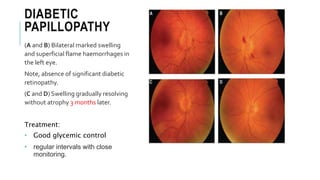
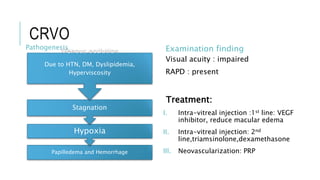
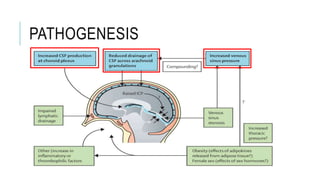
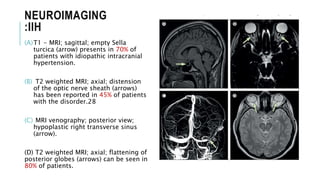
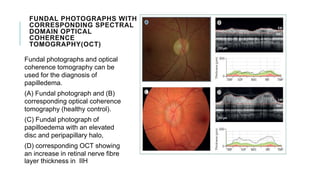
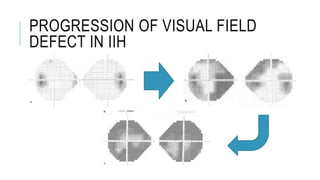
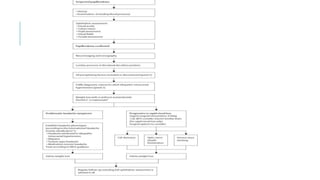
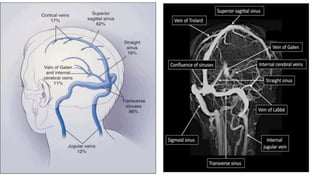
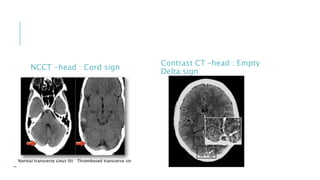
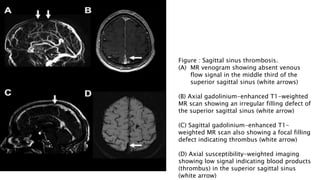
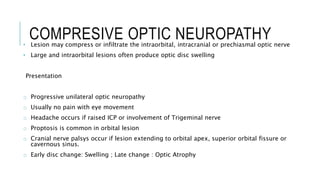
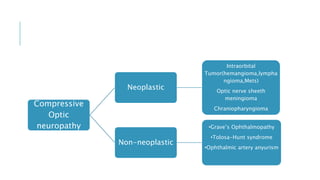
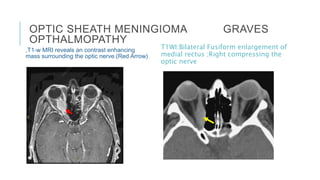
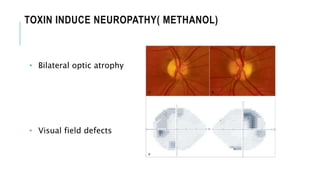
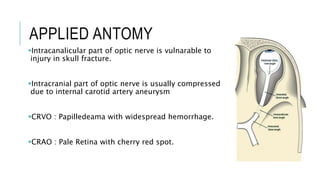
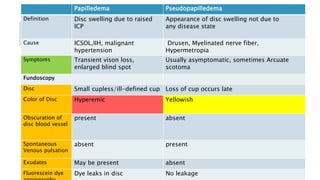
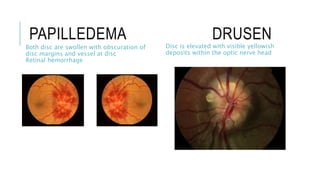
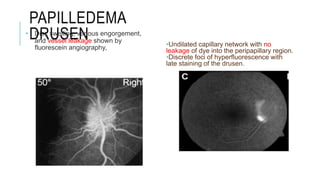
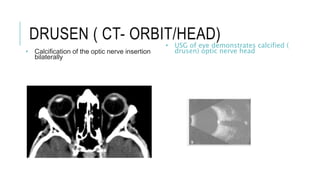
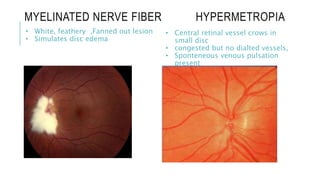
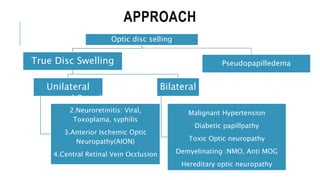
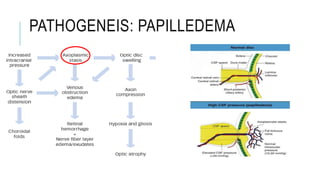
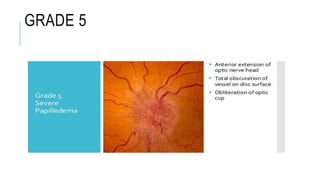
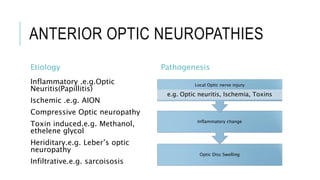
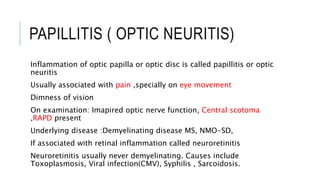
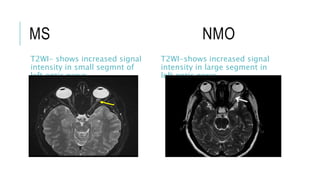
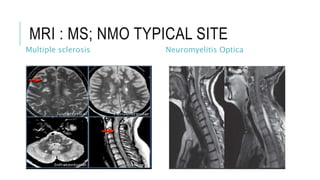
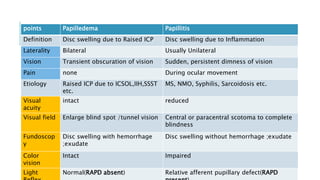
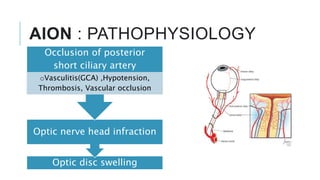
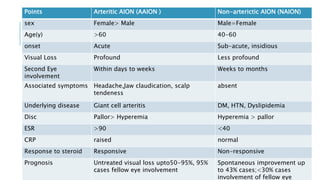
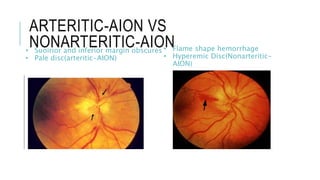
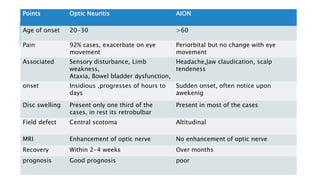
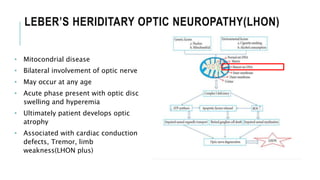
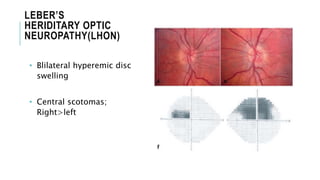
This document provides an overview of optic disc swelling, including the anatomy of the optic nerve, blood supply, causes of optic disc swelling like papilledema and pseudopapilledema, differential diagnosis, and treatments. Key points include the definition of papilledema as optic disc swelling due to increased intracranial pressure, distinguishing features between papilledema and pseudopapilledema, grading scales for papilledema severity, causes of increased ICP like idiopathic intracranial hypertension, and distinguishing anterior ischemic optic neuropathy from optic neuritis.















![TREATMENT
It’s medical emergency
Must be managed promptly and
adequately to prevent further
target organ damage.
[AHA guideline,2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/truepapilloedema-210428151019/85/Optic-Disc-Swelling-47-320.jpg)