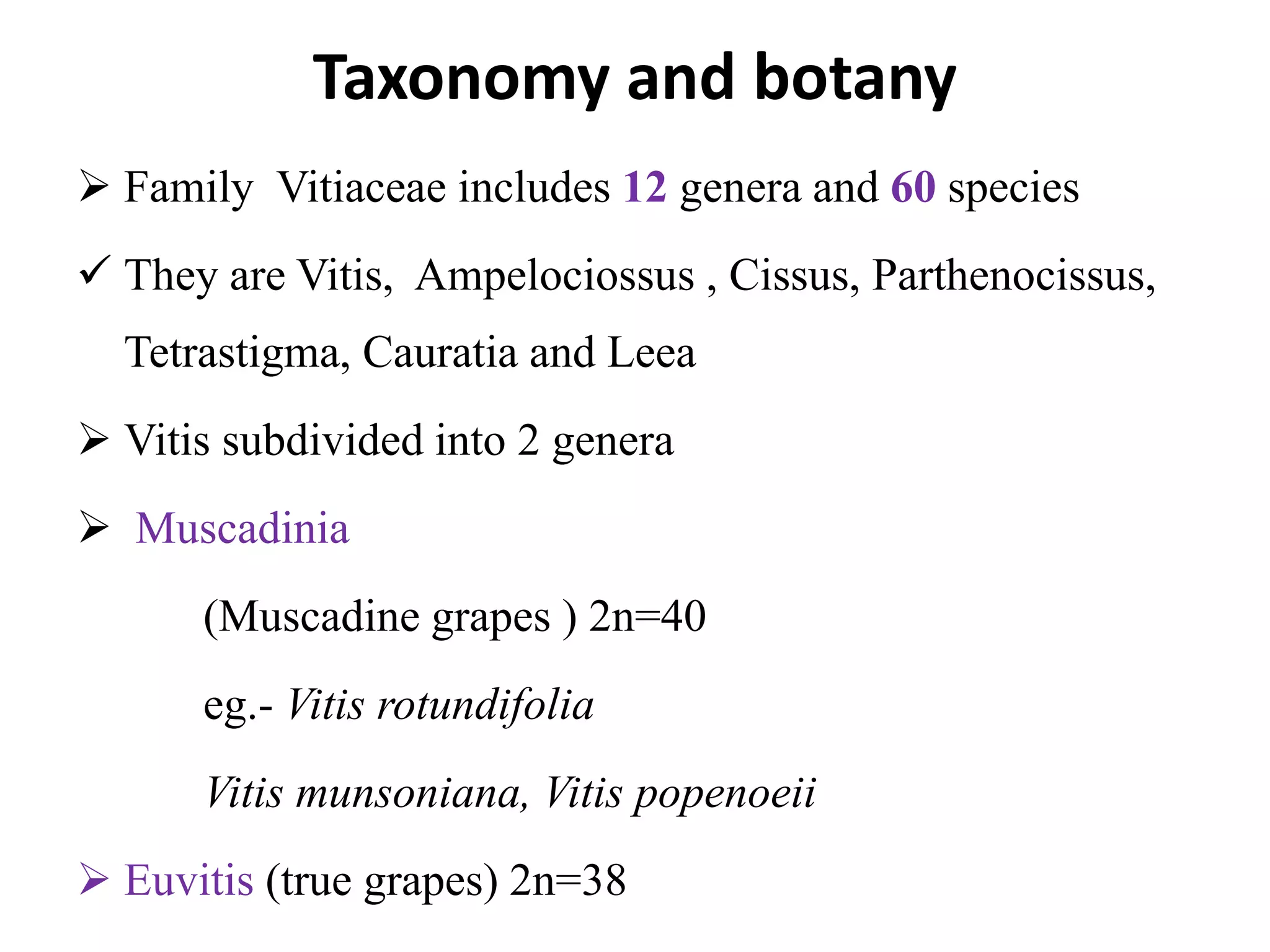
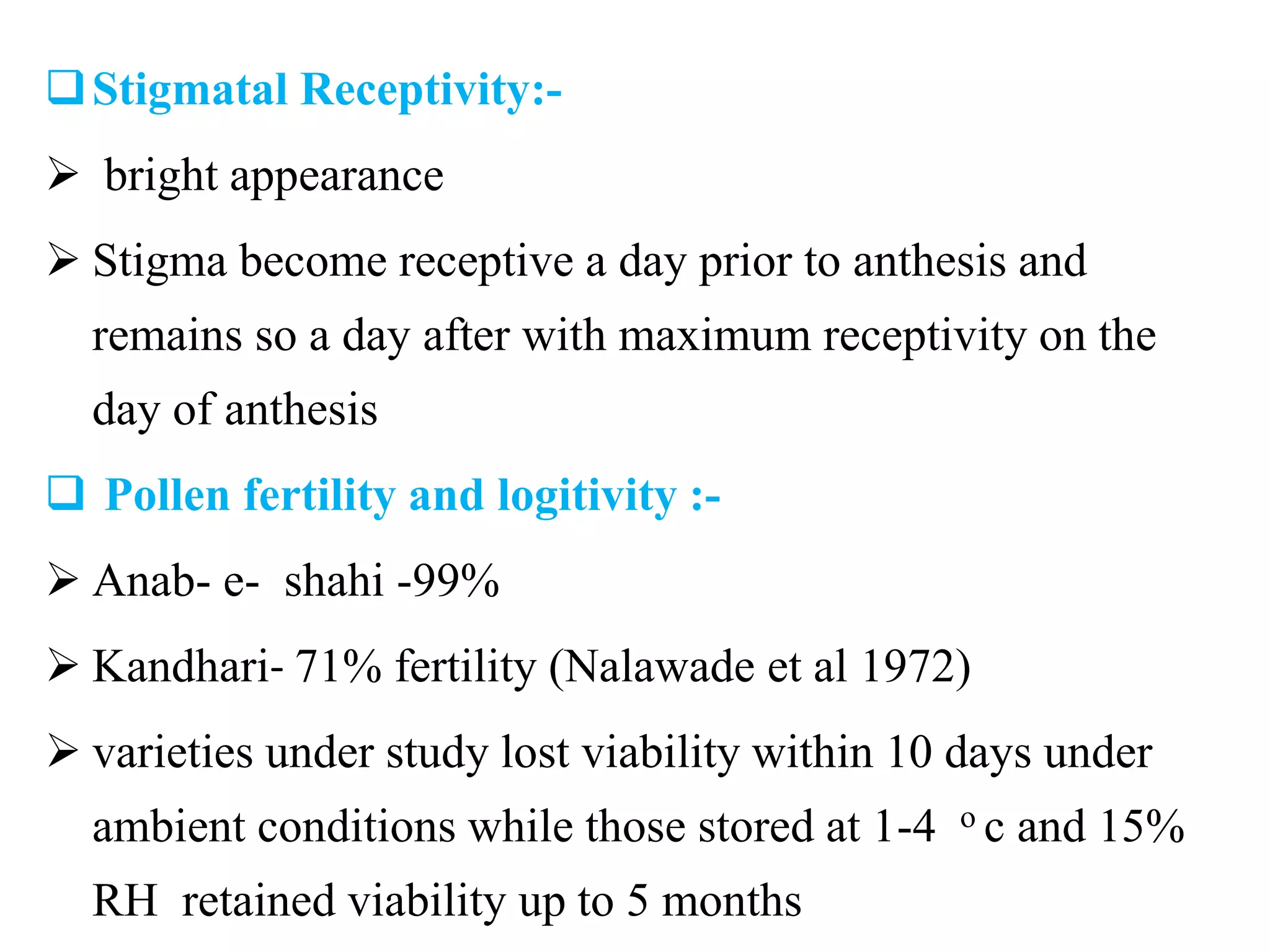
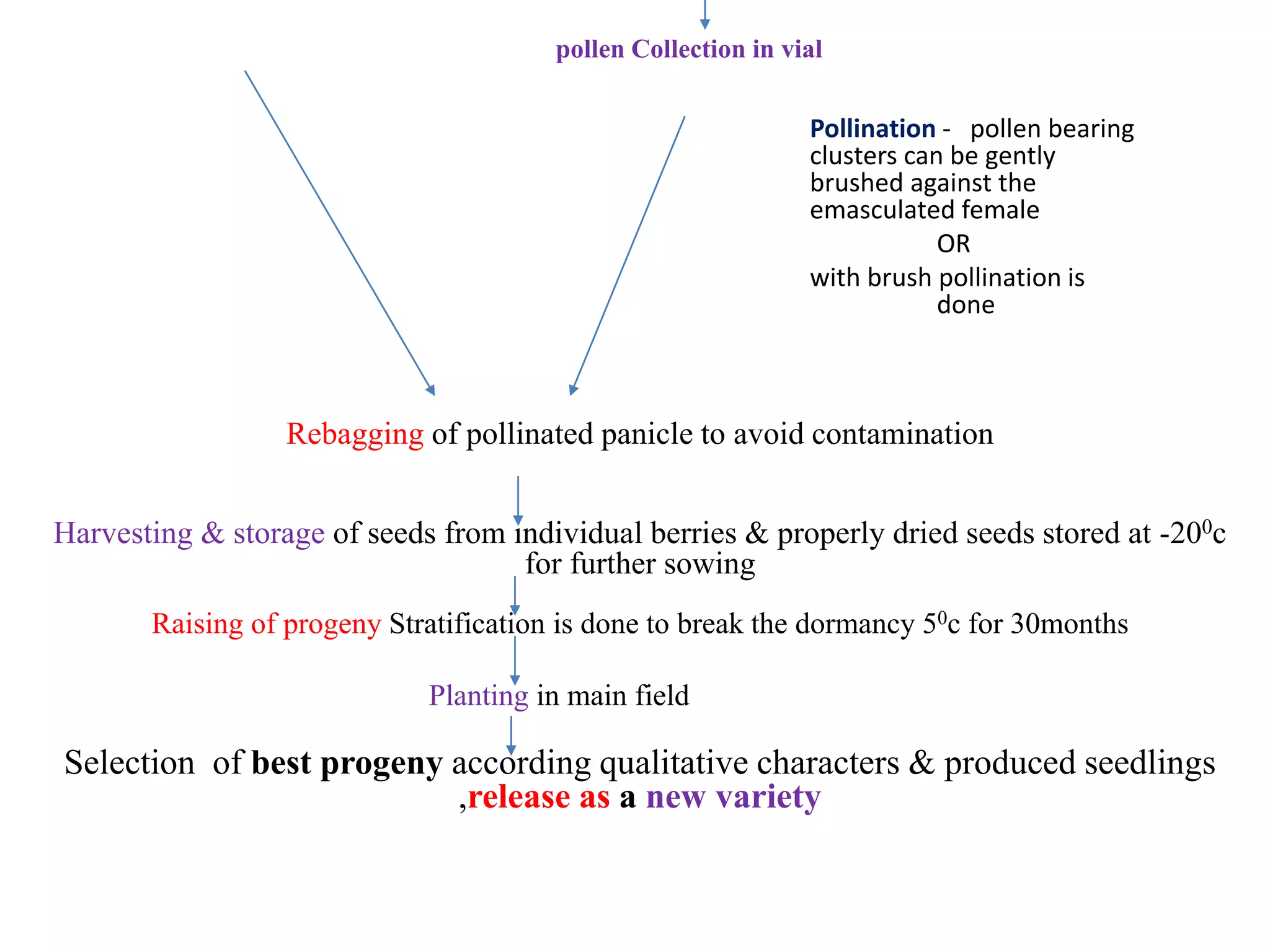
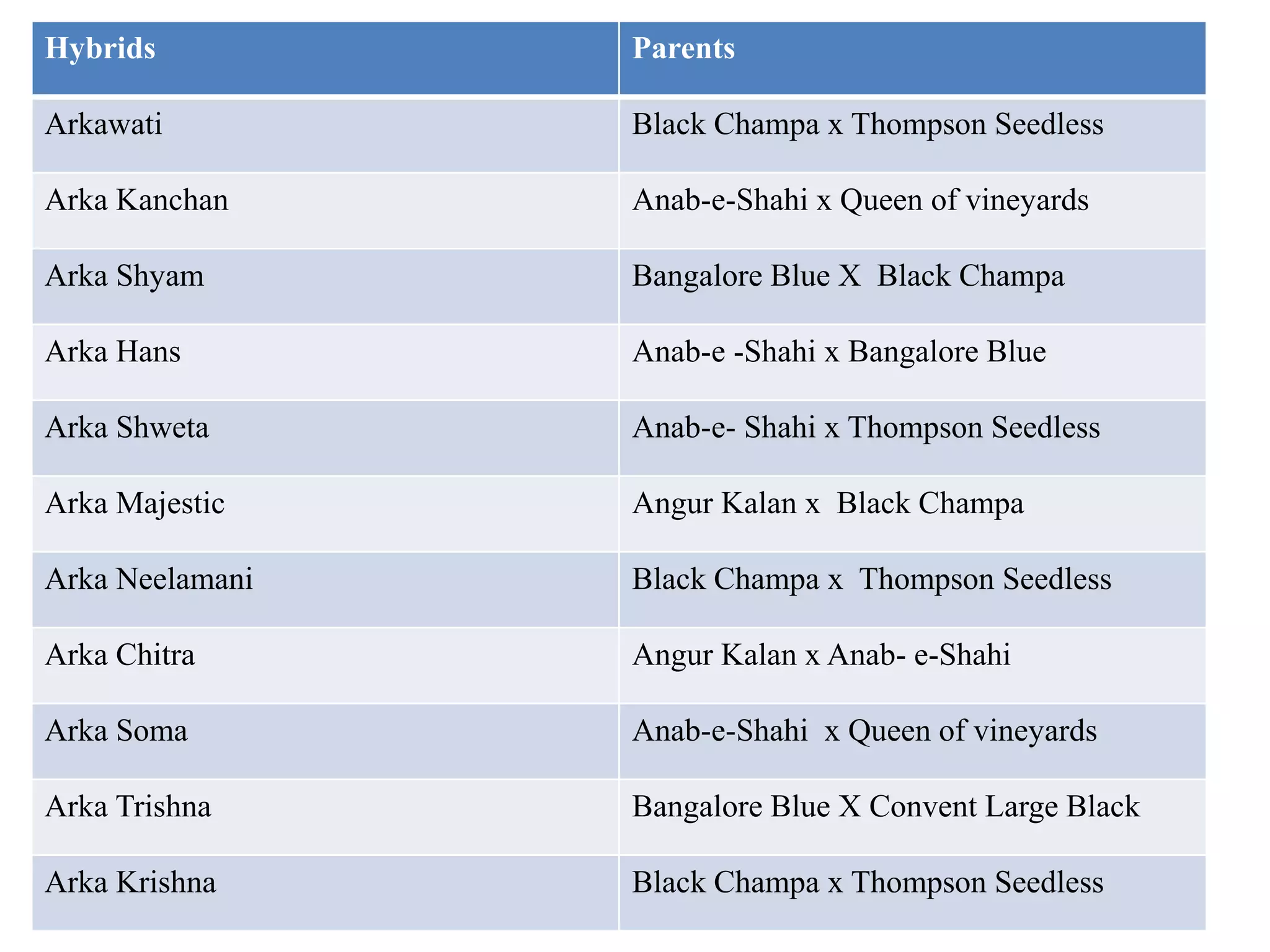
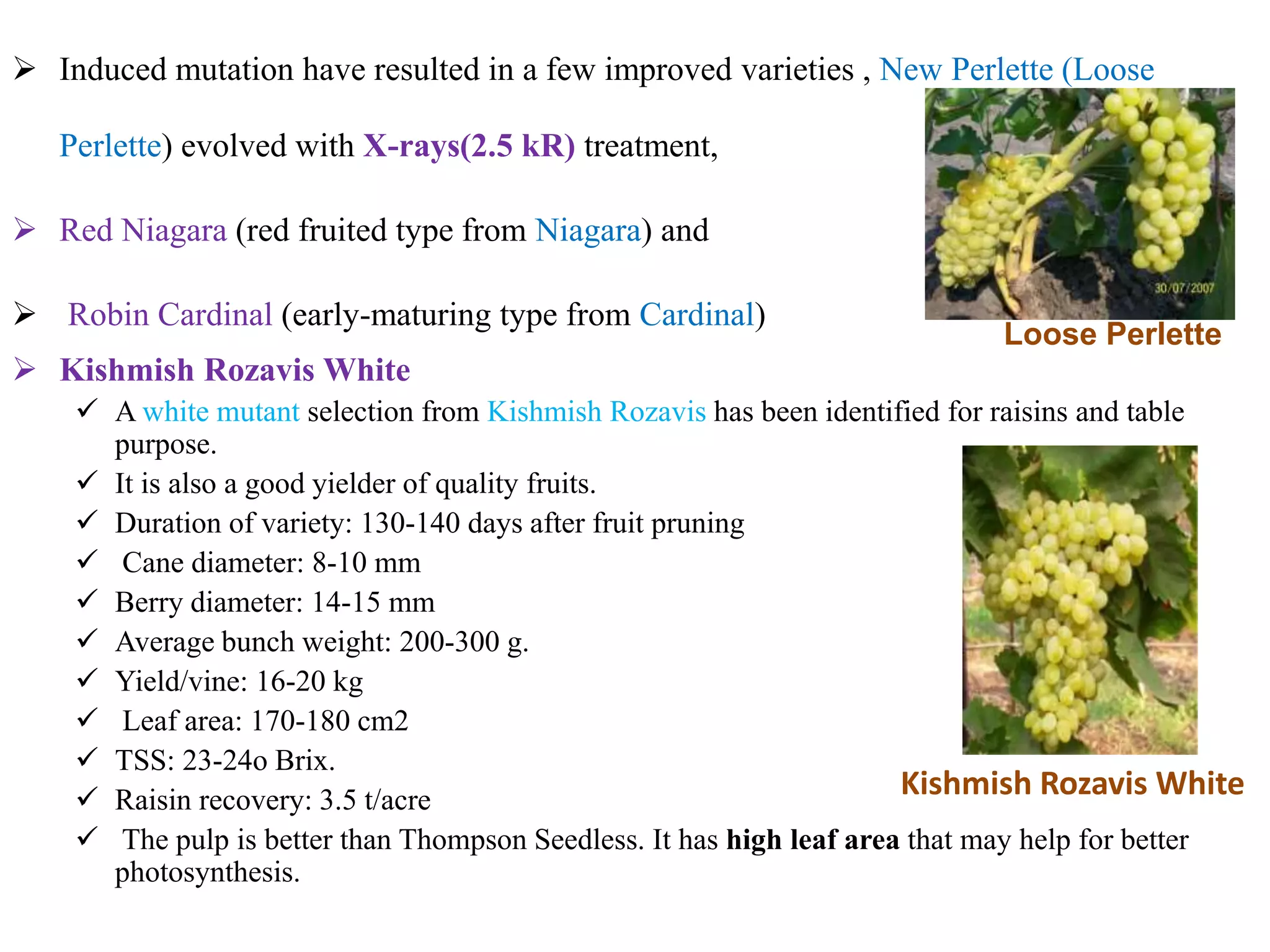
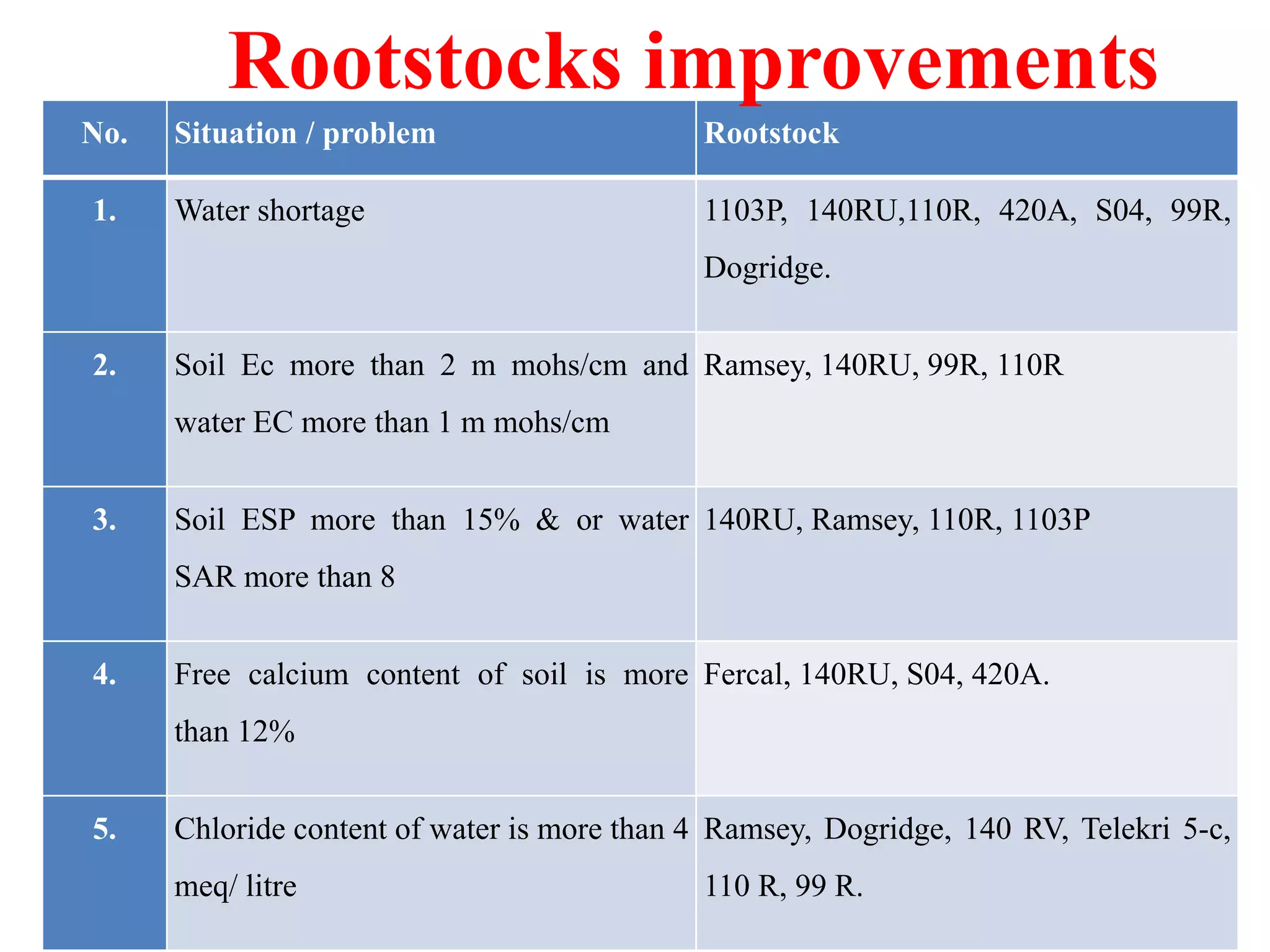
The document provides an extensive overview of grape breeding, detailing various grape varieties, their characteristics, and their origins, particularly within India. It outlines the objectives of breeding programs aimed at improving grape cultivars for table, raisin, and wine production, along with the methods of grape flower biology and inheritance patterns. Additionally, it reviews historical introductions of grape varieties to India and highlights key breeding achievements and newly developed varieties.