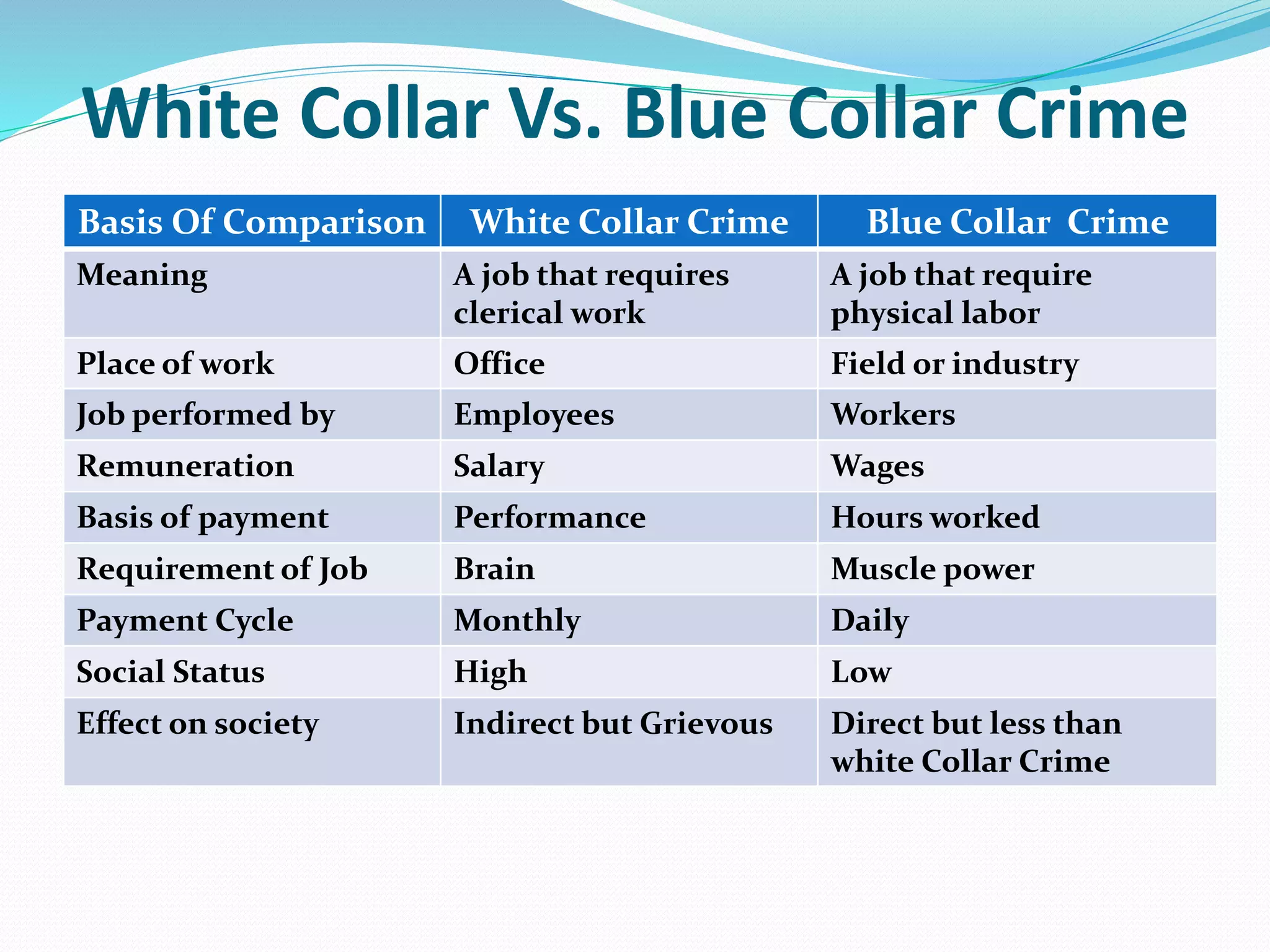
White collar crimes are non-violent crimes committed by high-status individuals for financial gain. Edwin Sutherland, the "father of white collar crime," defined it as crimes committed by respectable people in the course of their occupation. White collar crimes include fraud, embezzlement, insider trading, tax evasion, and other offenses that involve deception. They cause significant harm to society through financial losses, unsafe products, pollution, and an attitude of being above the law. Common in India due to its fast-growing economy, white collar crimes are addressed through laws like the Prevention of Money Laundering Act and the Indian Penal Code. Education and awareness of these crimes is needed to deter their growth.