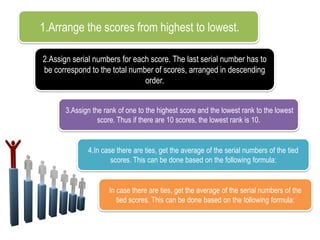
This chapter discusses organizing test scores for statistical analysis through ordering, ranking, and frequency distribution. Ordering refers to arranging scores numerically in ascending or descending order. Ranking determines the relative position of scores by assigning serial numbers from highest to lowest, with the highest score ranked 1. Tied scores are given the average of their serial numbers. Frequency distribution and stem-and-leaf plots are also examined as ways to organize test scores.