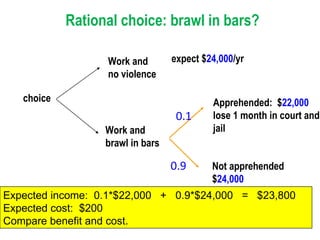
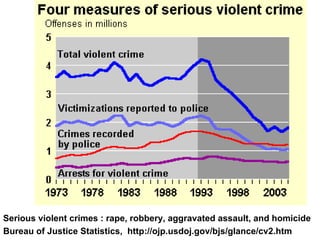
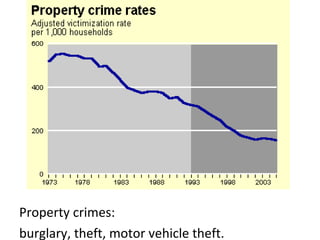
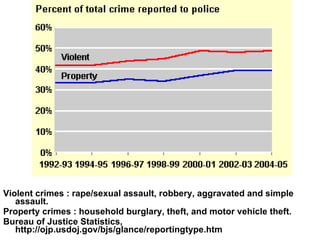
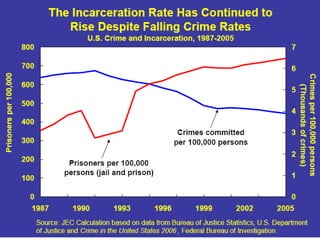
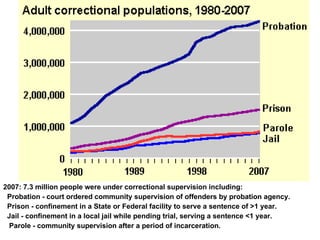
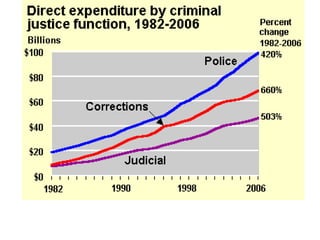
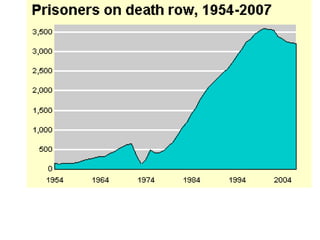
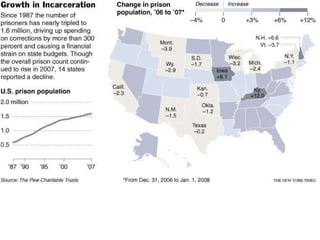
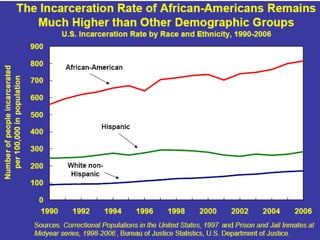
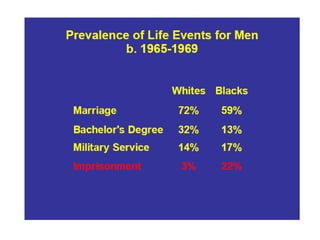
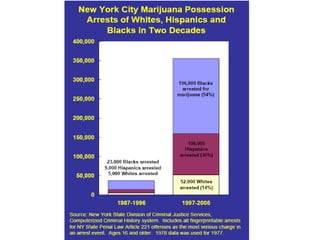
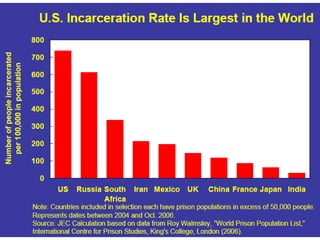
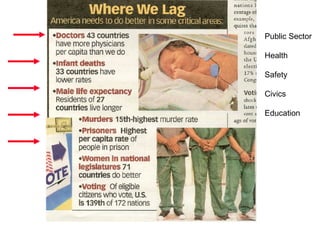
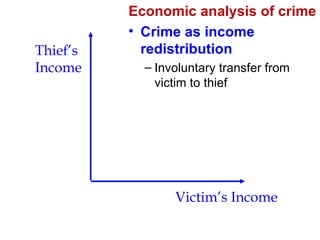
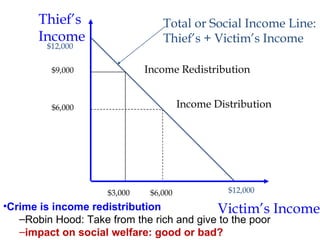
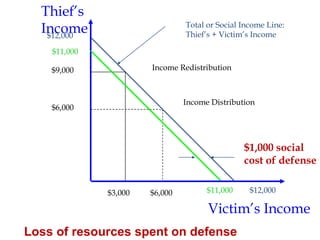
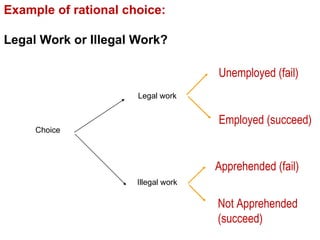
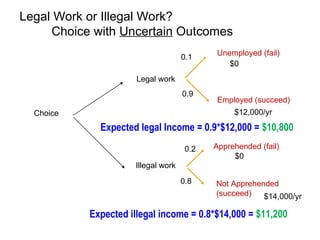
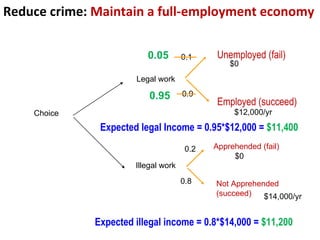
Crime is an economic issue that results in a loss of resources for society. Individuals make rational choices between legal work and illegal activities based on their economic status and potential earnings. Measures to reduce crime from an economic perspective include maintaining full employment opportunities, an effective criminal justice system with a high likelihood of apprehension, and punishments that make illegal acts less attractive.