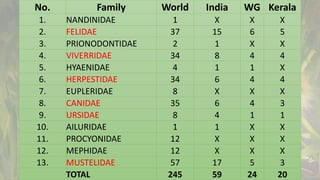
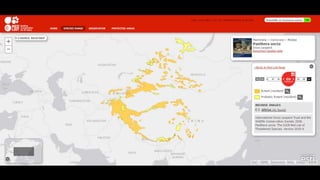
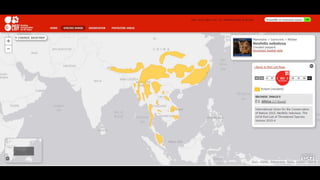
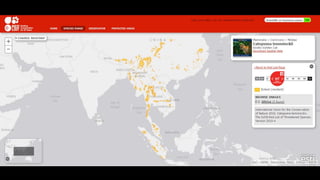
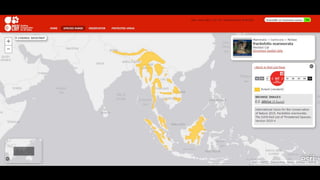
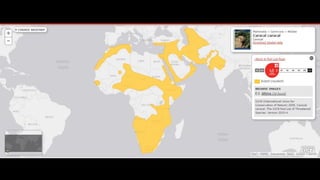
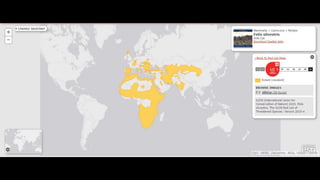
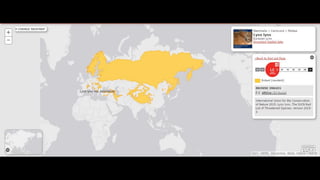
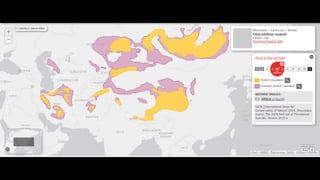
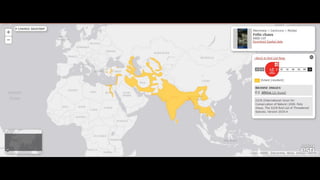
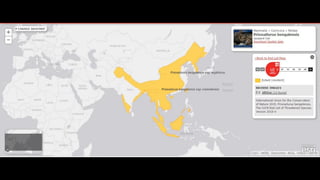
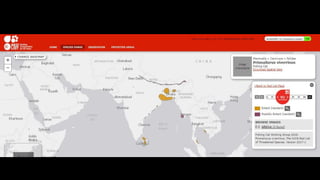
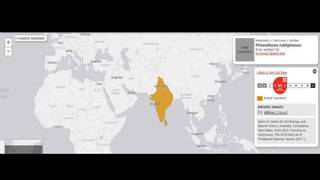
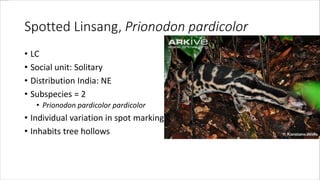
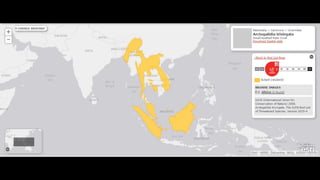
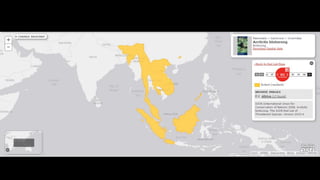
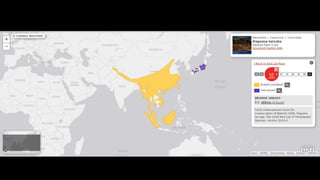
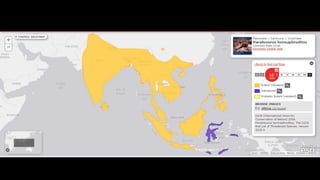
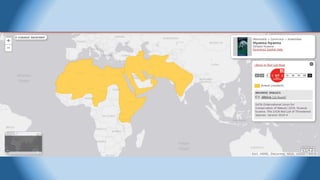
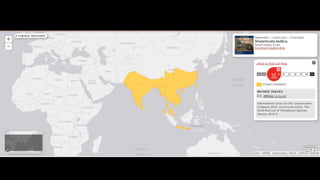
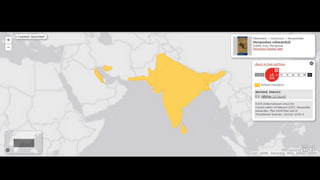
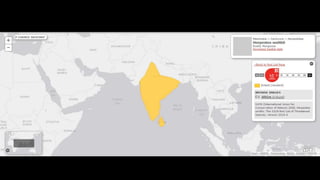
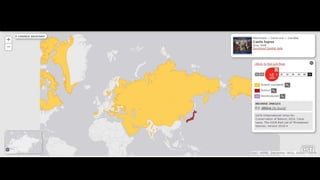
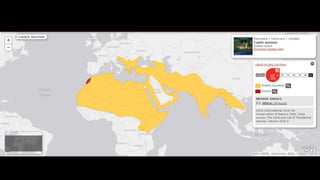
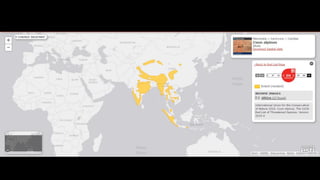
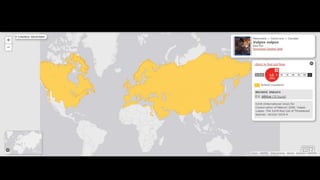
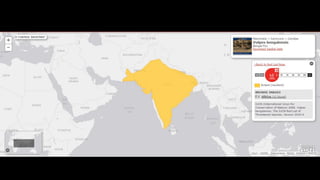
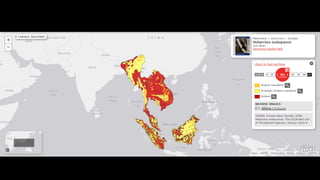
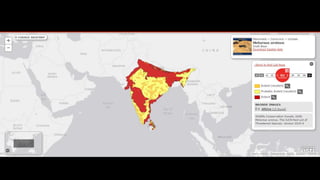
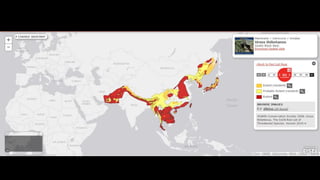
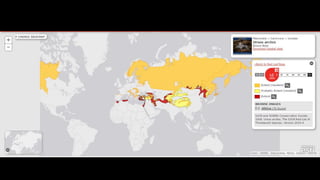
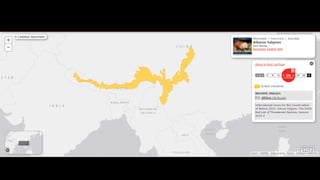
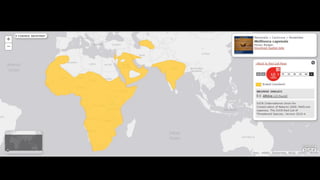
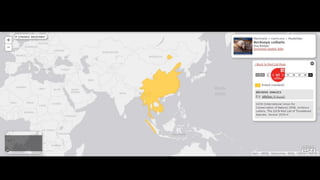
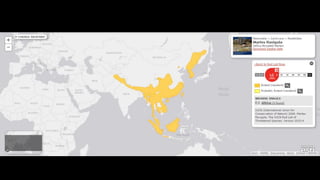
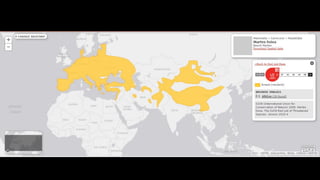
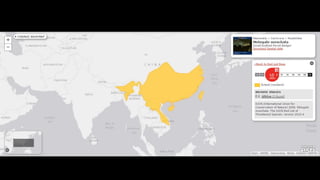
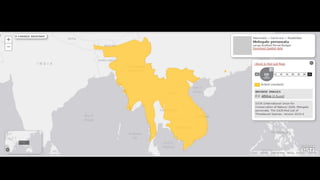
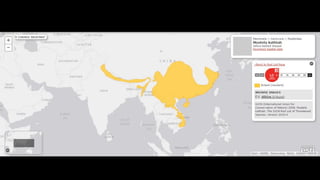
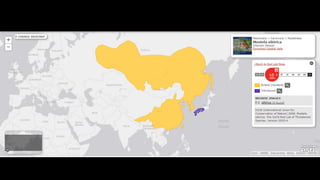
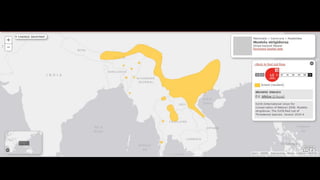
This document provides information on various carnivorous mammal species found in India, including their classifications, characteristics, distributions, conservation statuses, and subspecies. It covers 12 families containing over 200 total species found worldwide, with 59 species and 24 genera represented in India. For several example species, details are given on their physical traits, social behaviors, habitats and ranges. The document focuses on identifying information and conservation statuses to concisely summarize key facts about India's carnivorous mammal diversity.