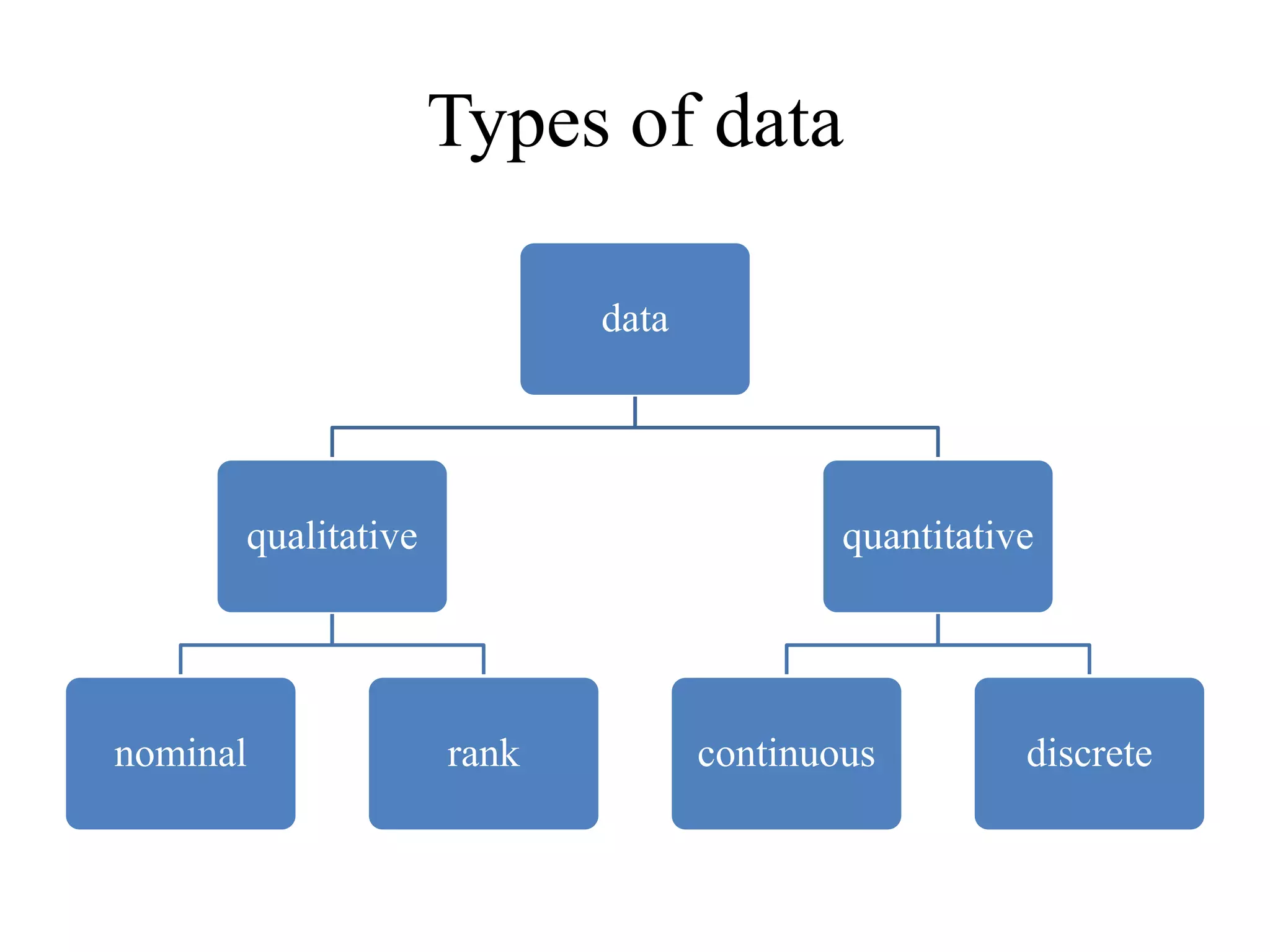
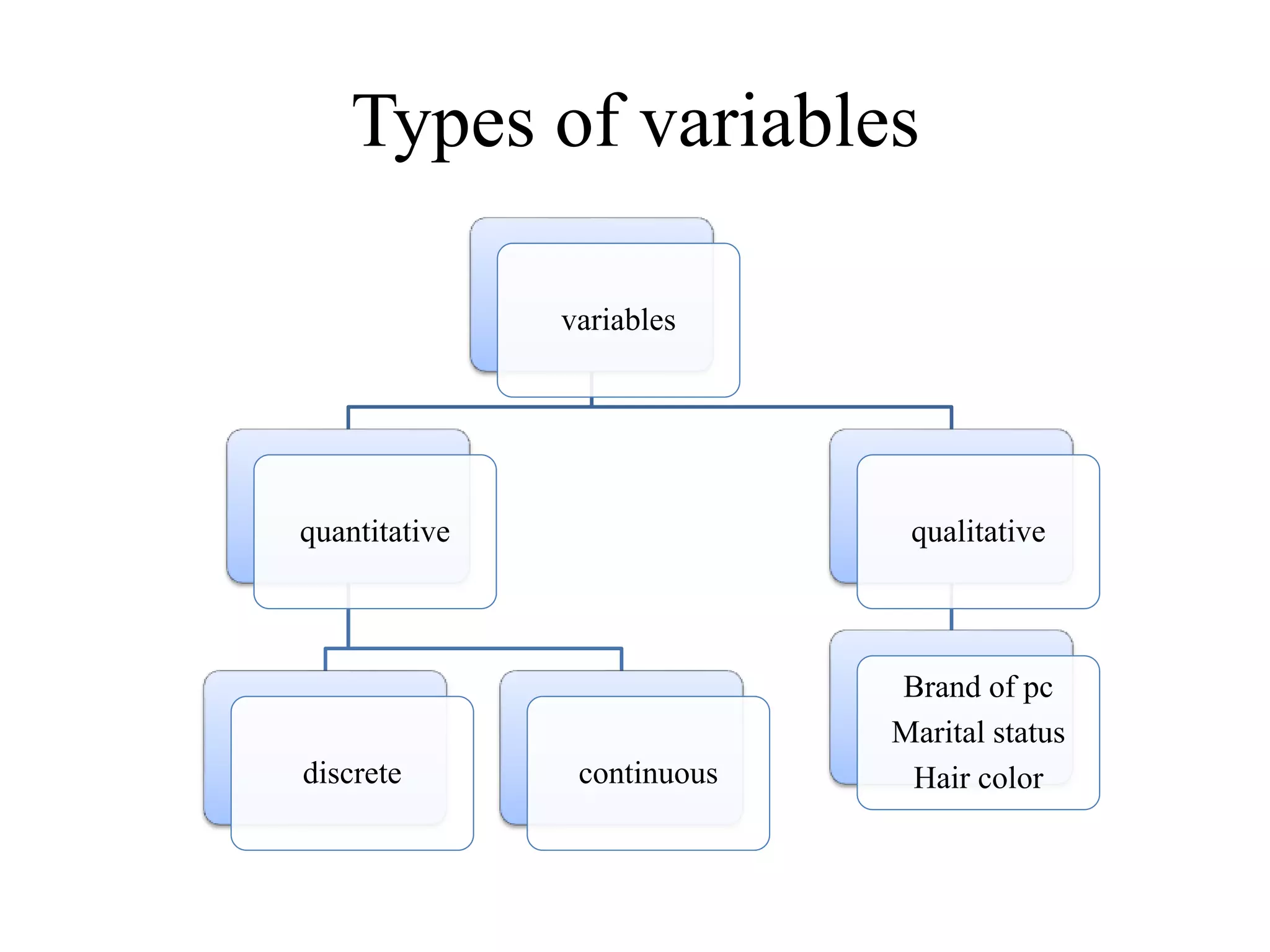
The document provides an overview of statistics, defining it as a mathematical analysis of data and detailing its characteristics, types, and significance across various fields such as business, economics, and sciences. It explores different methods of organizing and interpreting data, including descriptive and inferential statistics, and discusses the history and scope of statistics. Additionally, the document highlights the importance and limitations of statistical analysis, noting that it is most useful when applied to quantitative studies.