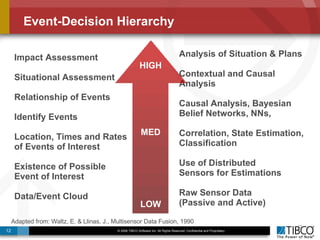
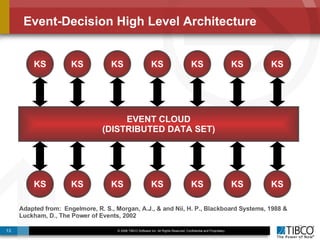
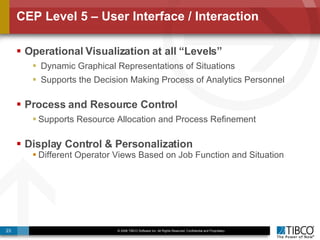
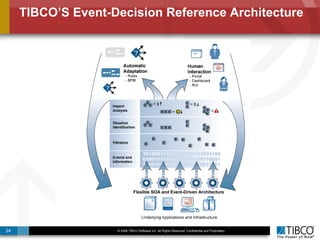
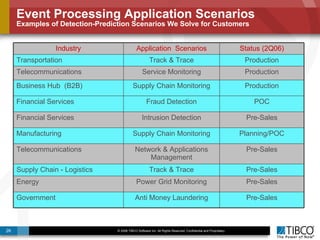
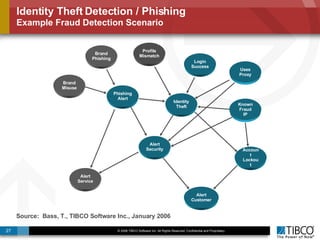
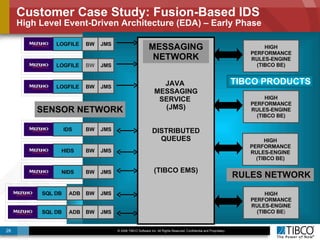
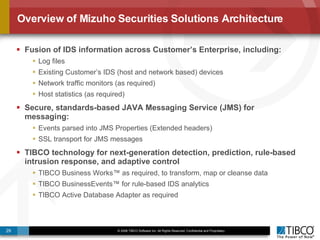
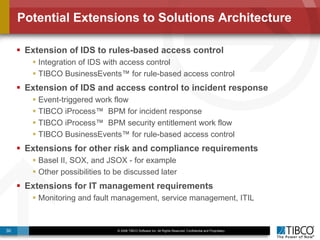
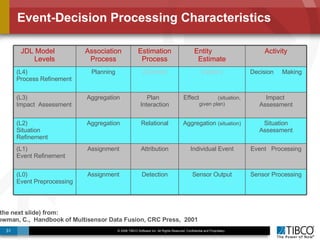
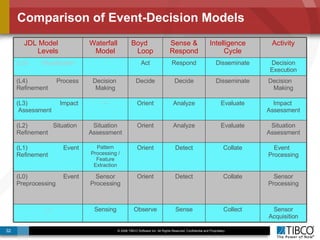
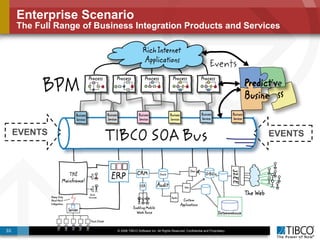
The document discusses the event-decision architecture for complex event processing (CEP) as applied in various business scenarios, emphasizing the need for a common vocabulary and functional architecture due to the computational intensity and complexity of CEP. It reviews various use cases, such as fraud detection in finance and other industries, while illustrating a multi-level inference approach for real-time data processing. TIBCO's solutions are positioned to meet these CEP challenges and enhance decision-making processes in businesses.













![Thank You! Tim Bass, CISSP Principal Global Architect [email_address] Complex Event Processing at TIBCO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cepeventdecisionarchpredictivebusinessjuly2006-1225708289894596-9/85/CEP-Event-Decision-Architecture-for-PredictiveBusiness-July-2006-35-320.jpg)