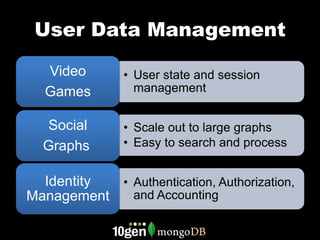
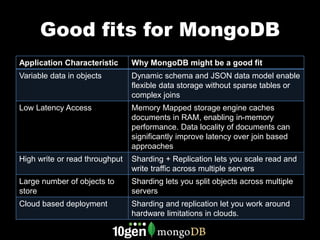
MongoDB is a NoSQL database that is well-suited for applications with certain characteristics. It uses a flexible document data model that allows for variable data in objects without sparse tables or complex joins. MongoDB provides low latency access through memory mapping and data locality. It can also scale to handle high read and write throughput through sharding and replication across multiple servers. MongoDB is a good fit for applications that need to store large numbers of objects or be deployed in the cloud.







![Behavioral Profiles
Rich profiles
collecting multiple
complex actions
1 See Ad
Scale out to support { cookie_id: “1234512413243”,
high throughput of advertiser:{
apple: {
activities tracked actions: [
2 See Ad { impression: ‘ad1’, time: 123 },
{ impression: ‘ad2’, time: 232 },
{ click: ‘ad2’, time: 235 },
{ add_to_cart: ‘laptop’,
sku: ‘asdf23f’,
time: 254 },
Click { purchase: ‘laptop’, time: 354 }
3 ]
}
}
}
Dynamic schemas
make it easy to track
Indexing and
4 Convert vendor specific
querying to support
attributes
matching, frequency
capping](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbusecases20121127-dataversity-121129224159-phpapp01/85/Common-MongoDB-Use-Cases-11-320.jpg)
![Content Management
Geo spatial indexing
Flexible data model for location based
GridFS for large
for similar, but searches
object storage
different objects
{ camera: “Nikon d4”,
location: [ -122.418333, 37.775 ]
}
{ camera: “Canon 5d mkII”,
people: [ “Jim”, “Carol” ],
taken_on: ISODate("2012-03-07T18:32:35.002Z")
}
{ origin: “facebook.com/photos/xwdf23fsdf”,
license: “Creative Commons CC0”,
size: {
dimensions: [ 124, 52 ],
units: “pixels”
Horizontal scalability }
for large data sets }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbusecases20121127-dataversity-121129224159-phpapp01/85/Common-MongoDB-Use-Cases-14-320.jpg)