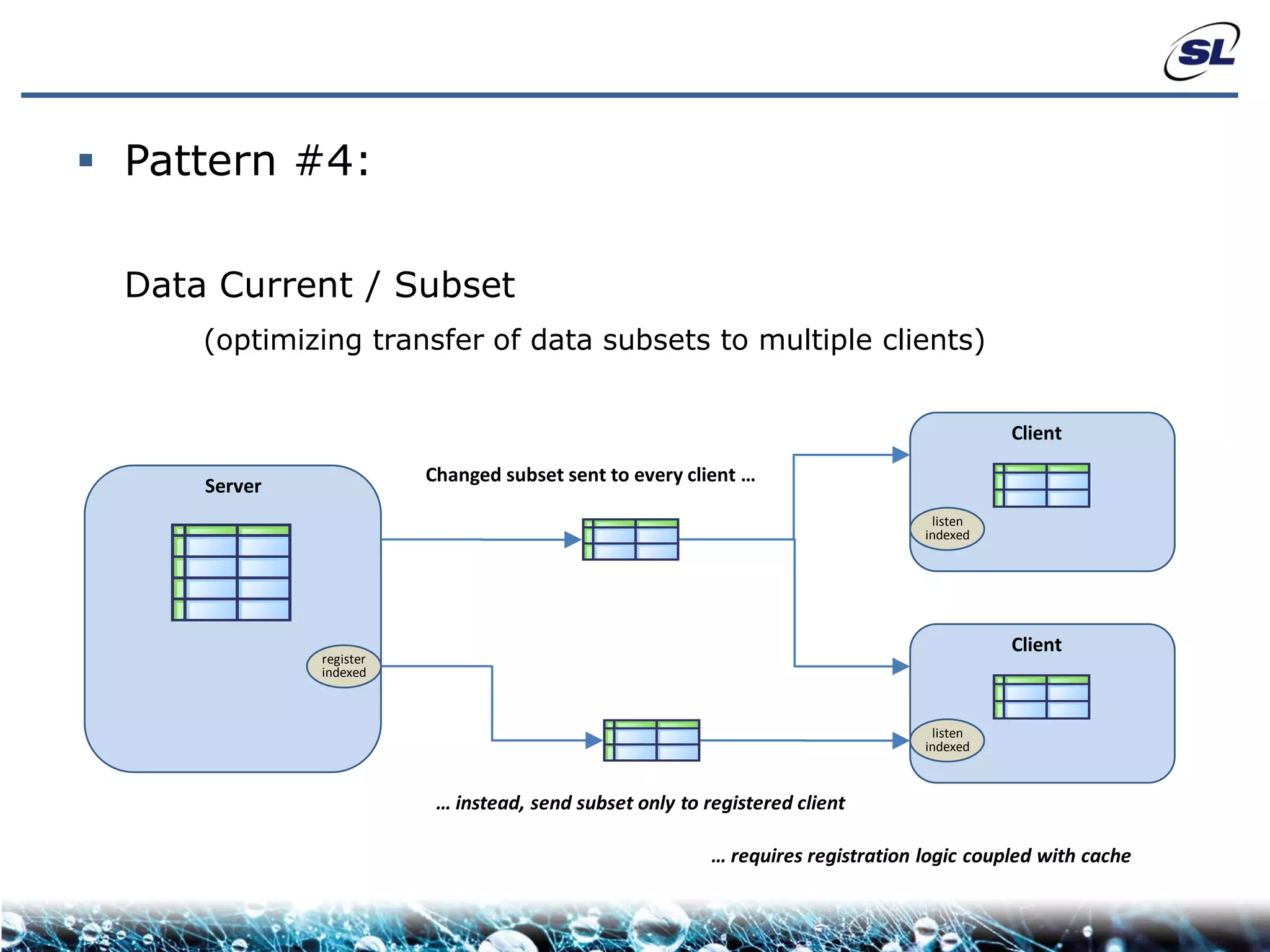
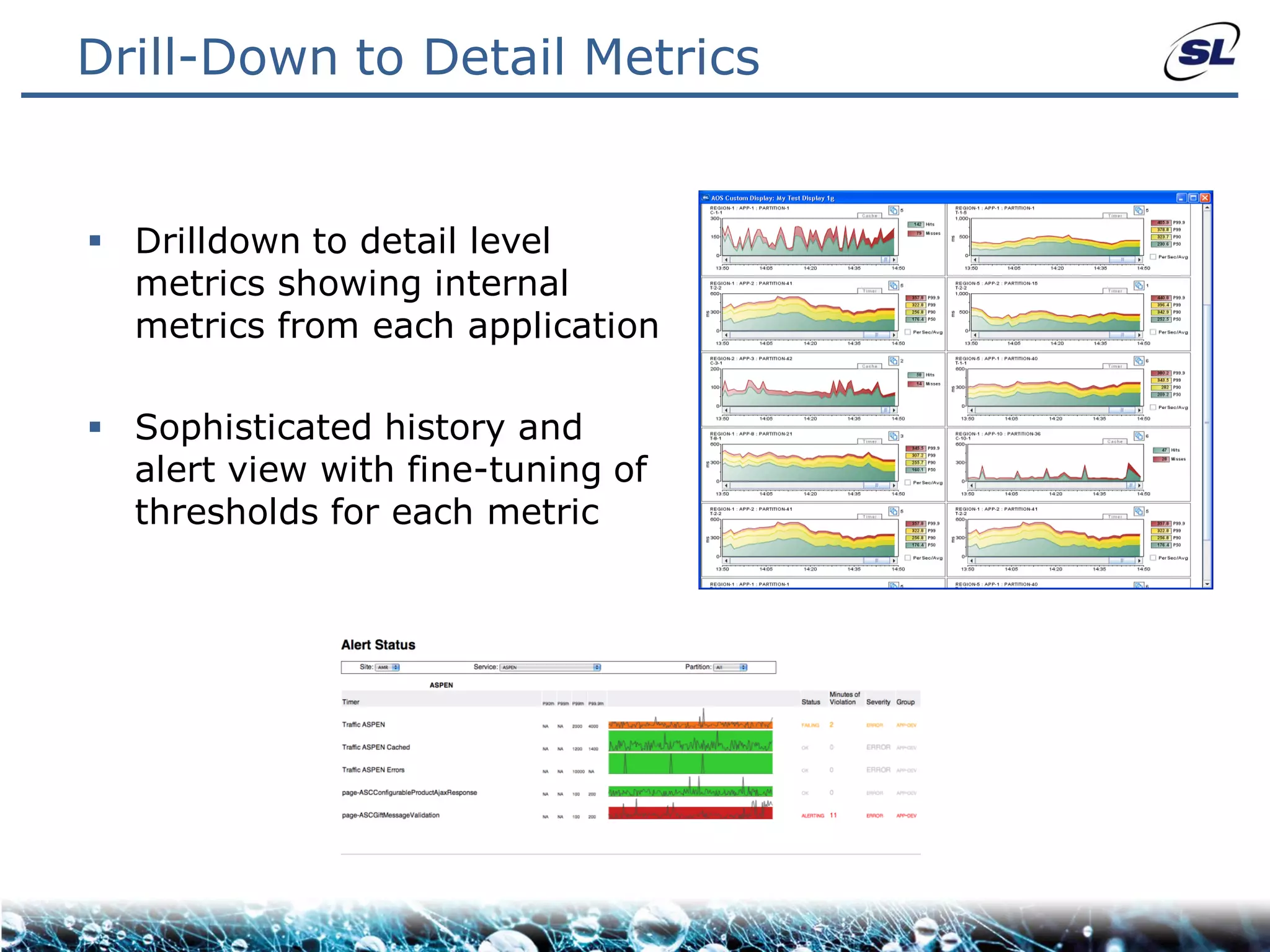
The document discusses the challenges of achieving real-time performance in large-scale, data-centric applications, particularly focusing on database performance, network bandwidth, processor capabilities, and the unpredictability of virtualization. It proposes solutions such as optimizing data models, using server-side aggregation, and implementing efficient design patterns for data transfer to enhance processing speed and reduce load. The author emphasizes the importance of understanding data needs and respecting design patterns to effectively tackle these challenges.