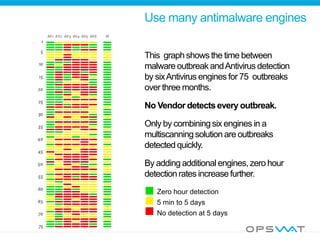
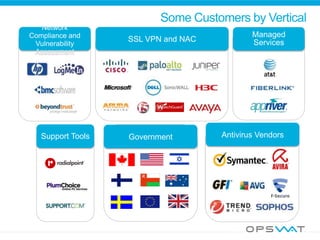
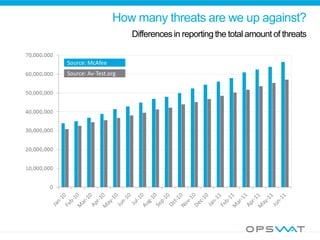
This document discusses securing data workflow between organizations. It introduces OPSWAT, an IT security company, and describes some of their products including secure data transfer solutions. It then asks questions about threats, including that viruses are an NP-complete problem and there are known and unknown threats. Detection rates between antivirus vendors can vary, and using multiple engines in a multiscanning solution provides better protection. Sanitizing data and protecting security systems themselves are also discussed.








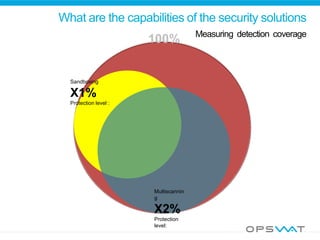
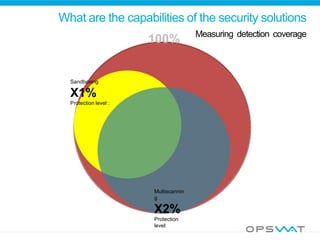
![What are the capabilities of the security solutions?
Antivirus productvulnerabilitiesfrom the National VulnerabilityDatabase
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012
NumberofVulnerabilitiesinAntivirusproducts[CVEs]
Year](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opswat-benny-czarny-inss-2013-130724120941-phpapp02/85/Securing-data-flow-to-and-from-organizations-14-320.jpg)