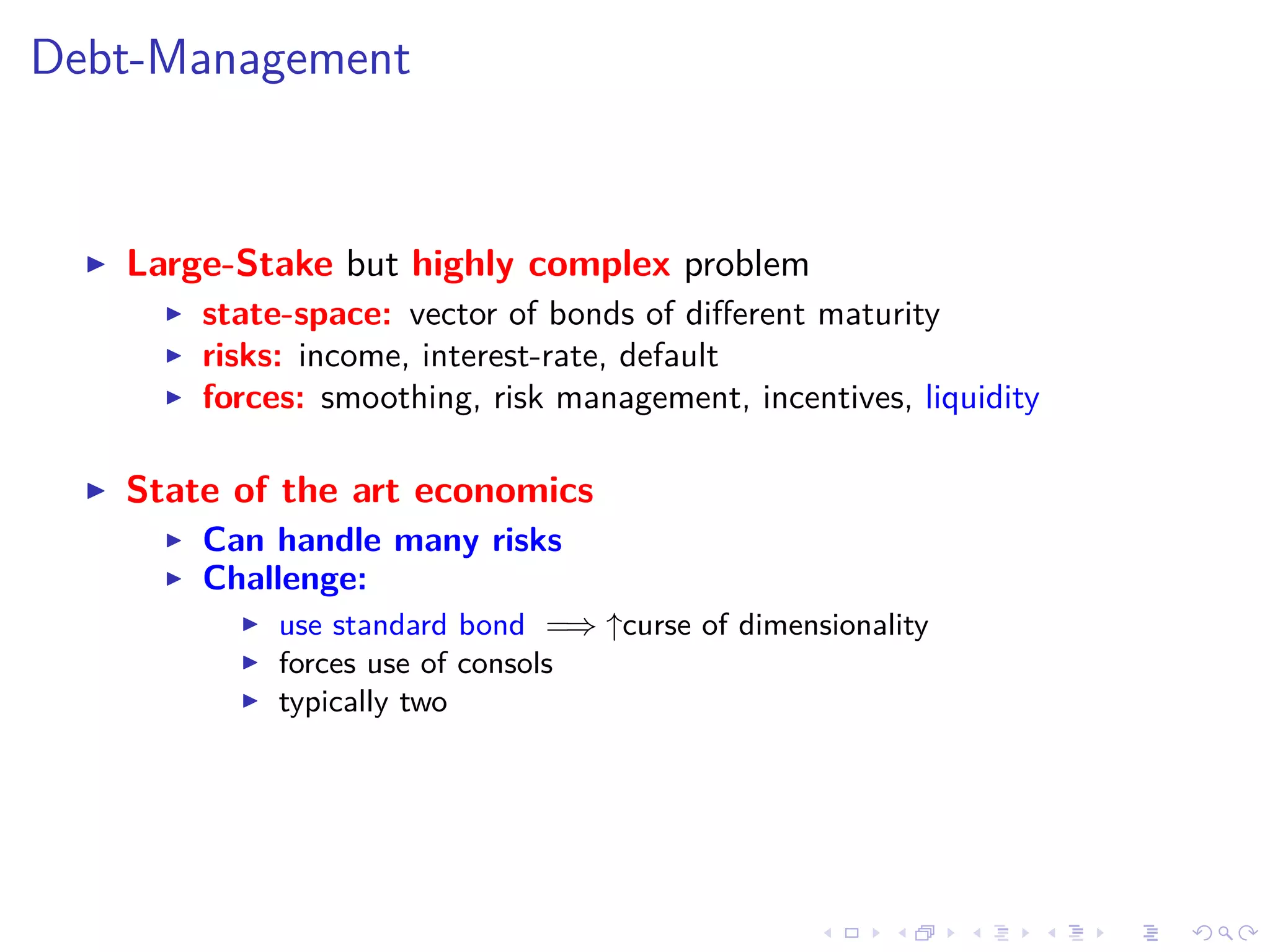
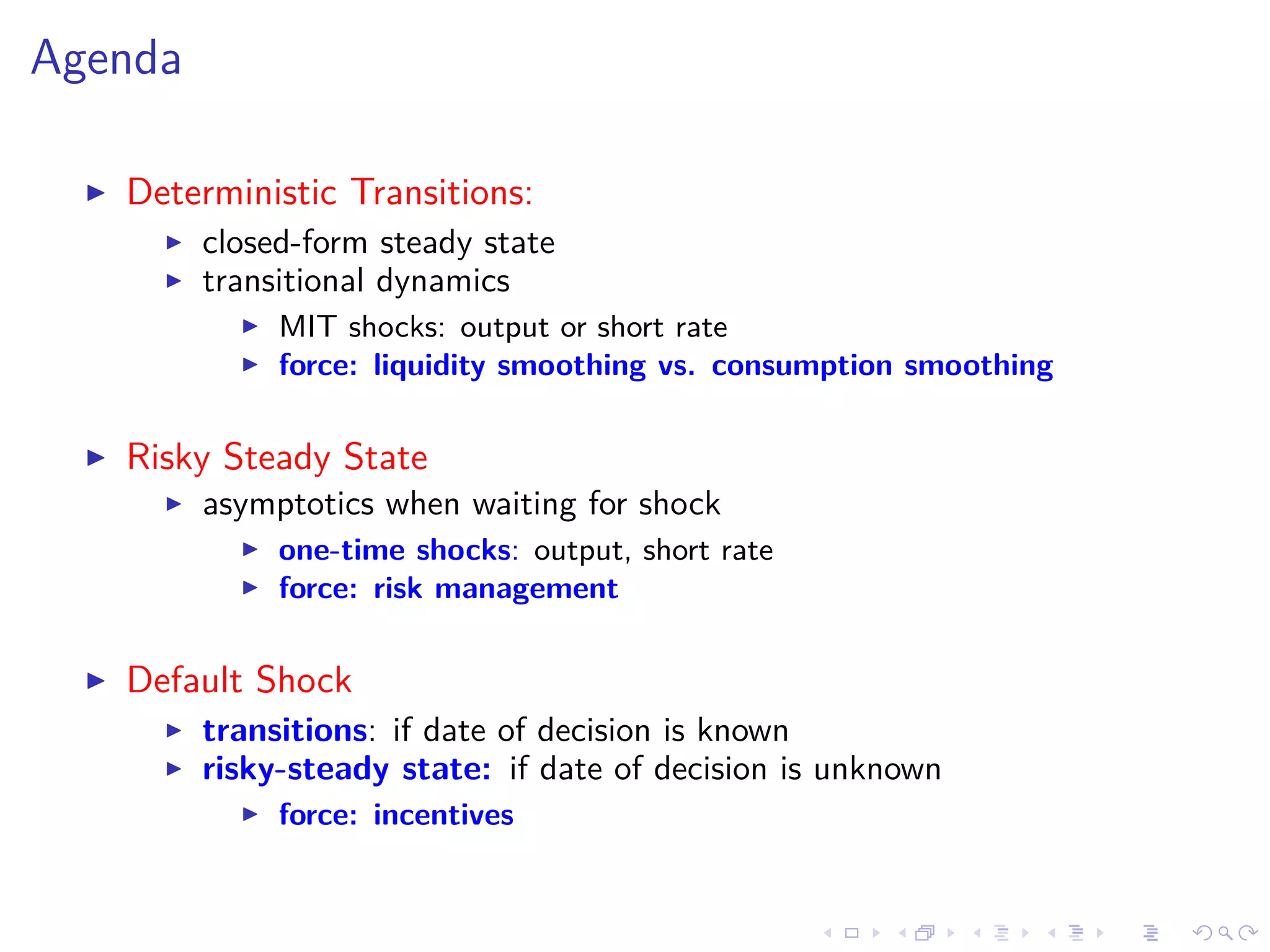
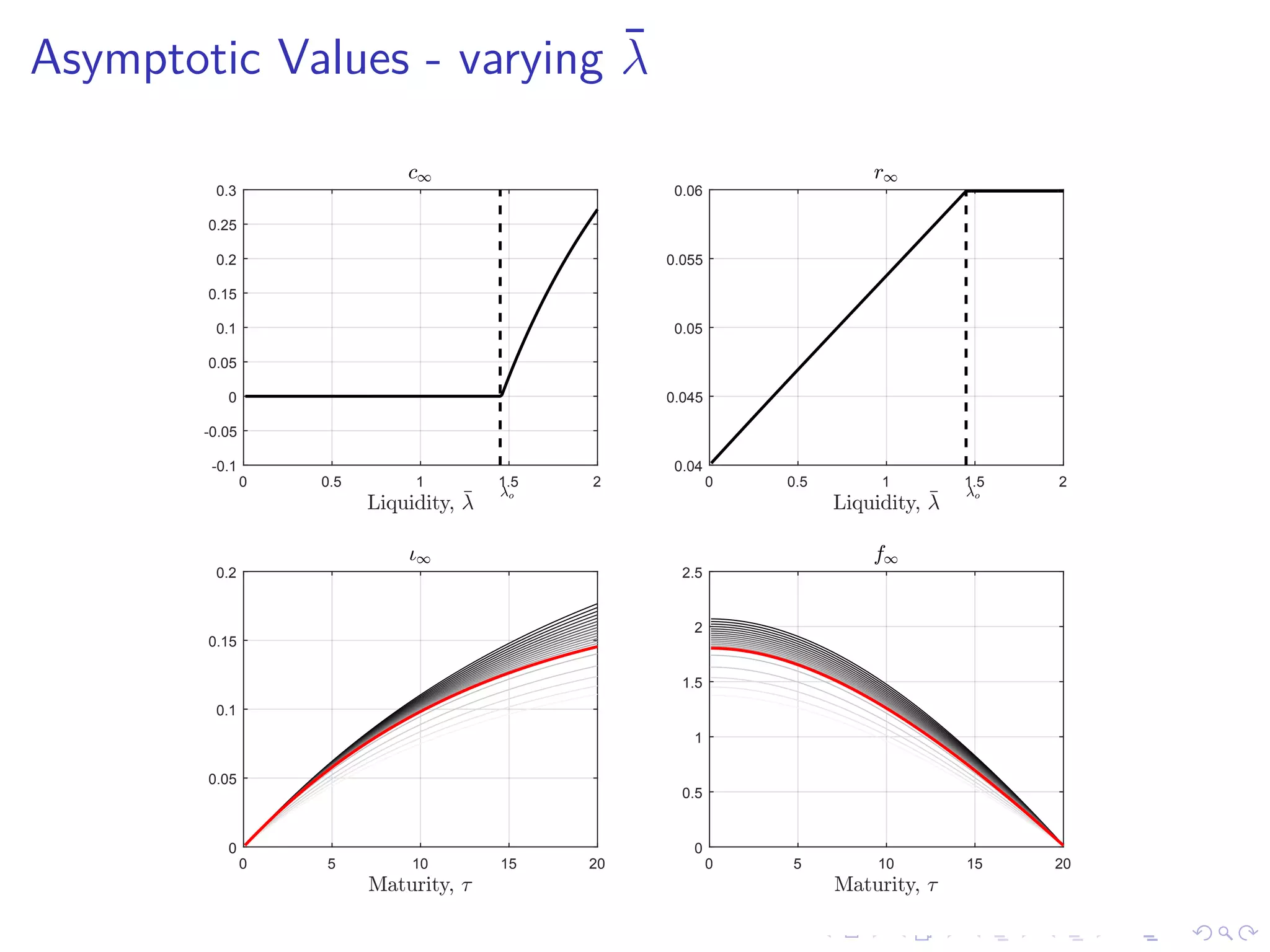
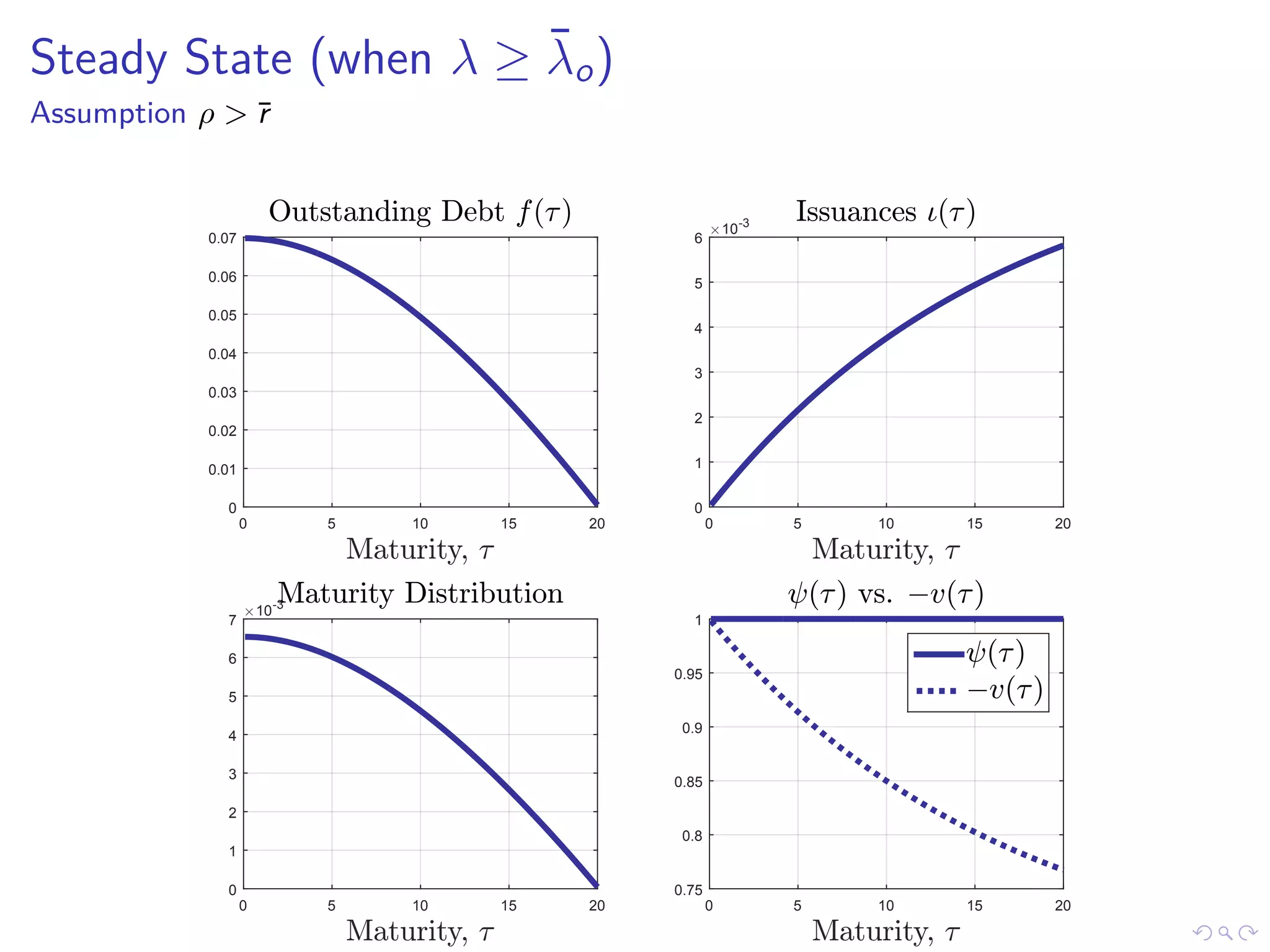
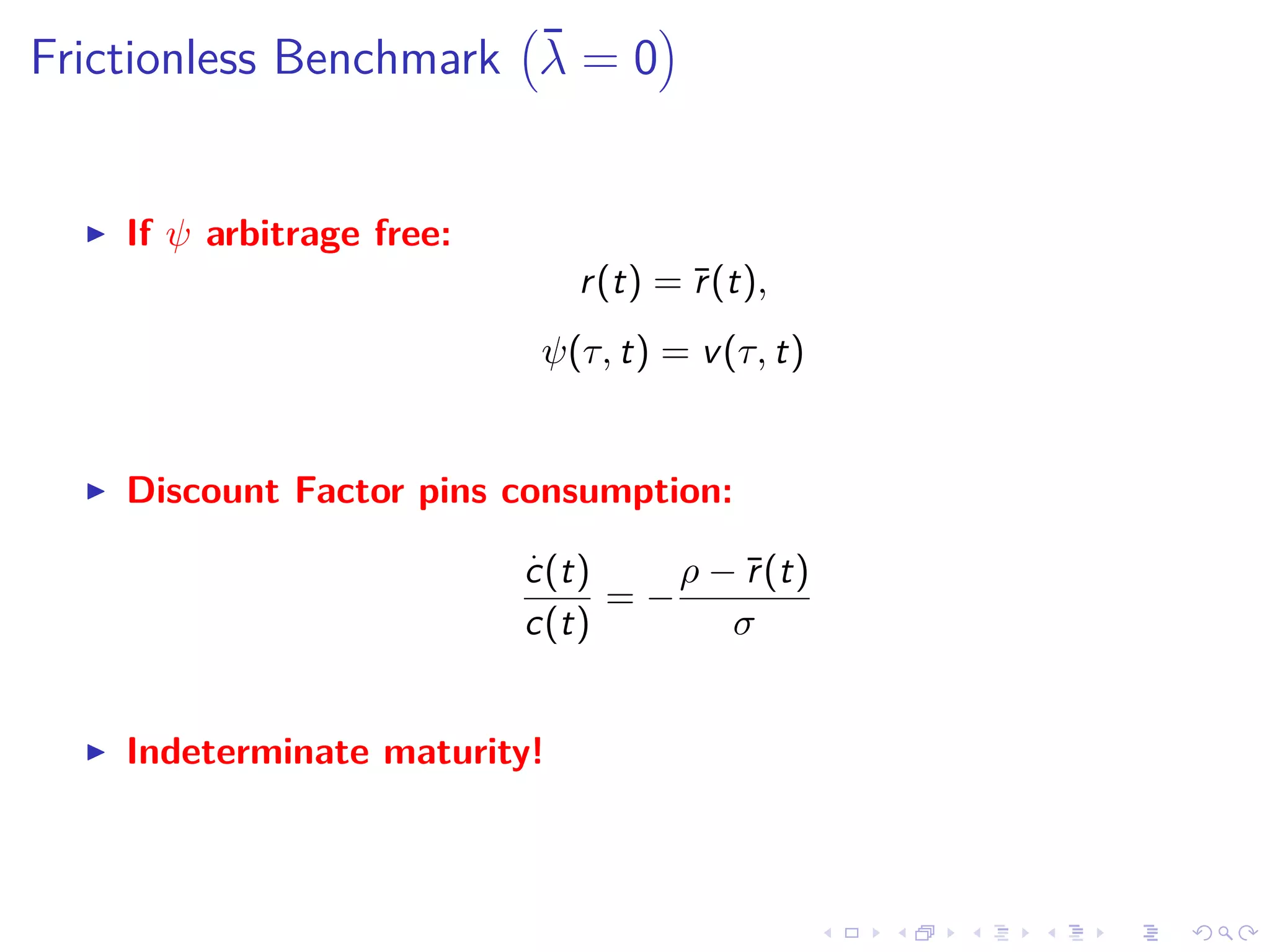
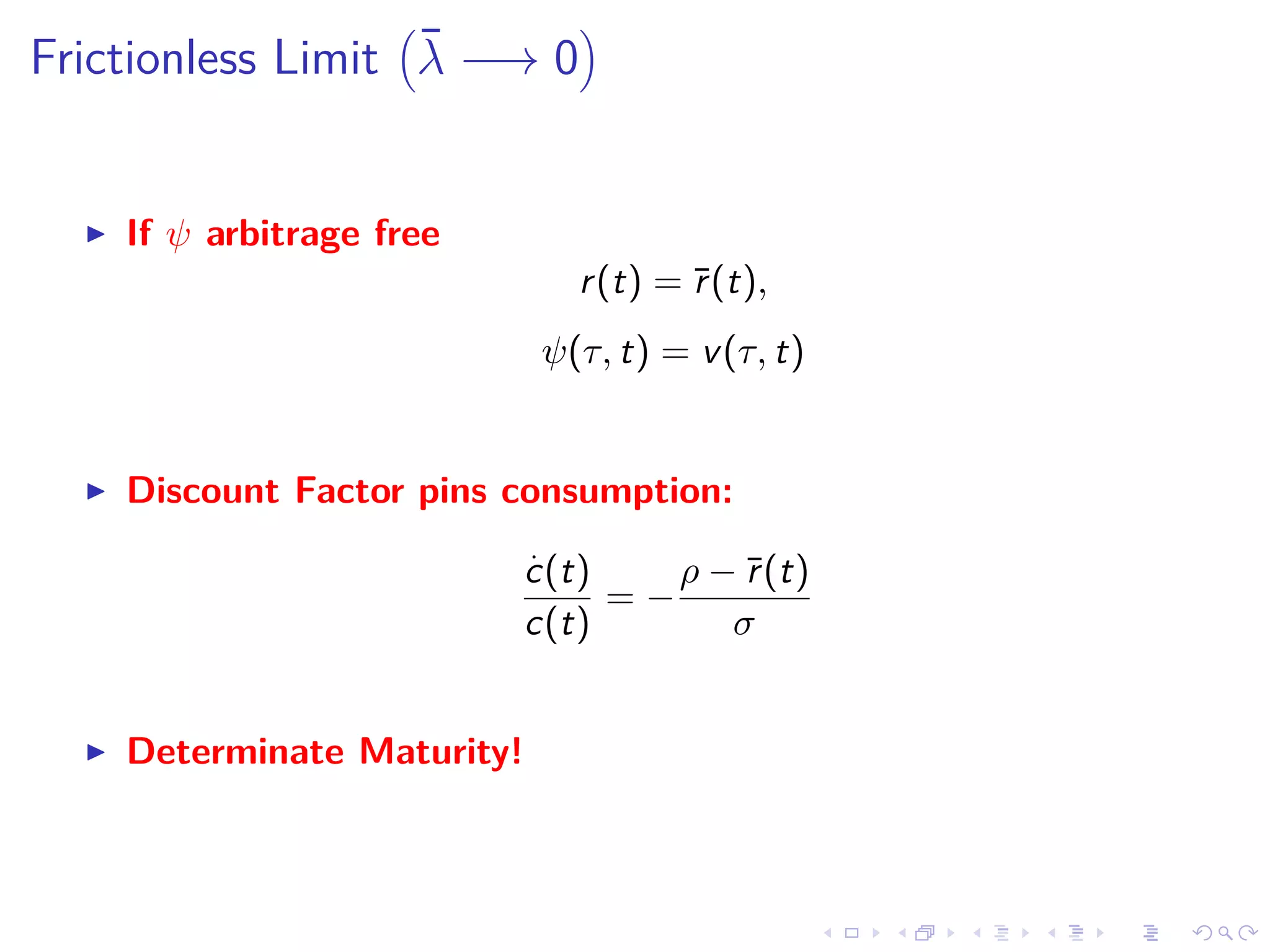
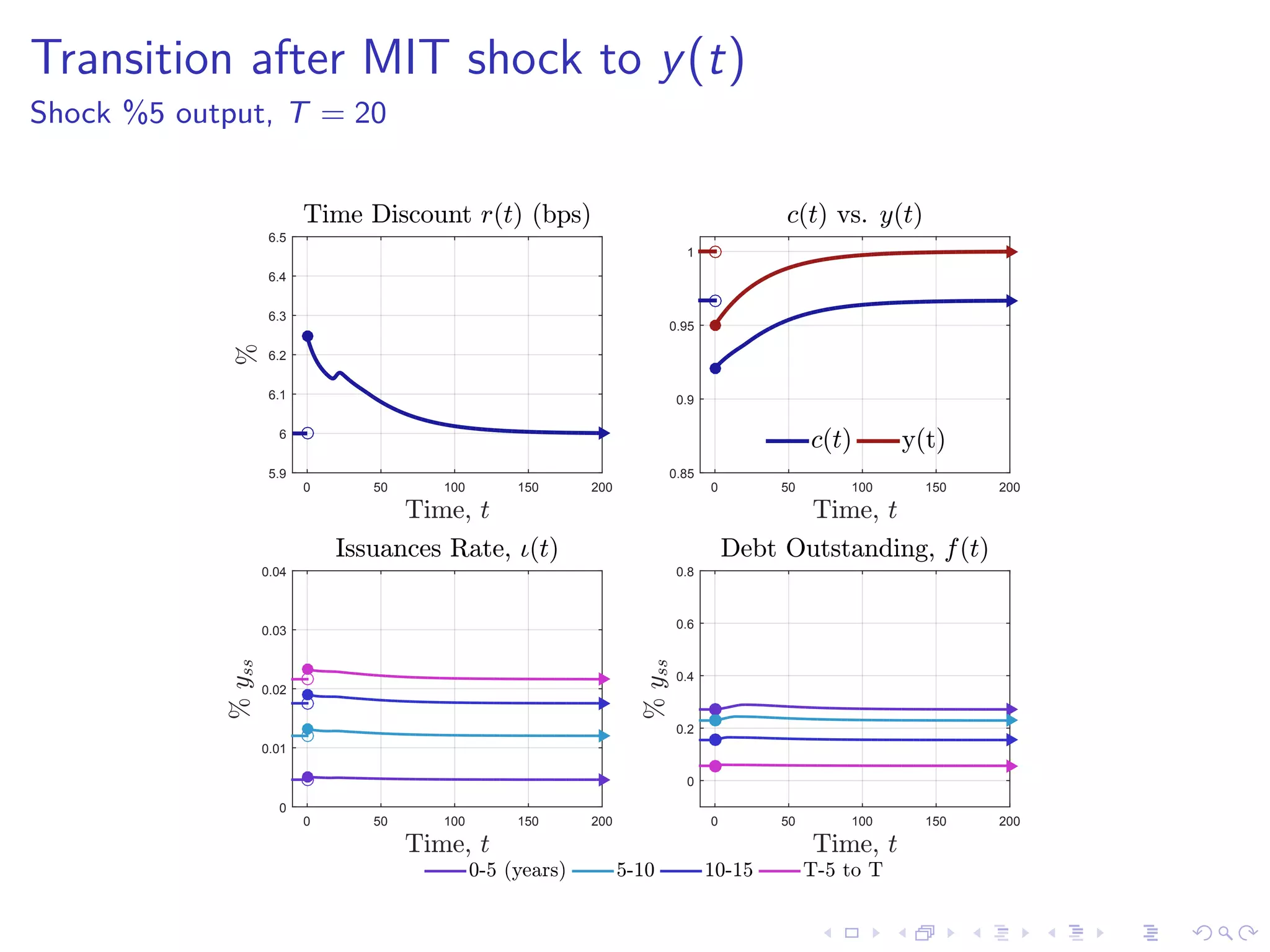
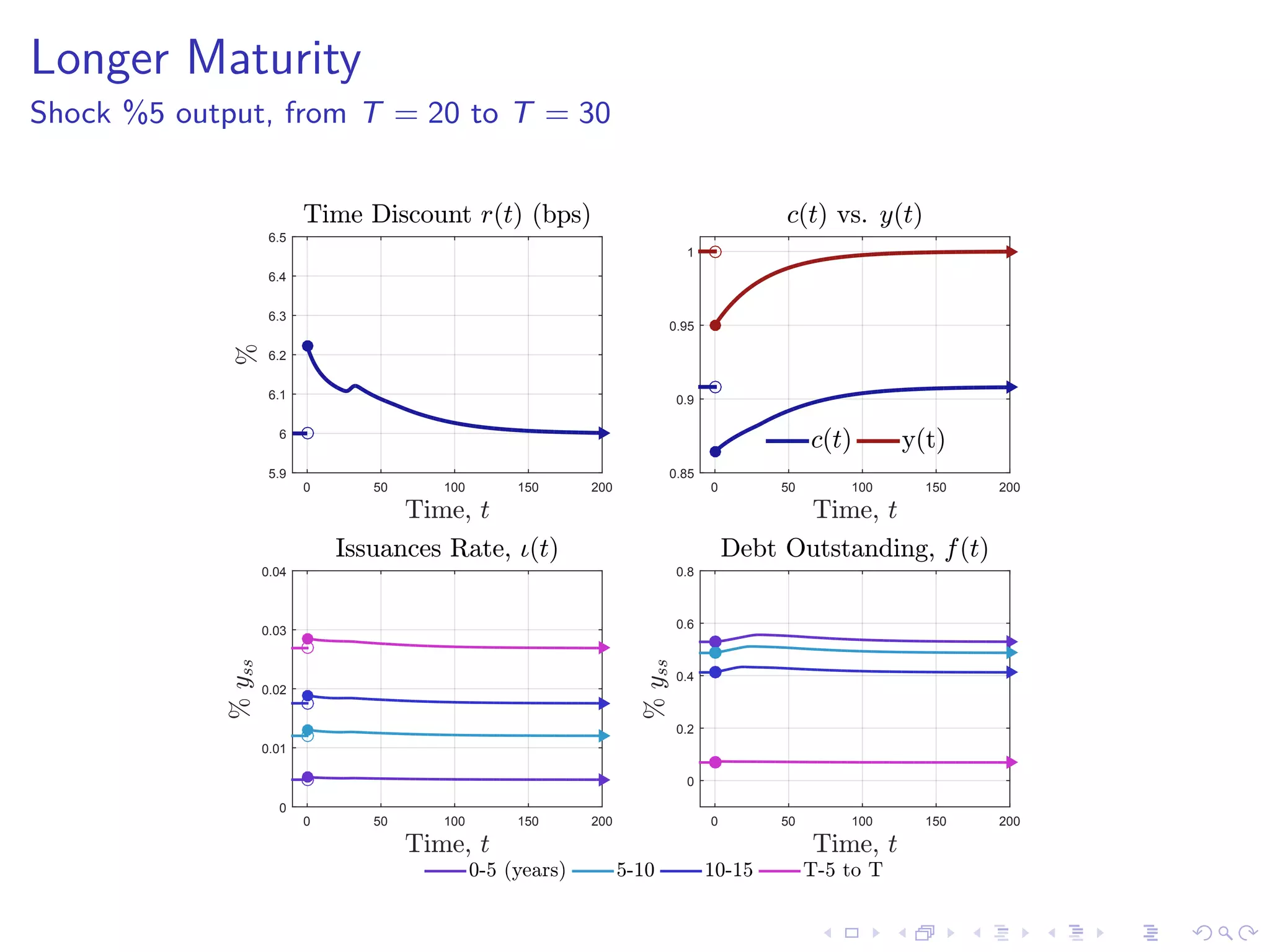
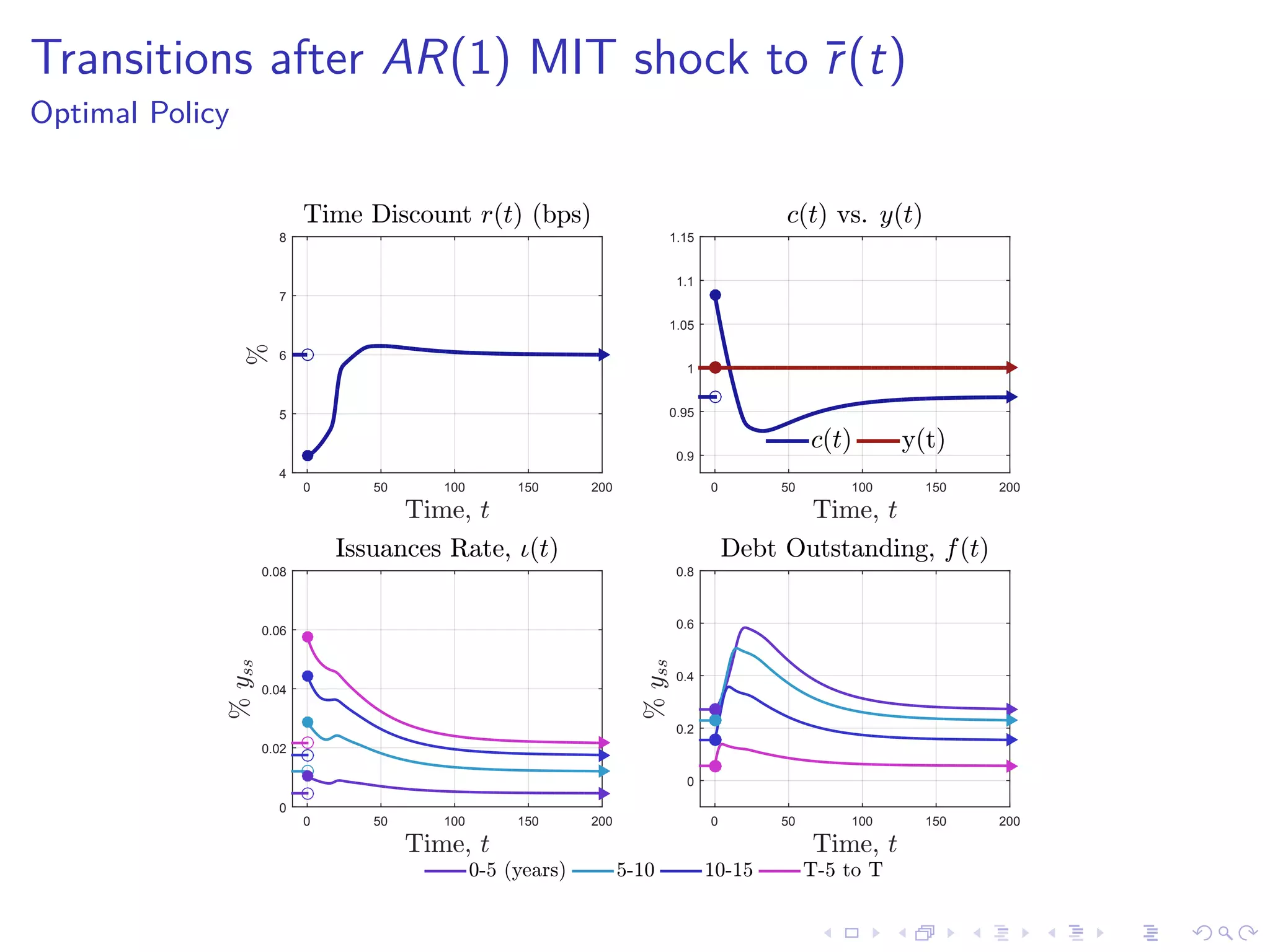
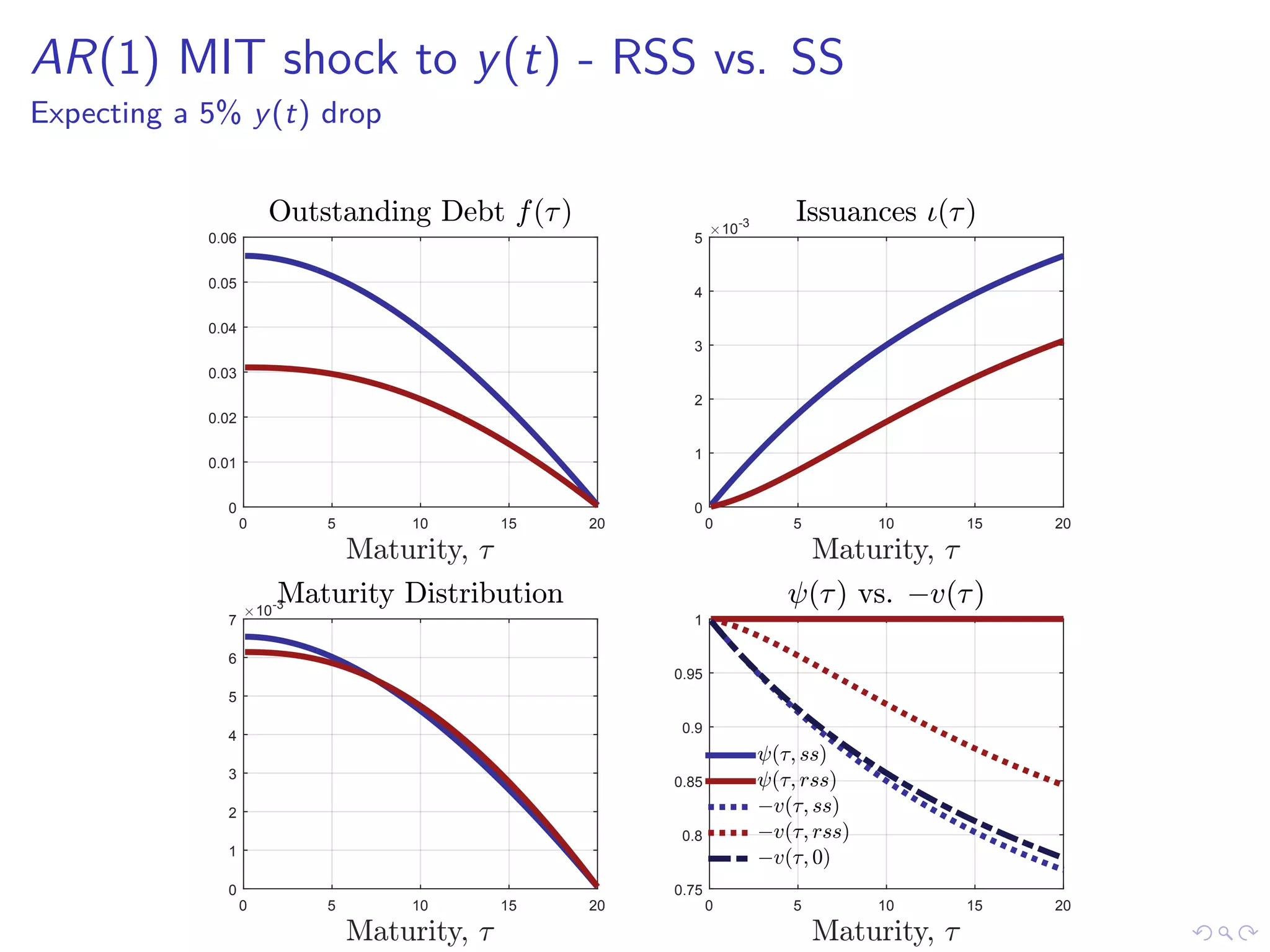
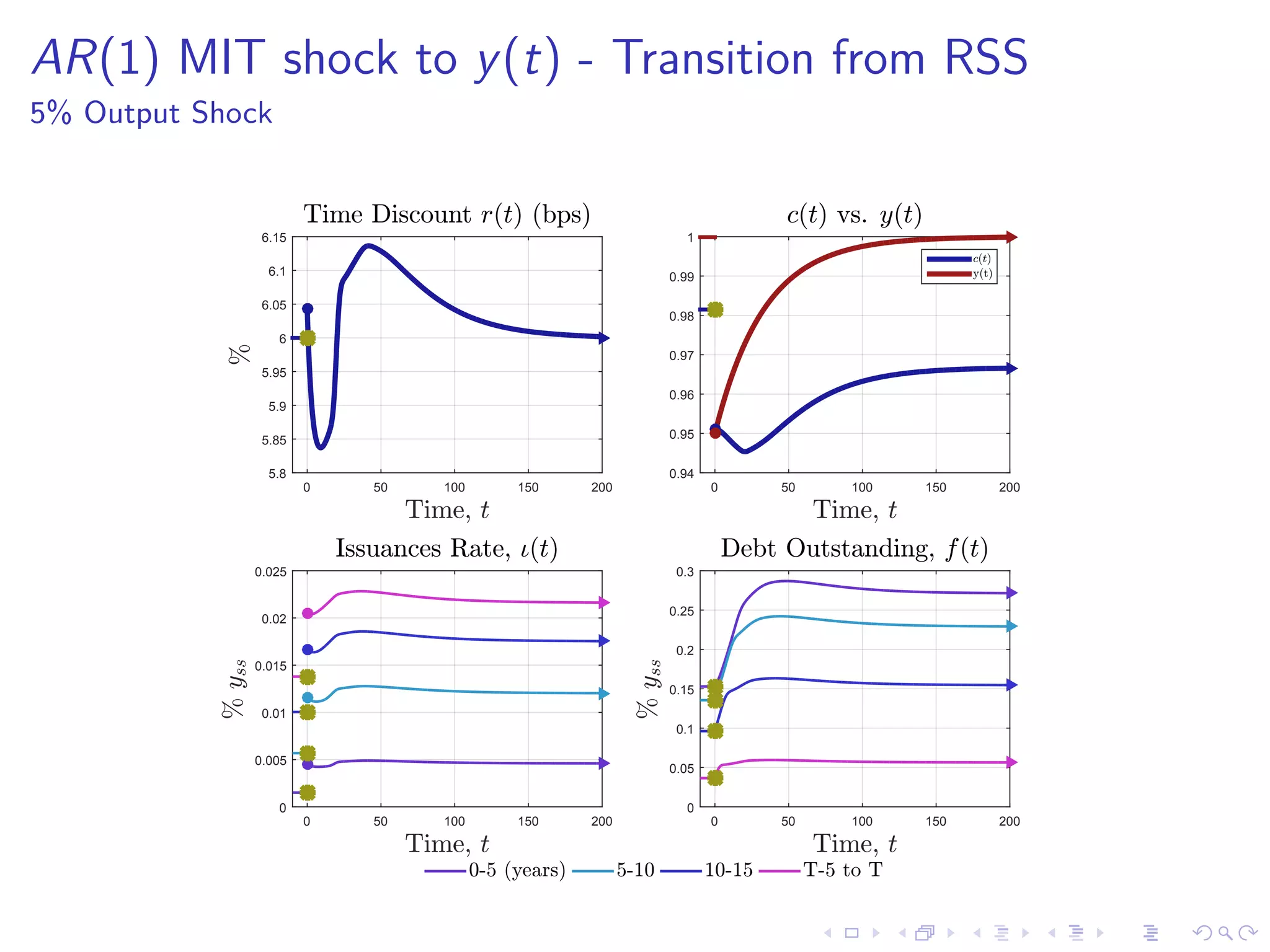
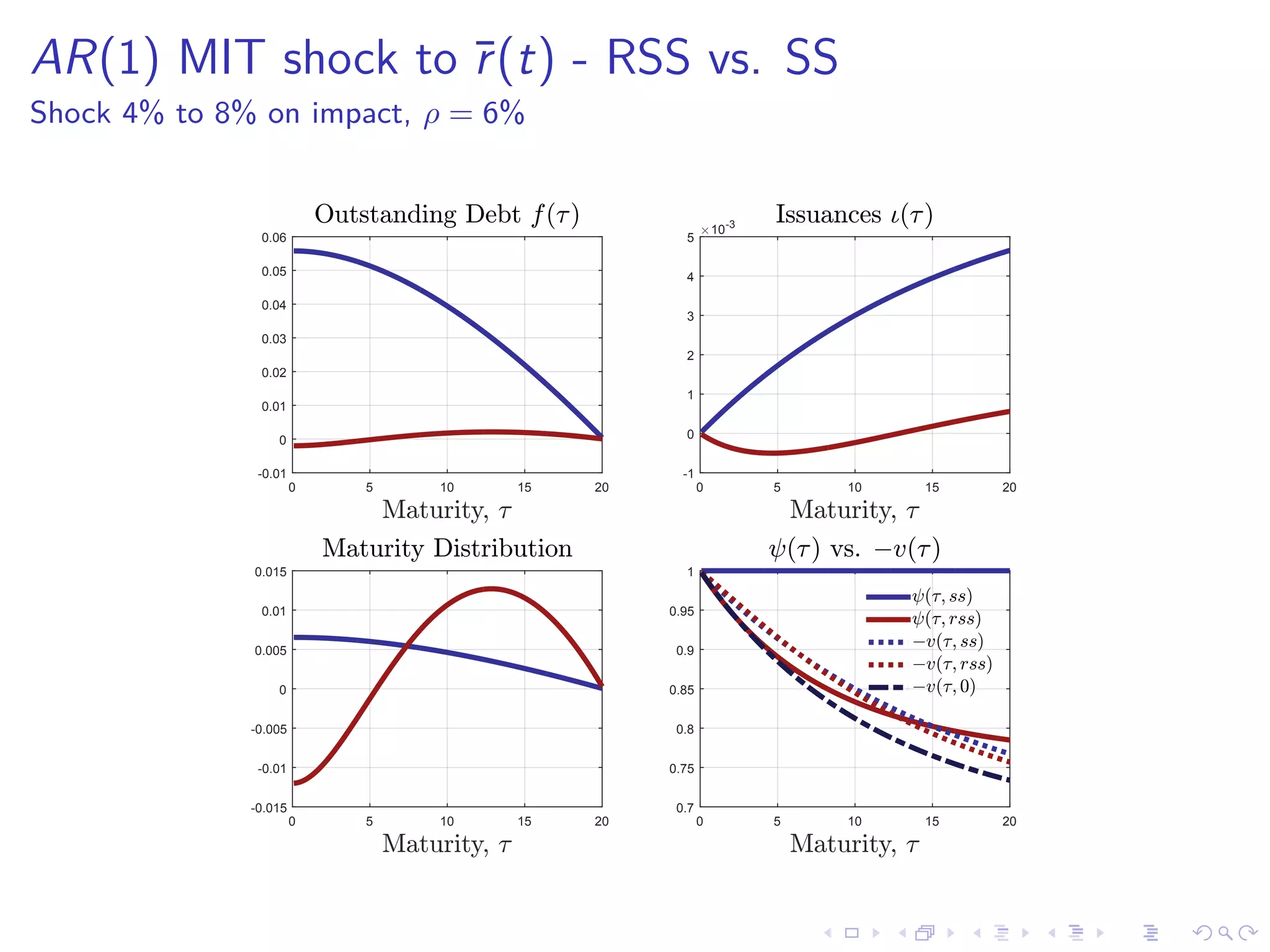
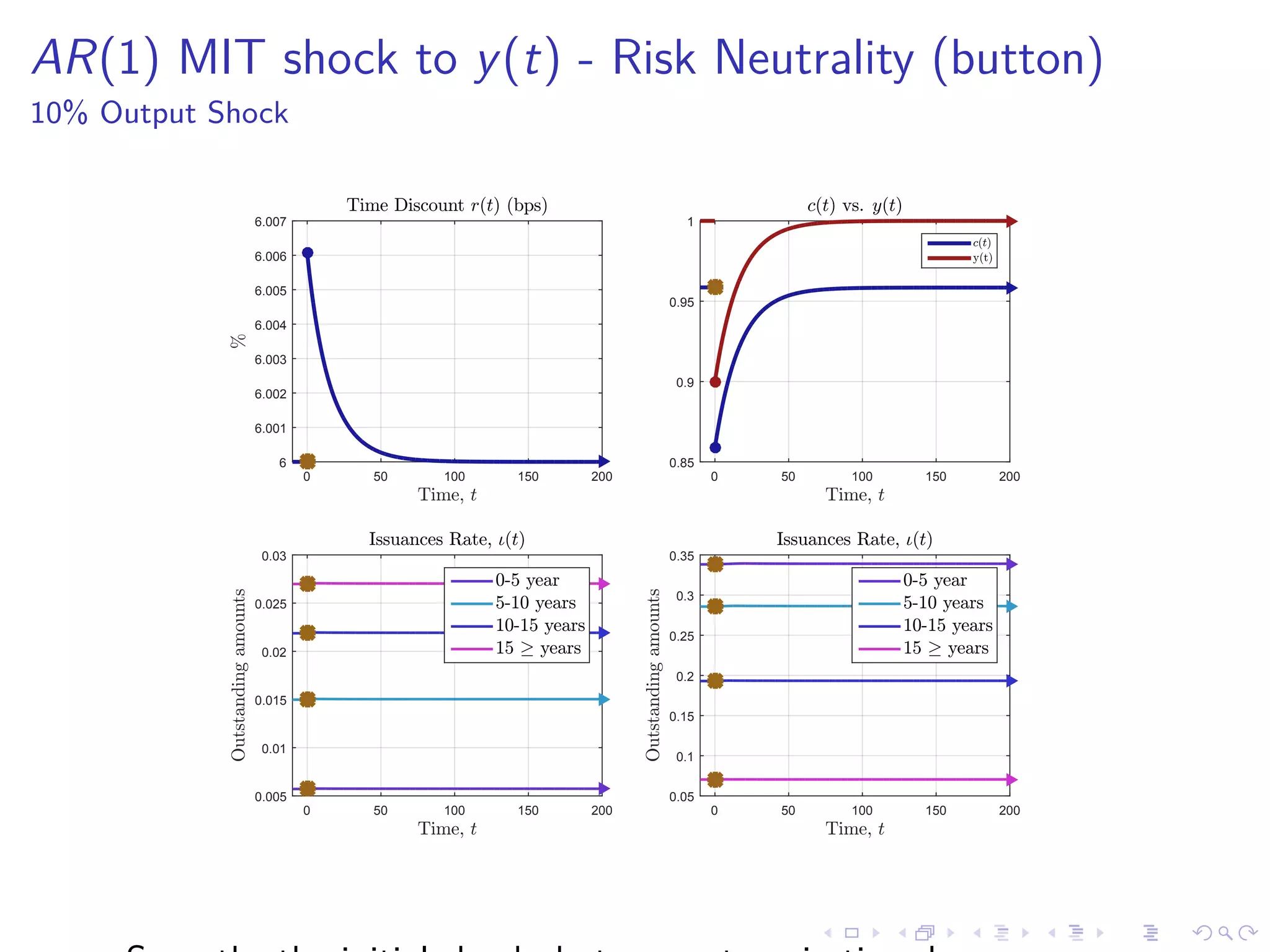
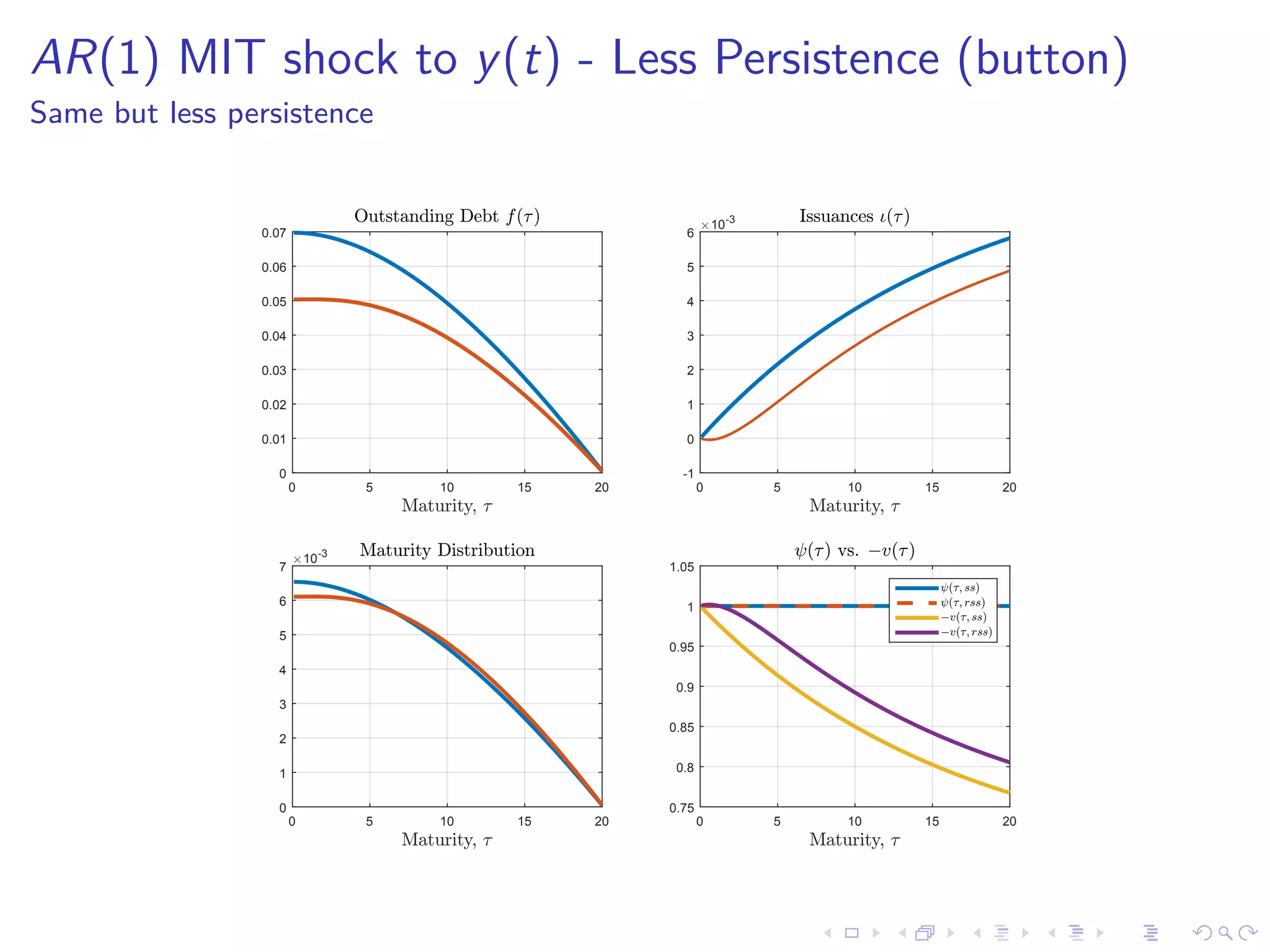
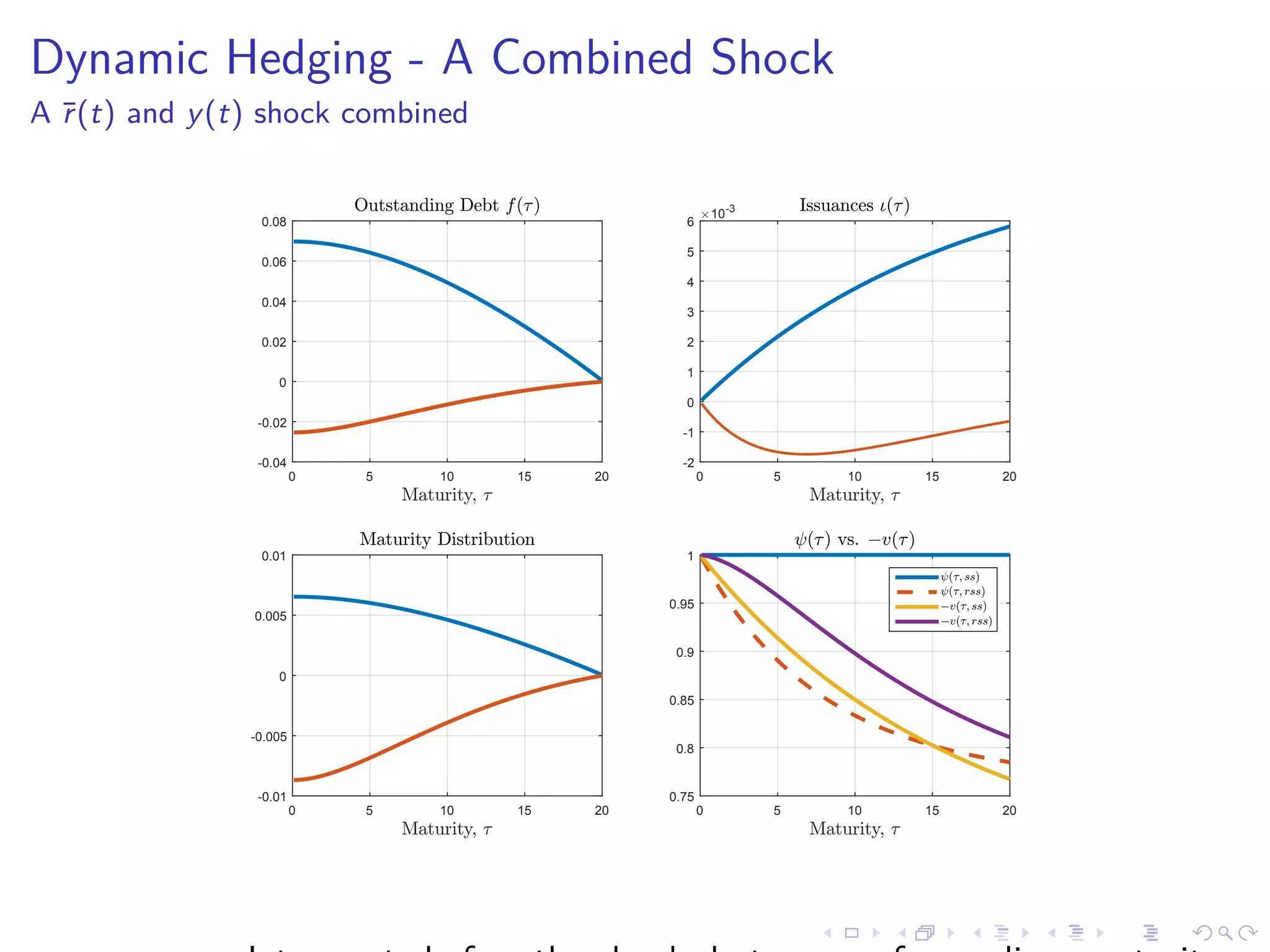
This document discusses optimal debt maturity management. It presents a model where a sovereign can issue a continuum of bonds with arbitrary cash flows to examine debt dynamics. The model highlights the role of liquidity costs in shaping issuance and maturity choices. It shows that income and interest rate shocks can lead to cycles in issuance as the sovereign balances liquidity smoothing versus consumption smoothing. Longer maturity horizons and interest rate shocks emphasize consumption smoothing over liquidity smoothing in transitions following shocks.


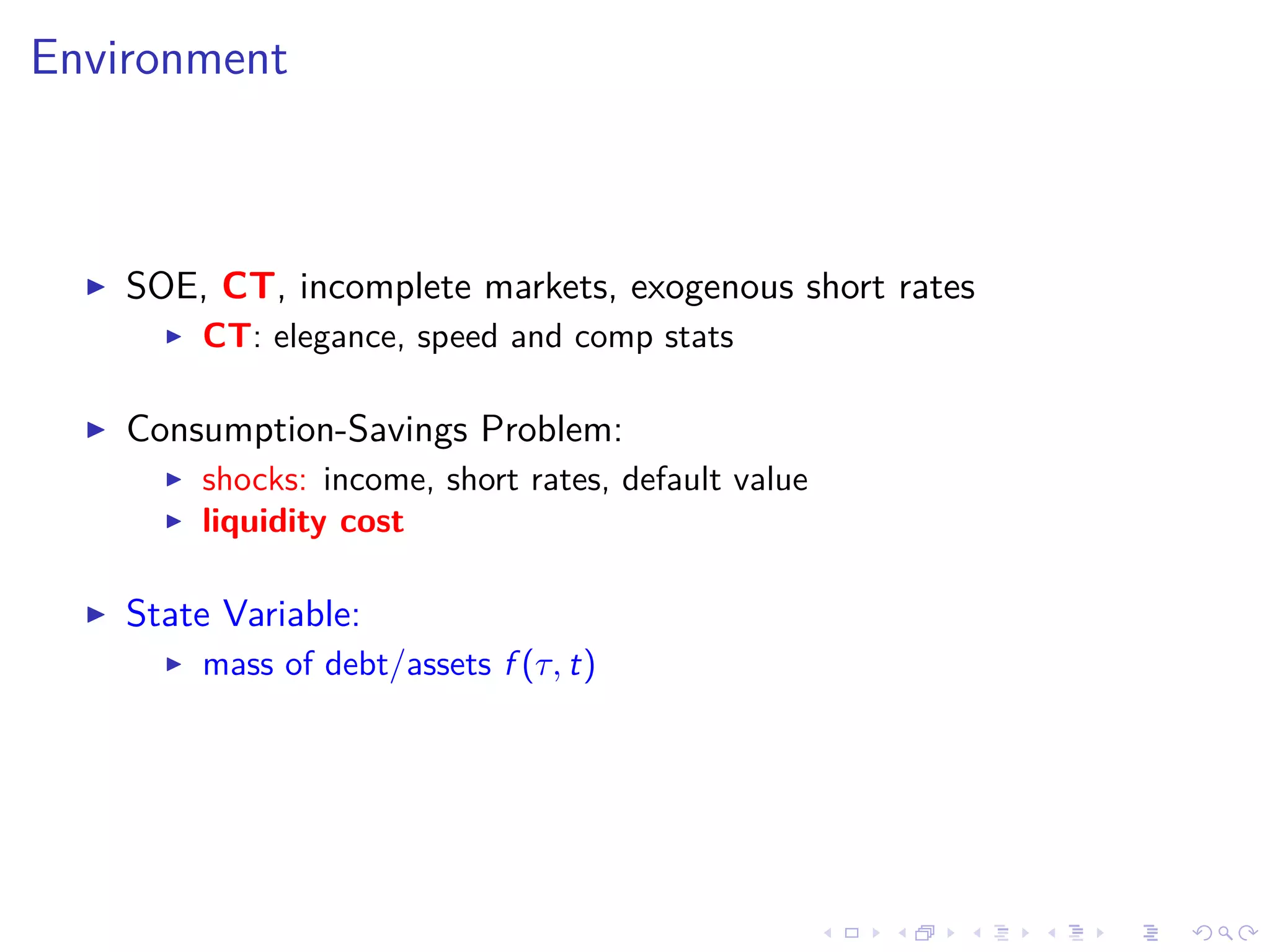

![Environment: shocks, preference and state
Random paths: income y(t), short rate ¯r(t)
later: default
Preferences:
V0 = E[
∞
0
e−ρt
u(c(t))dt] and u(x) ≡
c1−σ − 1
1 − σ
State: debt f (τ, t), expiration τ ∈ [0, T]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-9-2048.jpg)

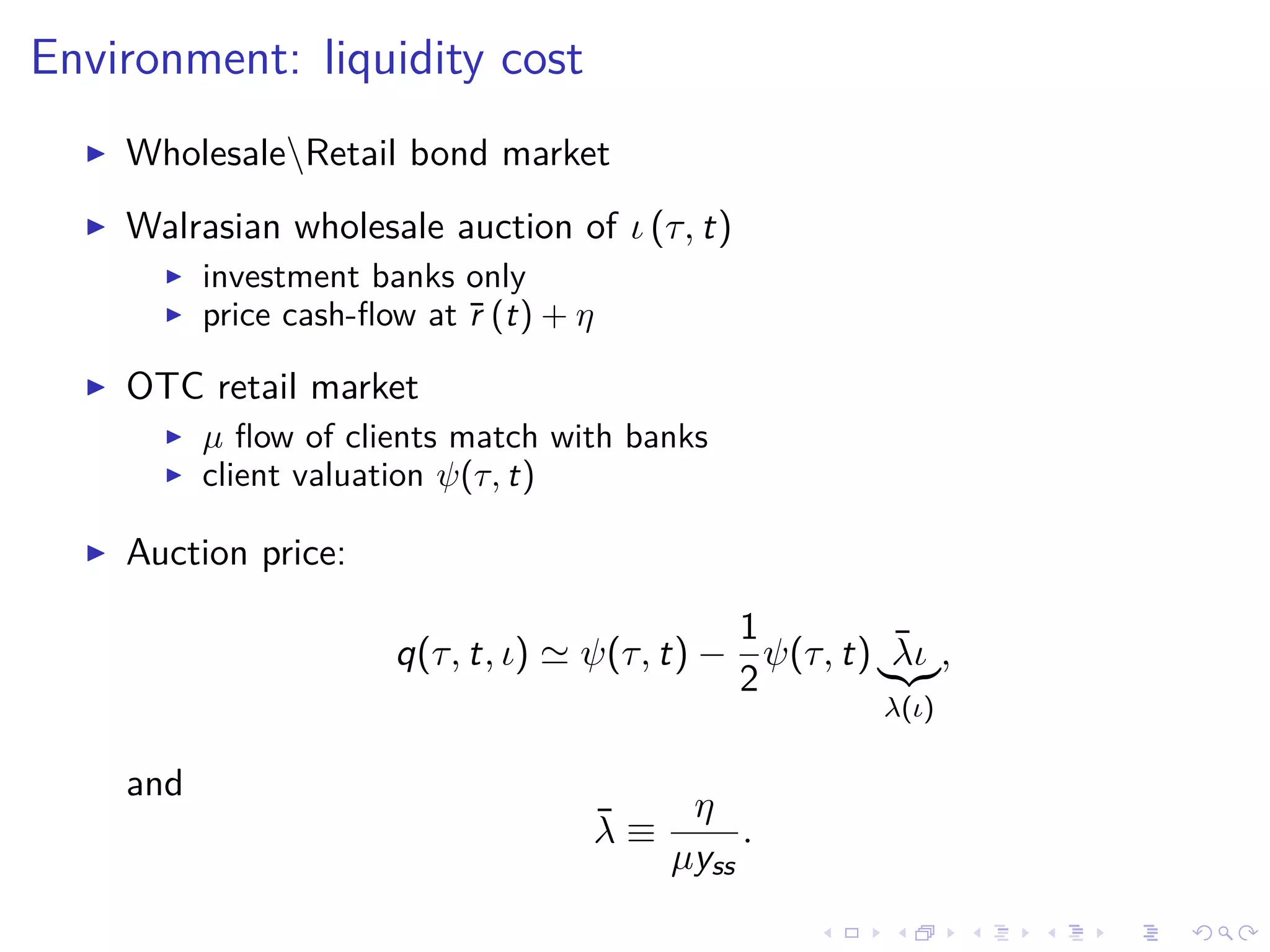
![Environment: bond price
Bond Price ψ(τ, t):
short rate ¯r(t) path and no-arbitrage:
ψ(τ, t) = E[e
−
τ
0
¯r(t+s)ds
+ δ
τ
0
e
−
s
0
¯r(t+z)dz
ds]
In HJB form:
¯r(t)ψ(τ, t) = δ +
∂ψ
∂t
−
∂ψ
∂τ
; ψ(0, t) = 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-11-2048.jpg)
![General Problem
Perfect Foresight
V [f (·, 0)] = max
{ι(τ,t)}t∈[0,∞),τ∈[0,T]
Et
∞
t
e−ρ(s−t)
u(c(s))ds s.t.
c (t) = y (t) − f (0, t) +
T
0
[q (τ, t, ι) ι (τ, t) − δf (τ, t)] dτ
∂f
∂t
= ι (τ, t) +
∂f
∂τ
; f (τ, 0) = f0(τ)
Dual: Dual](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-13-2048.jpg)

![Solving it
Step 1. Lagrangian
L (ι, f ) =
∞
0
e−ρt
u (c(t)) dt
+
∞
0
T
0
e−ρt
j (τ, t) −
∂f
∂t
+ ι (τ, t) +
∂f
∂τ
dτdt,
c(t) = y (t) − f (0, t) +
T
0
[q (t, τ, ι) ι (τ, t) − δf (τ, t)] dτ.
Step 2. First-Order Condition and Envelope
Marginal Value
u (c) q (τ, t, ι) +
∂q
∂ι
ι (τ, t) =
Marginal Cost
−j (τ, t)
ρj (τ, t) = −δu (c (t)) +
∂j
∂t
−
∂j
∂τ
, if τ ∈ (0, T]
and j (0, t) = −u (c (t)) .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-16-2048.jpg)
![Solving it
Step 1. Lagrangian
L (ι, f ) =
∞
0
e−ρt
u (c(t)) dt
+
∞
0
T
0
e−ρt
j (τ, t) −
∂f
∂t
+ ι (τ, t) +
∂f
∂τ
dτdt,
c(t) = y (t) − f (0, t) +
T
0
[q (t, τ, ι) ι (τ, t) − δf (τ, t)] dτ.
Step 2. First-Order Condition and Envelope
Marginal Value
u (c) ψ (τ, t) − ¯λψ (τ, t) ι =
Marginal Cost
−j (τ, t)
ρj (τ, t) = −δu (c (t)) +
∂j
∂t
−
∂j
∂τ
, if τ ∈ (0, T]
and j (0, t) = −u (c (t)) .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-17-2048.jpg)
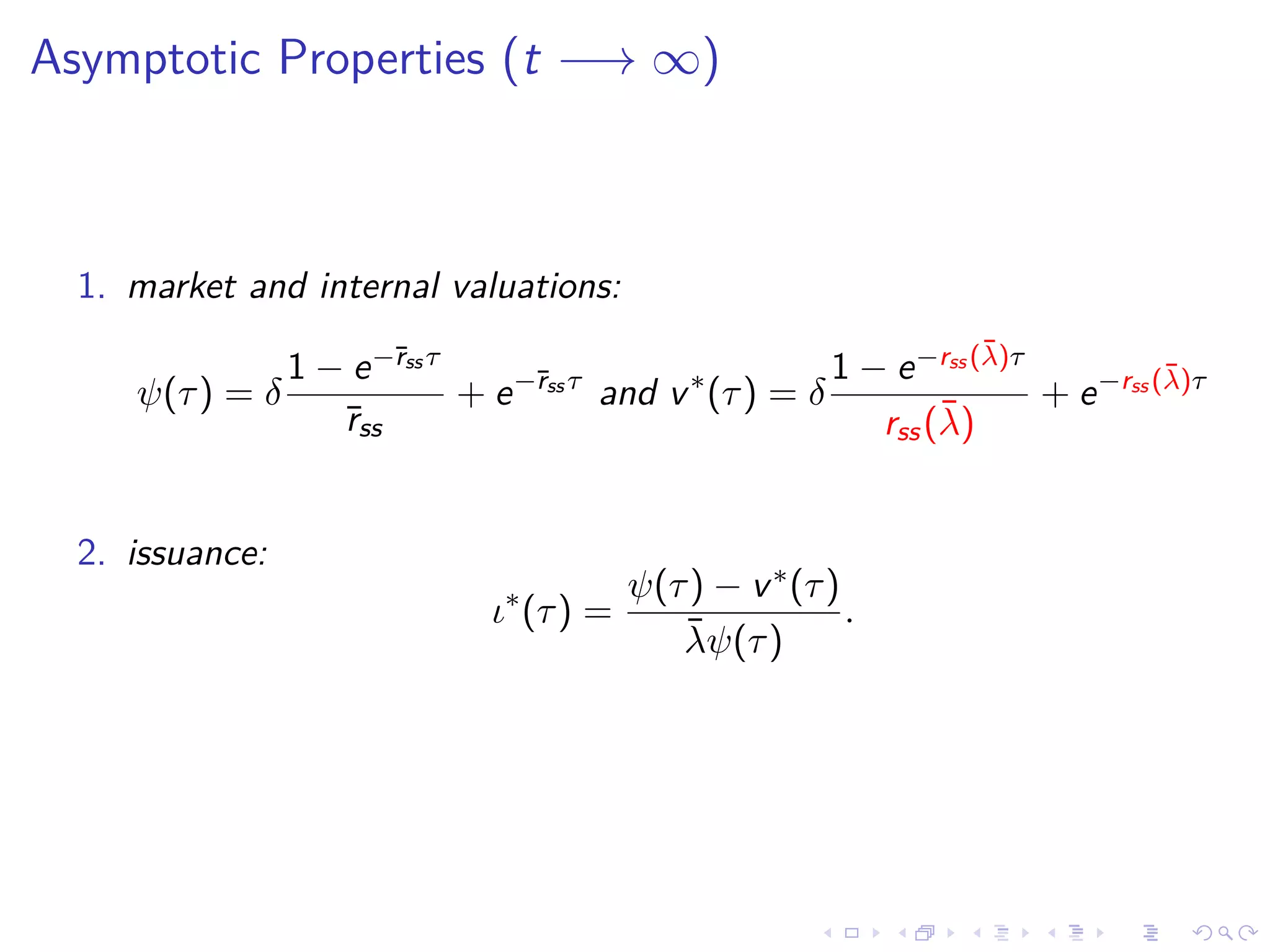
![Optimal Path
Proposition:
1) v(τ, t) ≡ − j(τ,t)
u (c(t)) solves "individual trader” price-PDE:
r(t)
ρ+σ
.
c(t)/c(t)
v (τ, t) = δ +
∂v
∂t
−
∂v
∂τ
, if τ ∈ (0, T]
v (0, t) = 1
2) issuances ι(τ, t):
ψ (τ, t) − ¯λψ (τ, t) ι
marginal income
= v (τ, t)
discounted payouts
3) PDE given f0, c(t) given by BC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-18-2048.jpg)
![Optimal Path
Proposition:
1) v(τ, t) ≡ − j(τ,t)
u (c(t)) solves ‘"ndividual trader” price-PDE:
r(t)
ρ+σ
.
c(t)/c(t)
v (τ, t) = δ +
∂v
∂t
−
∂v
∂τ
, if τ ∈ (0, T]
v (0, t) = 1
2) issuances ι(τ, t):
ι =
ψ (τ, t) − v (τ, t)
¯λψ (τ, t)
3) PDE given f0, c(t) given by BC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-19-2048.jpg)






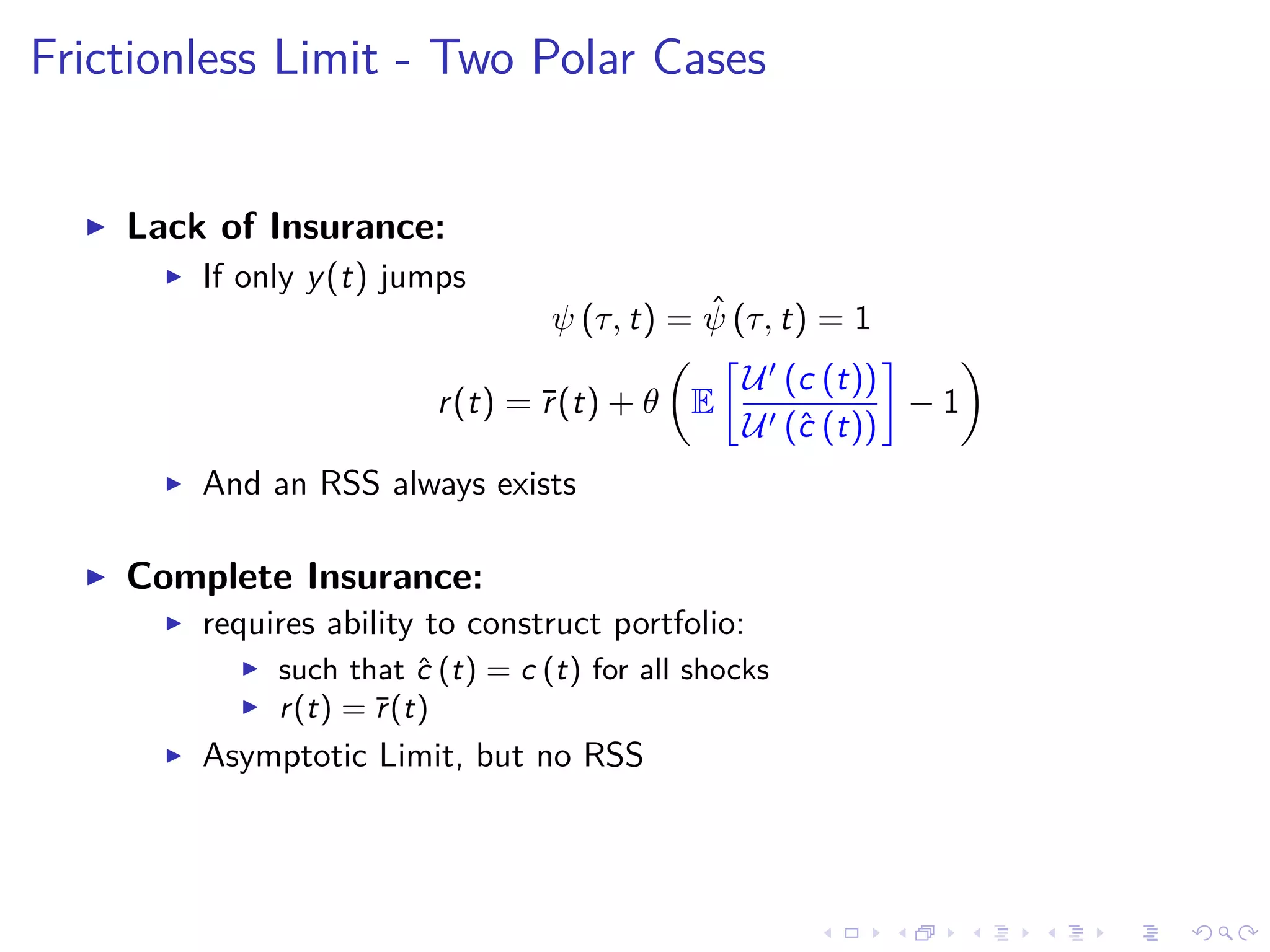
![Frictionless Limit - Pre-shock Transition
ˆψ (τ, t) = ˆv (τ, t)
Price Equation:
¯r (t) ˆψ (τ, t) = δ +
∂ ˆψ
∂t
−
∂ ˆψ
∂τ
+ θ E [ψ (τ, t)] − ˆψ (τ, t)
HJB and ˆψ (τ, t) = ˆv (τ, t)
r(t) ˆψ (τ, t) = δ +
∂ ˆψ
∂t
−
∂ ˆψ
∂τ
+ θ E
U (c (t))
U (ˆc (t))
ψ (τ, t) − ˆψ (τ, t)
both equations must be consistent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-39-2048.jpg)



![Dual
Given {c(t)}t≥0, then planner’s discount:
r(t) = ρ + σ
˙c(t)
c(t)
Dual Problem
D [f (·, 0)] = min
{ι(τ,t)}t=τ∈[0,∞),τ∈[0,T]
∞
0
e−
t
0
r(s)ds
ytdt s.t.
∂f
∂t
= ι (τ, t) +
∂f
∂τ
, f (T, t) = 0; f (τ, 0) = f0(τ)
y (t) = c (t) + f (0, t) −
T
0
[q (τ, t, ι) ι (τ, t) − δf (τ, t)] dτ
back](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-49-2048.jpg)
![Dual (button)
Given {c(t)}t≥0, then planner’s discount:
r(t) = ρ − σ
˙c(t)
c(t)
Dual:
D [f (·, 0)] = min
{ι(τ,t)}t=τ∈[0,∞),τ∈[0,T]
∞
0
e−
t
0
r(s)ds
(f (0, t)−
T
0
(ψ(τ, t) − λ
∂f
∂t
= ι (τ, t) +
∂f
∂τ
, f (τ, 0) = f0(τ)
back](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-50-2048.jpg)




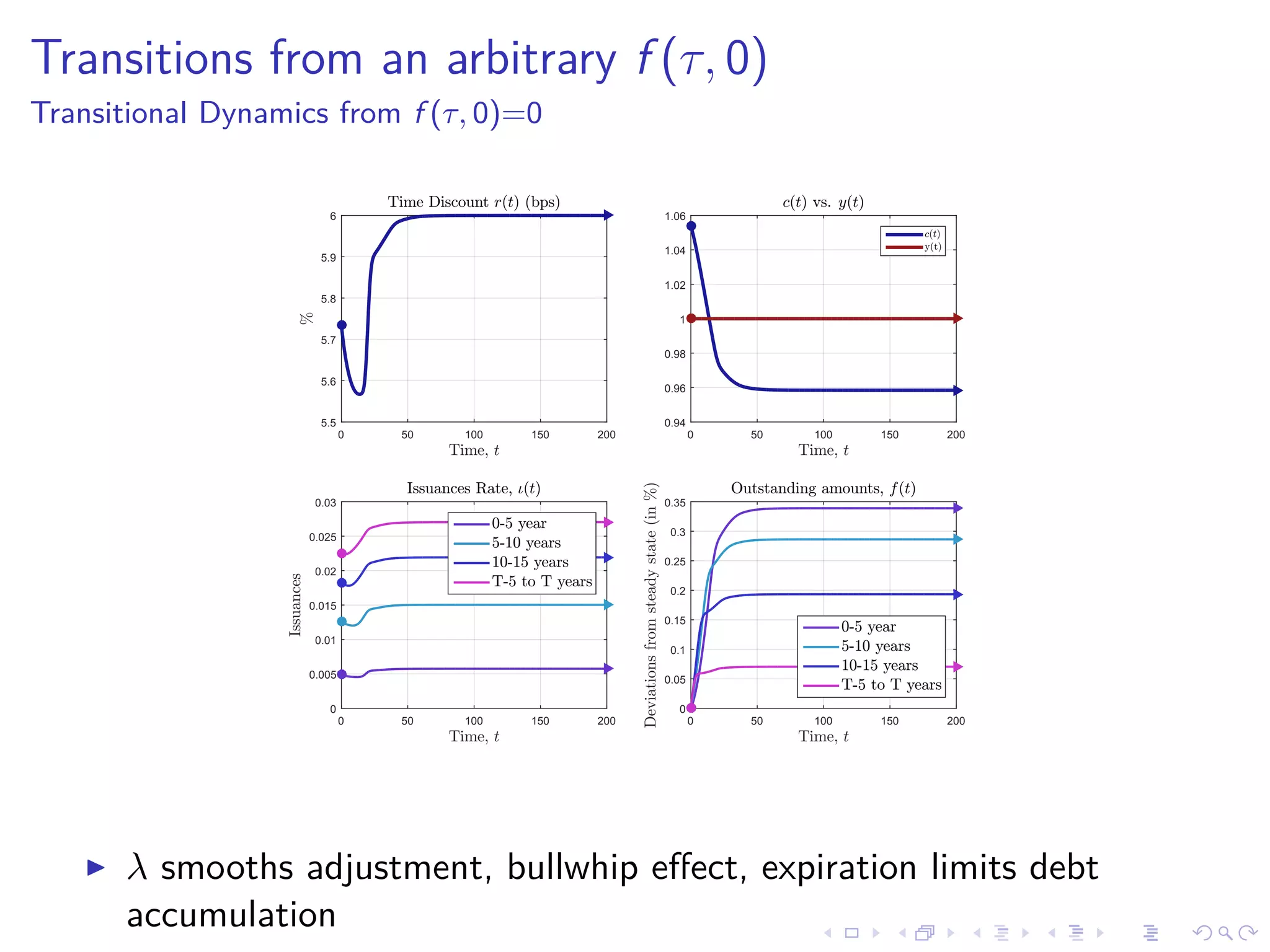
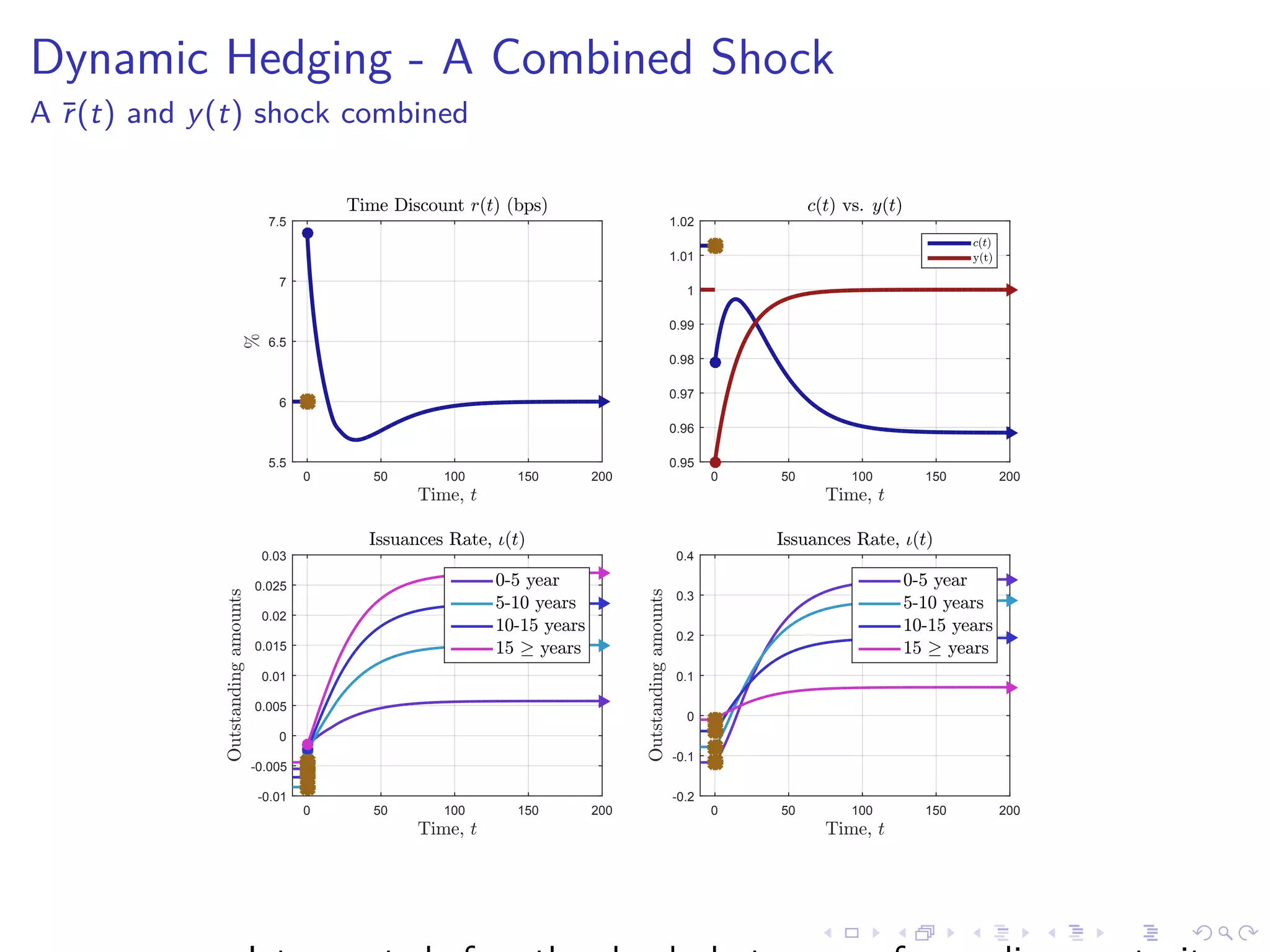
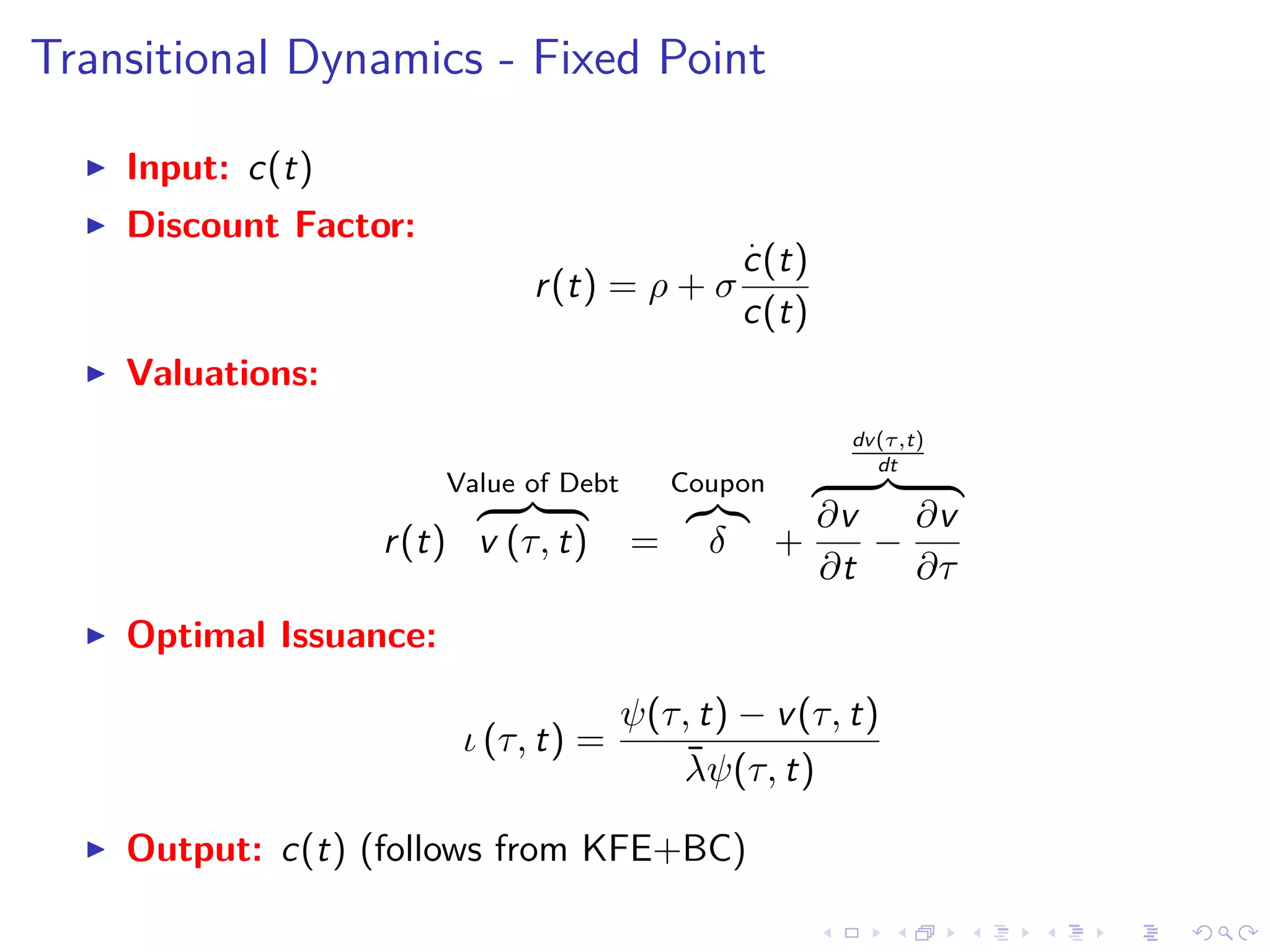
![Transitional Dynamics - Fixed Point Algorithm in r(t)
1. Build:
r(t) = ρ − σ
˙c(t)
c(t)
2. Plug r(t) into value PDE:
r(t)v (τ, t) = −δ +
∂v
∂t
−
∂v
∂τ
3. Build issuances:
ι (τ, t) =
ψ(τ, t) + v(τ, t)
¯λ
4. Obtain f (t, τ):
f (τ, t) =
min{T,τ+t}
τ
ι(t + τ − s, s)ds + I[T > t + τ] · f (τ + t, 0)
5. c(t) given by
cout
(t) = y (t) − f (0, t) +
T
0
[q (τ, t, ι) ι (τ, t) − δf (τ, t)] dτ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-180613205204/75/Optimal-debt-maturity-management-62-2048.jpg)
