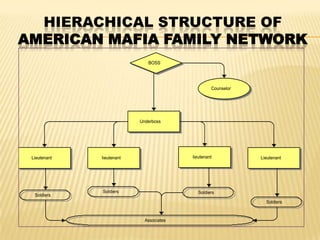
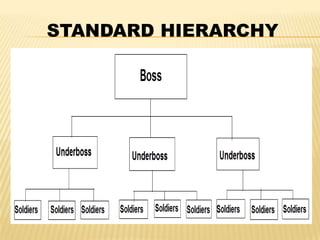
This document discusses organized crime. It defines organized crime as groups that use unlawful means like violence, threats, or corruption to gain money or advantages. It describes the characteristics of organized crime groups as having teamwork, hierarchies, planning, and effective member control. The activities of organized crime include narcotics, gambling, human trafficking, and money laundering. There are different types of organized crime like gangs, racketeering, and syndicates. The document also discusses the levels of relationship between organized crime and political corruption.