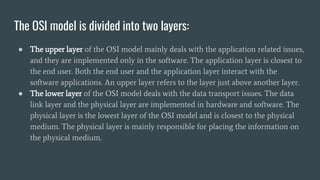
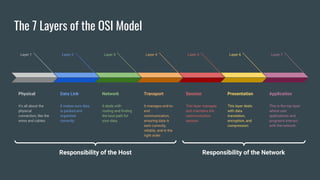
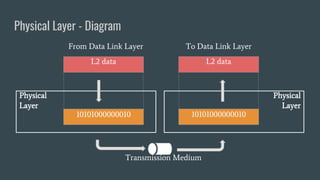
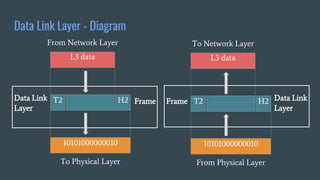
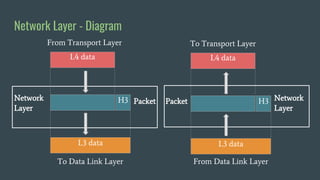
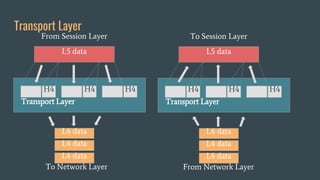
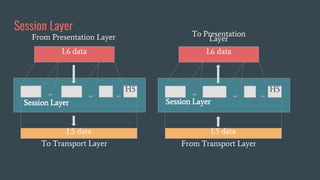
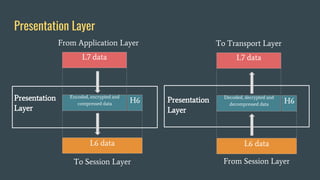
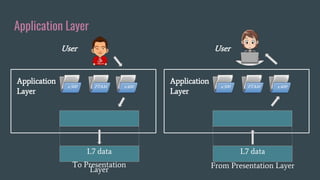
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a framework for understanding data transmission in computer networking, divided into seven layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. Each layer has specific functions, with the upper layers focusing on application-related tasks and the lower layers on data transport issues. The model helps in organizing how data is handled and ensures reliable communication between devices.