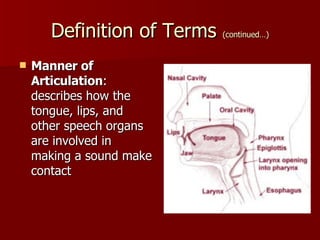
Oral communication has evolved over time, from basic speech around 200,000 years ago to the development of symbols 30,000 years ago and writing 7,000 years ago. Oral communication can be verbal, using words, or nonverbal, using sounds, gestures, and paralanguage to modify meaning and convey emotion. It serves various purposes from conveying ideas to expressing emotions and attitudes in business contexts. While oral communication allows retransmitting information through word of mouth and transcending some language barriers, it is limited to face-to-face contact and most nonverbal elements are subject to language barriers.