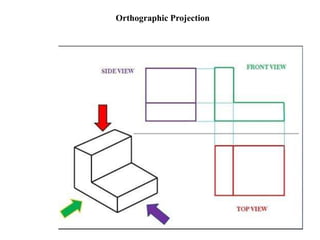
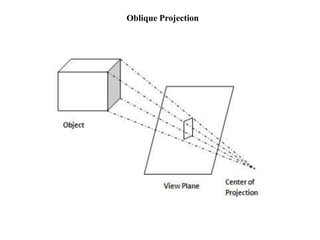
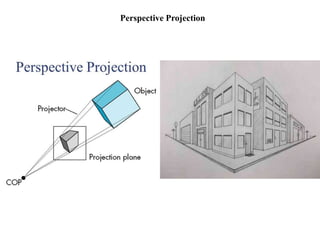
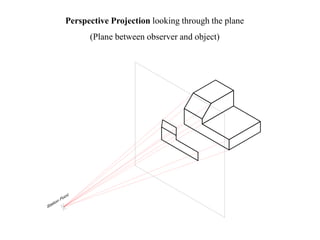
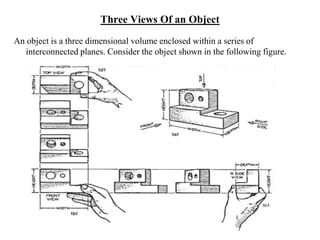
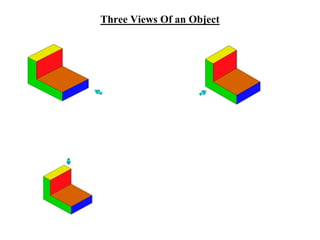
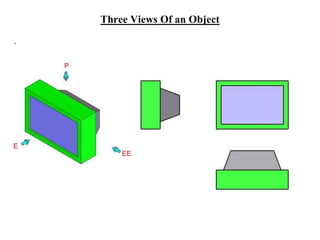
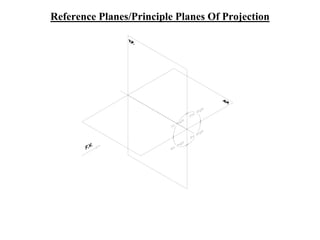
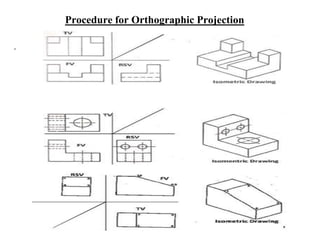
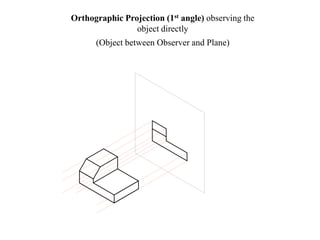
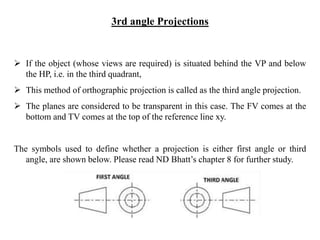
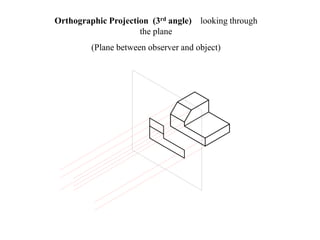
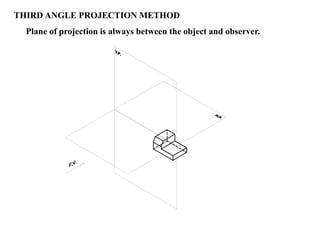
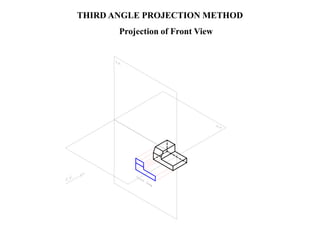
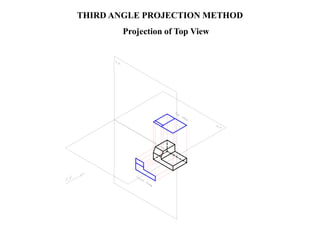
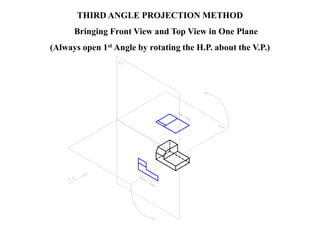
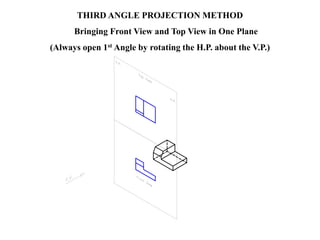
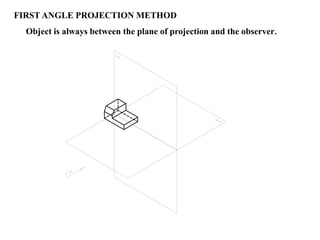
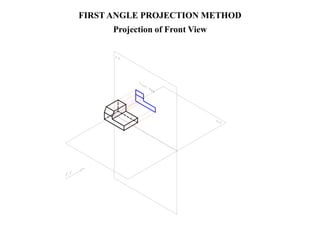
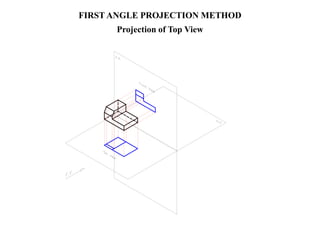
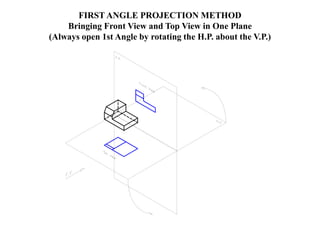
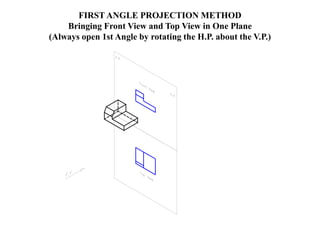
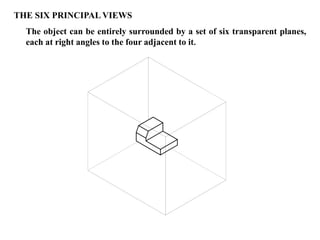
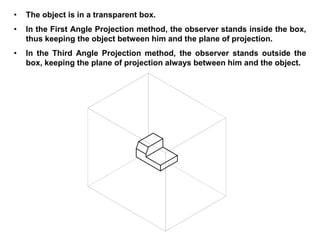
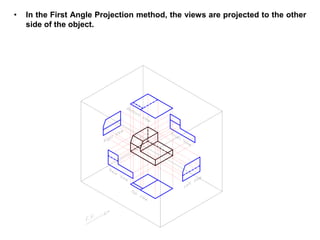
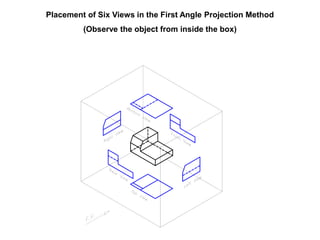
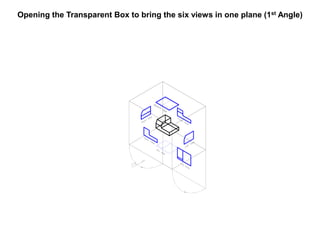
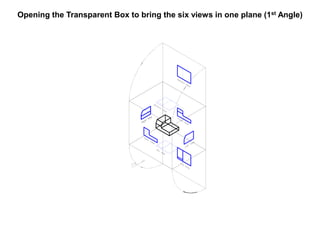
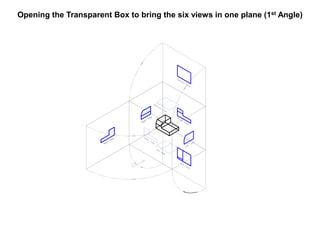
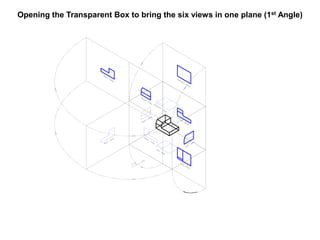
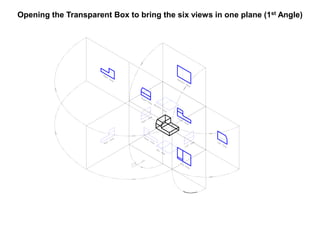
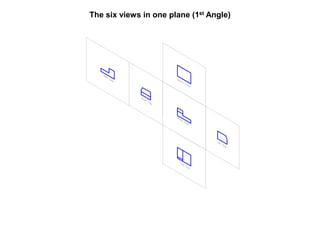
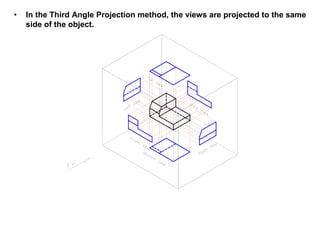
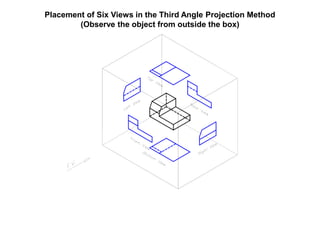
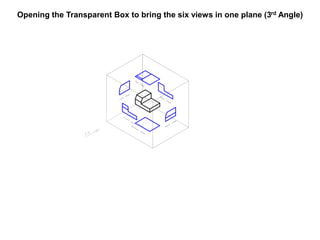
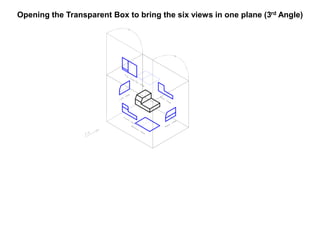
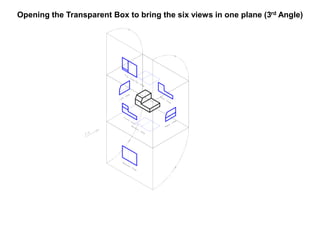
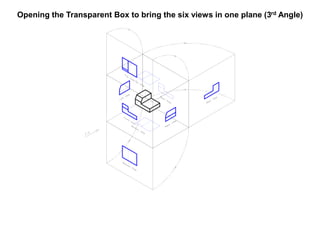
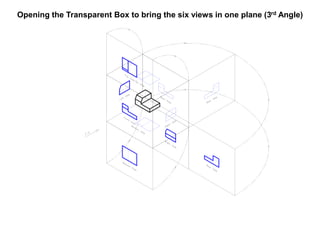
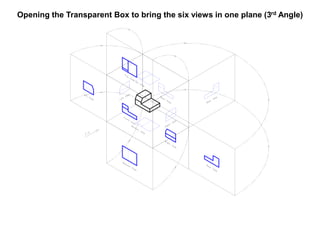
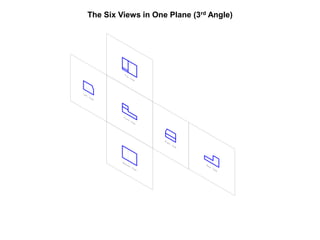
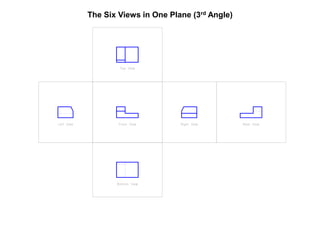
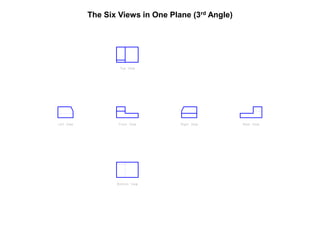
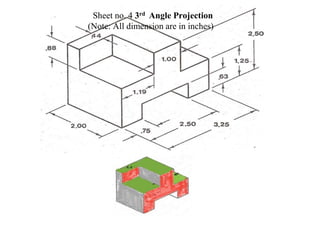
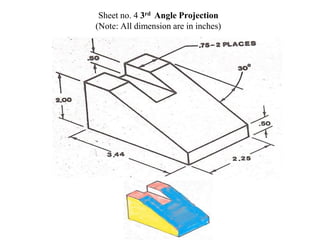
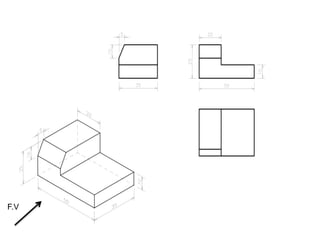
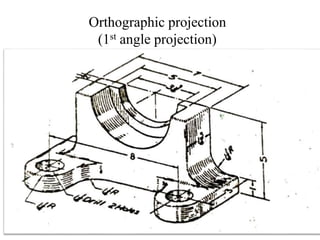
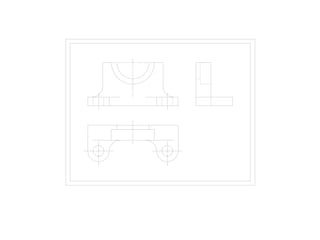
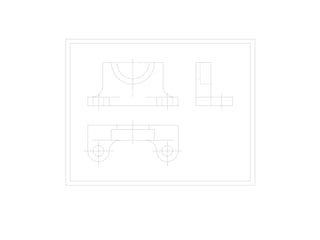
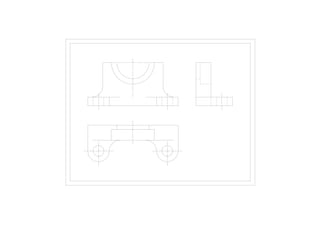
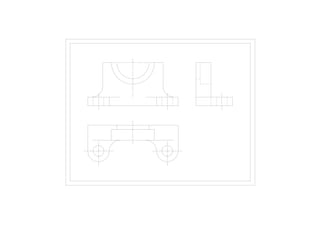
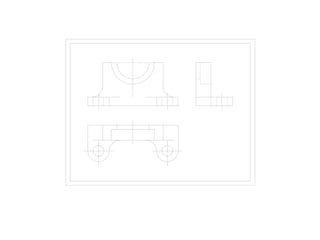
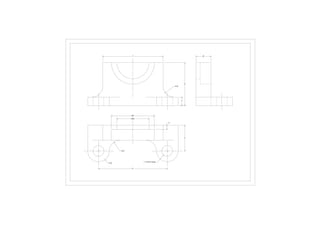
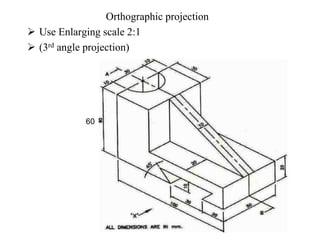
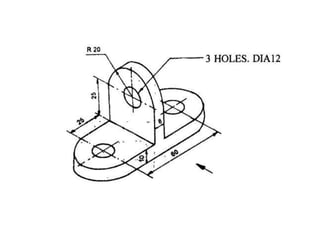
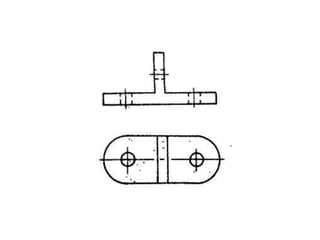
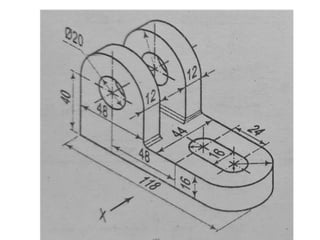
The document outlines various methods of projection used to represent three-dimensional objects, including orthographic, oblique, and perspective projections. It explains the principles behind orthographic projection, detailing the first and third angle projection methods and their respective reference planes. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate views for accurately depicting an object while maintaining balanced spacing in the drawings.