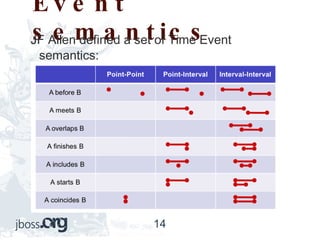
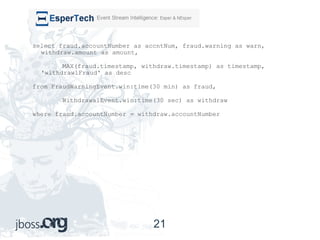
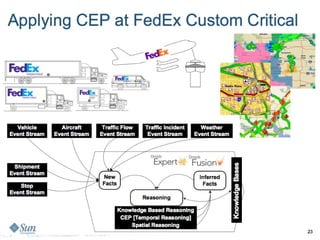
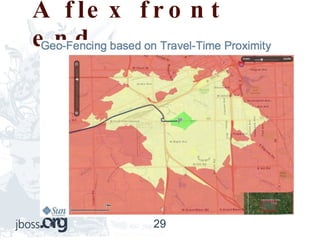
This document provides an overview of complex event processing (CEP). It defines CEP as treating inputs as events to look for patterns and correlations in order to extract meaning and act on inferred events. CEP is used in logistics, stock markets, and anywhere with a need to find patterns in large amounts of time-based event data. It discusses events, patterns, time windows, temporal reasoning, event definitions, CEP libraries like Drools and Esper, and provides an example of a FedEx tracking application.




![eg Event: [Hand In Air] Pattern: Lots of [Hand In Air] (possibly waving, as if they didn't care), happening in close (time and space) quarters... Infer: A party](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osdccep2009-091128154726-phpapp02/85/Osdc-Complex-Event-Processing-5-320.jpg)