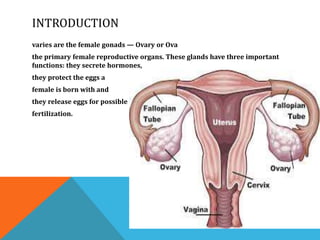
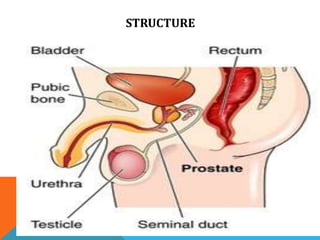
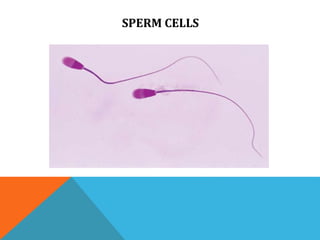
The document discusses the ovaries and testes. It describes the ovaries' location, size, and functions, including hormone production and egg release. It also discusses diseases like polycystic ovary syndrome. For testes, it describes their structure, sperm production process (spermatogenesis), and diseases/disorders like hydrocele and testicular cancer. It lists symptoms of testes problems and some treatment options like self-exams and wearing loose clothing.