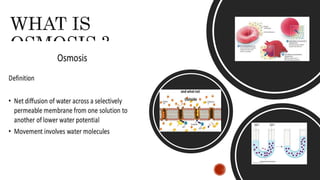
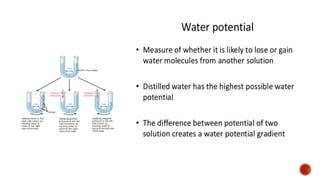
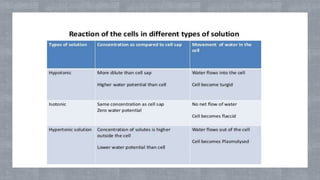
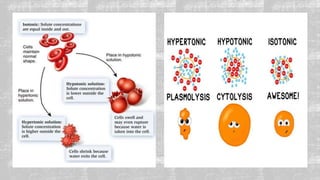
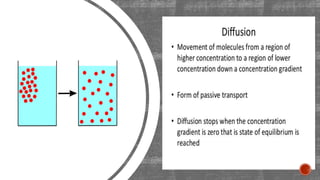
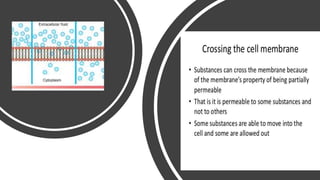
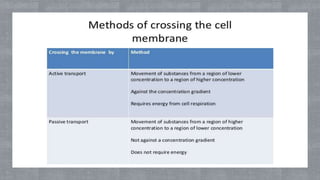
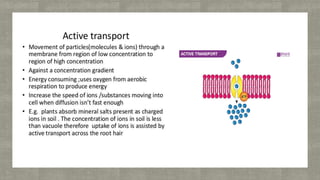
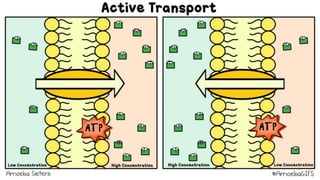
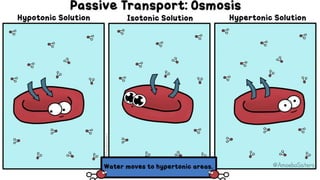
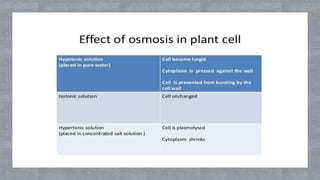
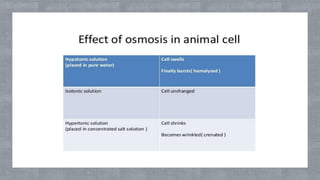
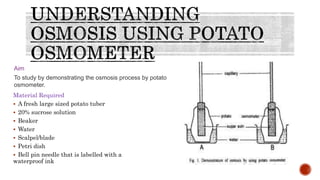
The document describes an experiment to demonstrate osmosis using a potato osmometer. Key steps of the procedure include slicing a potato and creating a cavity, filling half the cavity with a 20% sucrose solution, and submerging the potato in water. Over about an hour, osmosis occurs where water moves from the higher water potential area (the beaker of water) through the potato and into the lower water potential area (the sucrose solution), causing the level of the sucrose solution to rise. This demonstrates how a selectively permeable membrane like the potato tissues allows for osmosis and the movement of water across membranes to equalize water potential gradients.