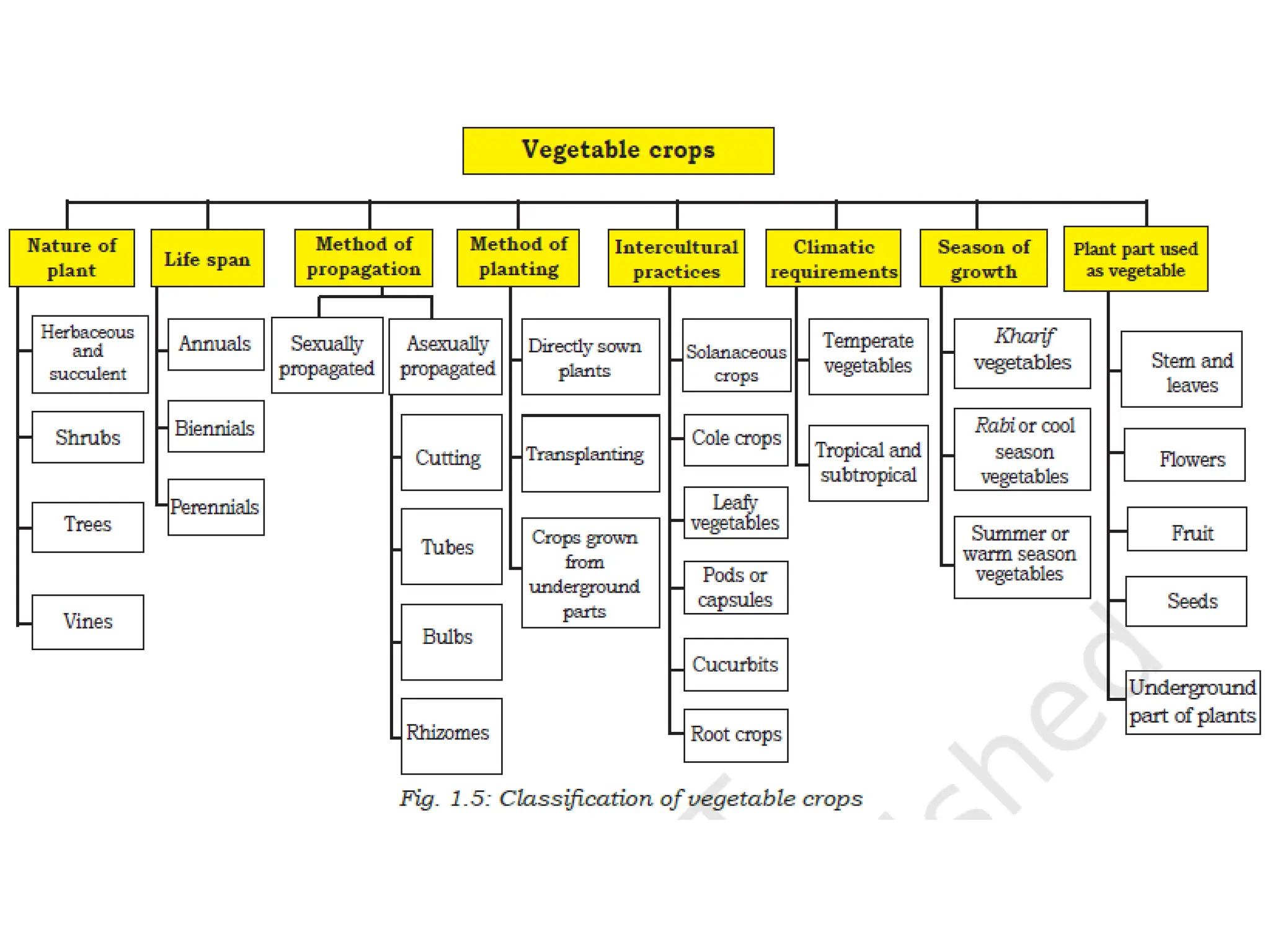
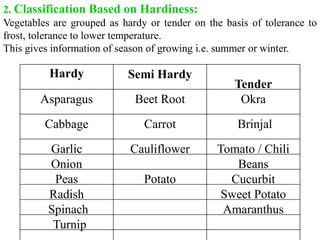
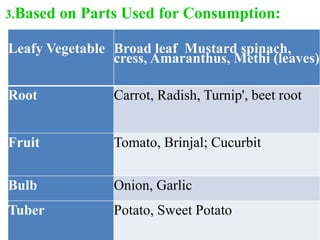
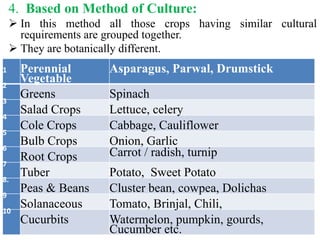
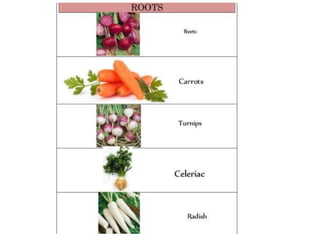
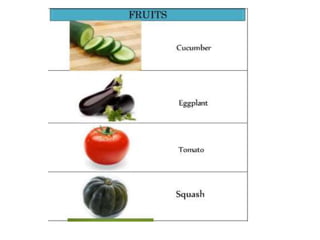
There are four main methods of classifying vegetable crops: 1) botanical relation, 2) tolerance to temperature (hardiness), 3) parts consumed, and 4) culture methods. Botanical classification groups vegetables by family and is useful for breeding and avoiding confusion but not for growers. Classification by hardiness categories vegetables as hardy, semi-hardy, or tender based on frost tolerance. Classification by part consumed groups vegetables as leafy, root, fruit, bulb, or tuber. Classification by culture method groups vegetables with similar growing requirements together, such as cole crops or cucurbits.