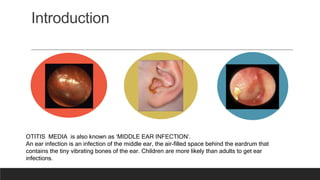
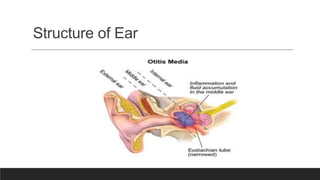
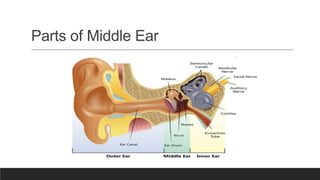
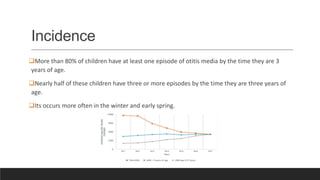
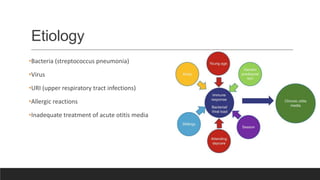
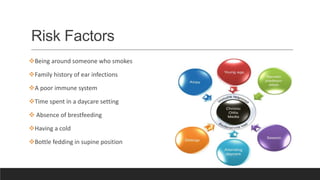
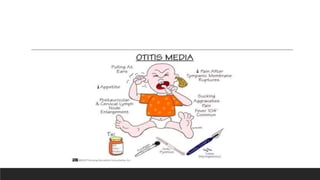
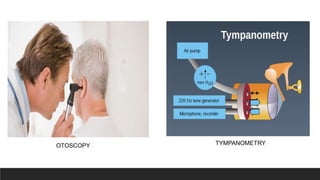
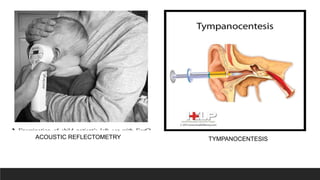
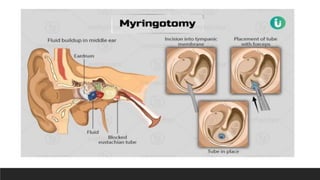
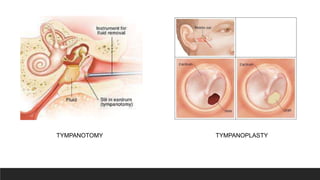
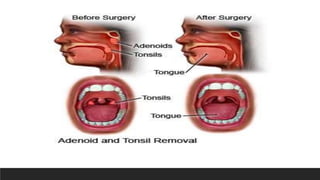
Otitis media, or middle ear infection, is a common condition in children characterized by inflammation and fluid accumulation in the middle ear, often resulting in pain, fever, and hearing difficulties. The document outlines its incidence, risk factors, diagnostic methods, and treatments, including antibiotic therapy and surgical options. Prevention strategies include minimizing exposure to respiratory infections and avoiding secondhand smoke.