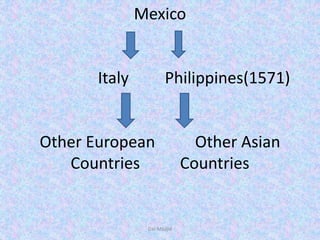
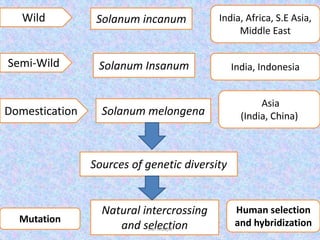
This document provides information on the history and evolution of several vegetable crops, including tomato, brinjal, chilli, potato, cole crops, cabbage, cauliflower, onion, garlic, radish, carrot, turnip, bottle gourd, and French bean. For each crop, it discusses places of origin, early cultivation, spread to other regions, and progenitor wild species. It traces the domestication and development of modern varieties of these crops from their wild ancestors through human selection and breeding over thousands of years.