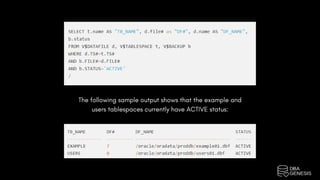
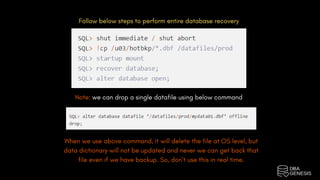
The document provides an overview of Oracle Database hot backup and recovery procedures, detailing the hot backup process while the database is operational and under fuzzy state with user transactions. It covers the implications of hot backup on data file headers and the generation of redo logs, as well as measures for recovering parameter files, control files, and data files in various failure scenarios. The document emphasizes best practices for maintaining data integrity during hot backups and outlines necessary steps for effective recovery when data files or logs are lost.