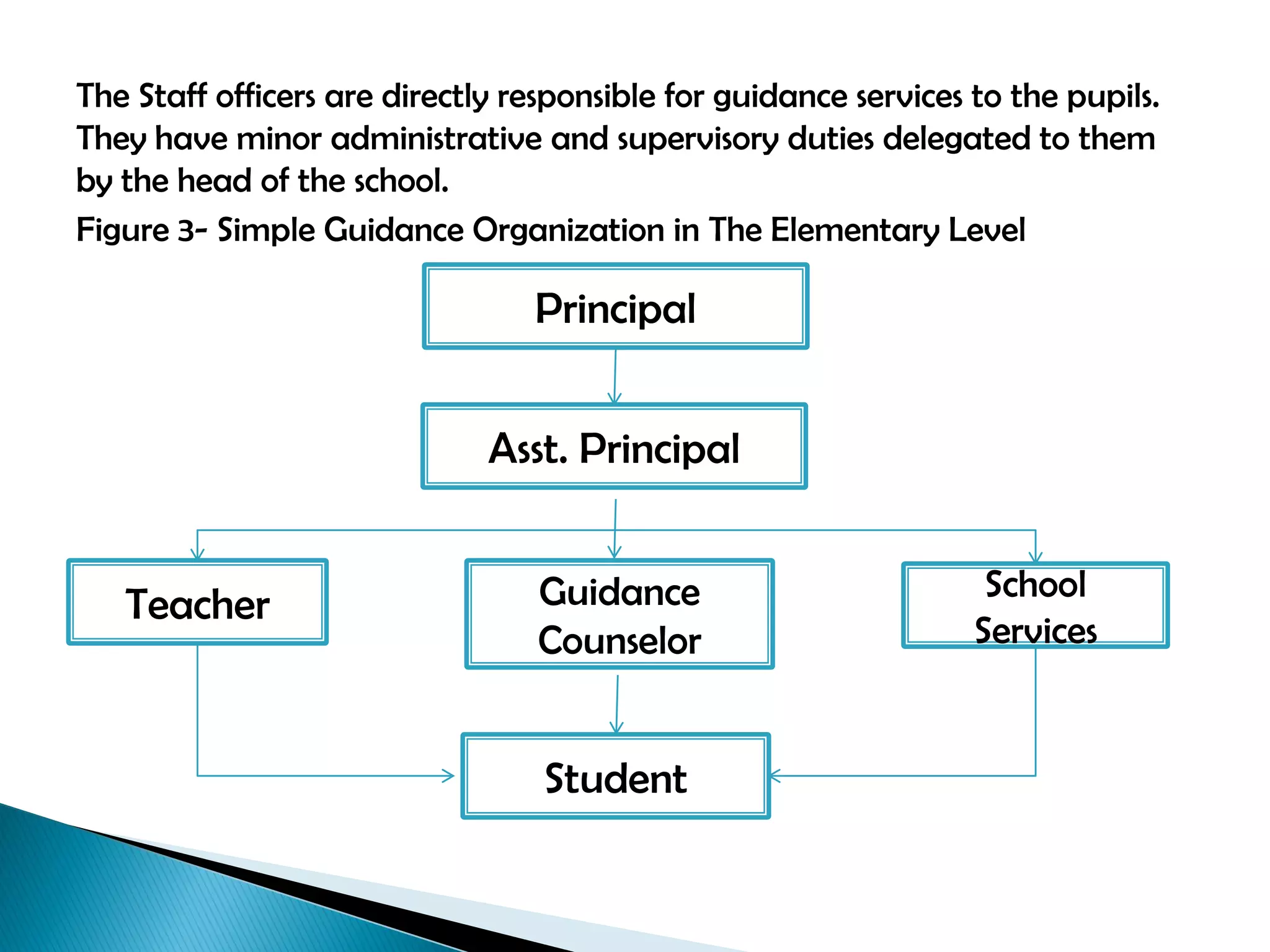
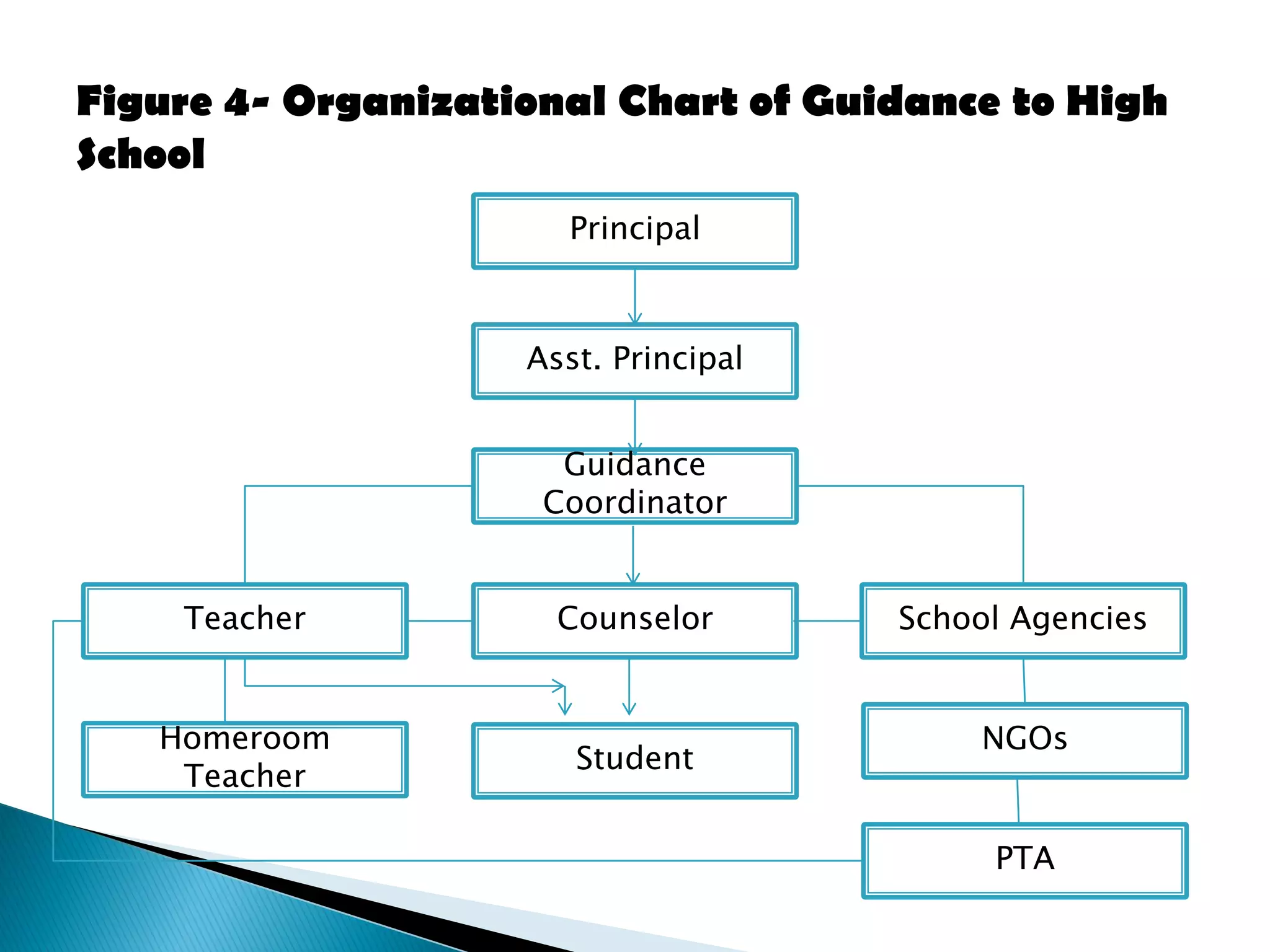
This document discusses different types of organizational structures for guidance programs in schools. It describes informal organizations that form based on personal relationships and formal organizations with clearly defined roles and hierarchies. The main organizational structures discussed are line organization with a direct chain of command, line and staff organization where staff support line roles, and examples of how guidance programs can be structured in elementary and high schools using these models. The key point is that the organizational design should facilitate information flow and accomplishing the goals of the guidance program.