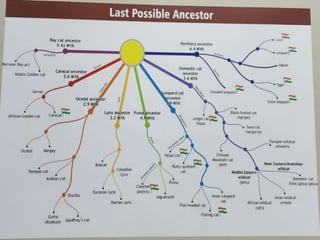
This document provides information about cats, including their evolution, different types of cats, habitats, diets, hunting behaviors, and threats to their survival. It discusses how cats evolved 30 million years ago from the suborder Felidae. There are both big cats, like tigers, lions, leopards and snow leopards, and small wild cats, including jungle cats, fishing cats and Pallas's cats. Big cats are distinguished by their larger size, prey base and home range. Tigers prefer dense forests while lions prefer open grasslands and forests. Leopards can survive in varied habitats from forests to rocky scrublands. Snow leopards live in rocky mountains and prey on mountain goats. Threats to