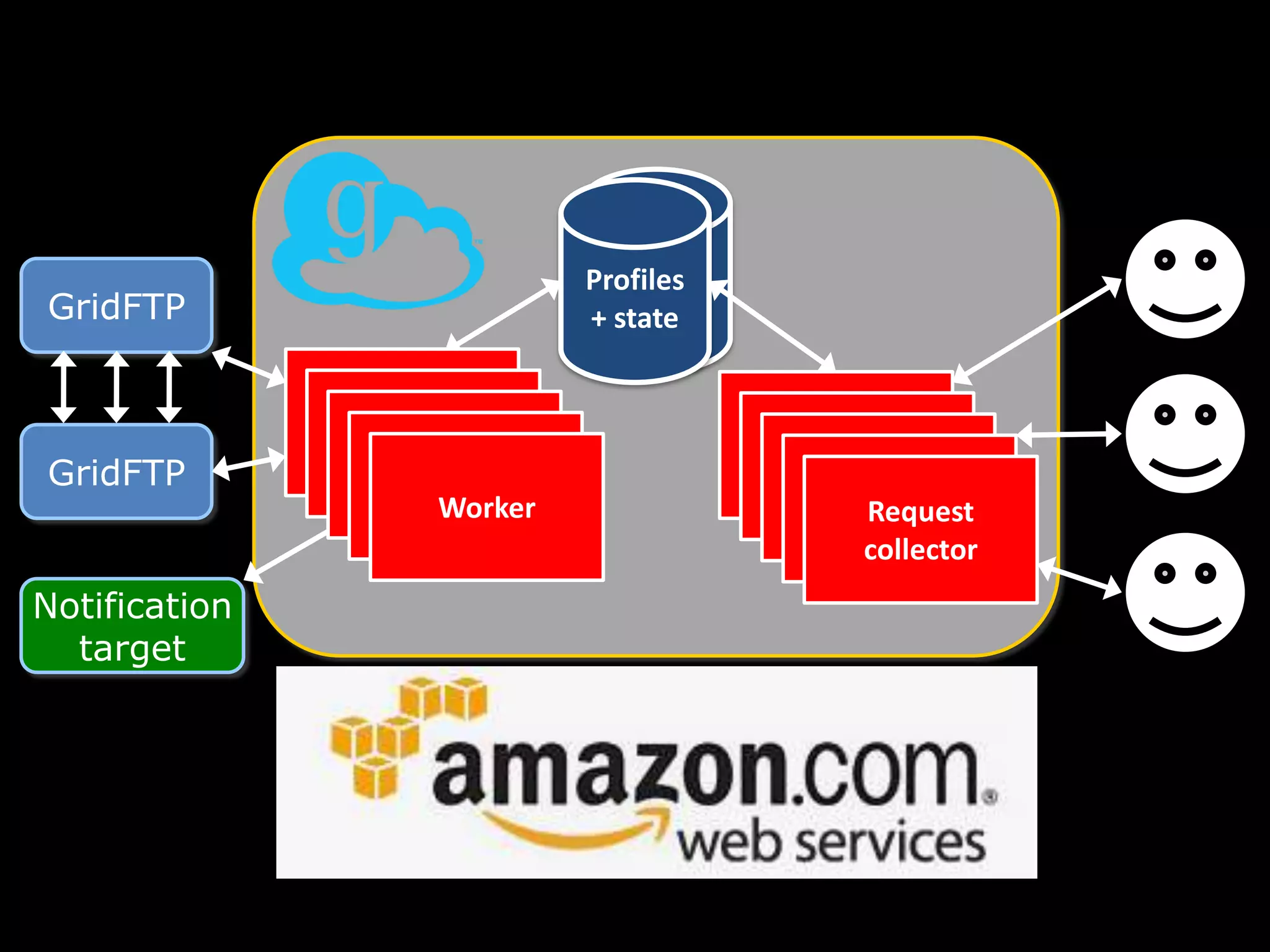
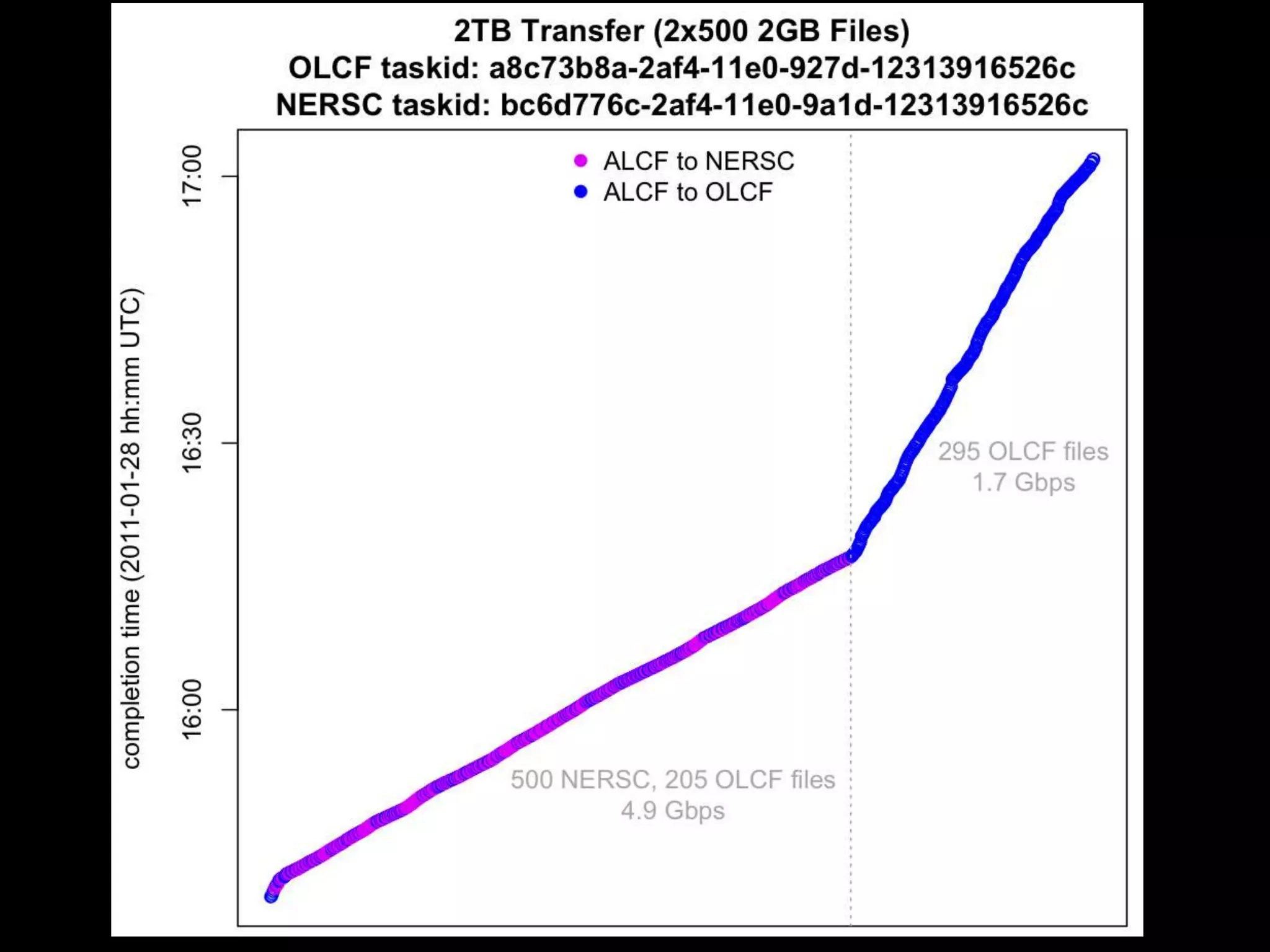
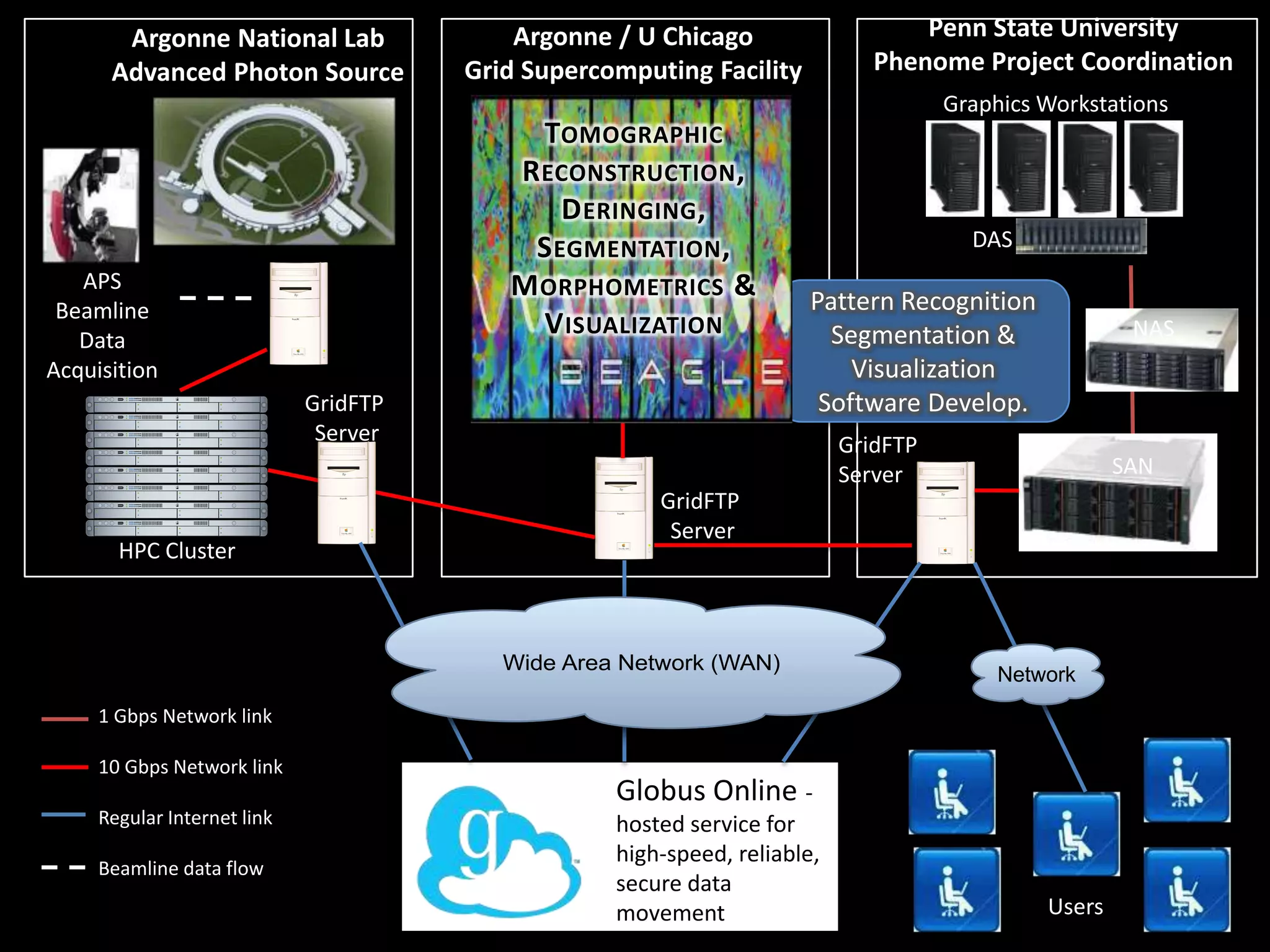
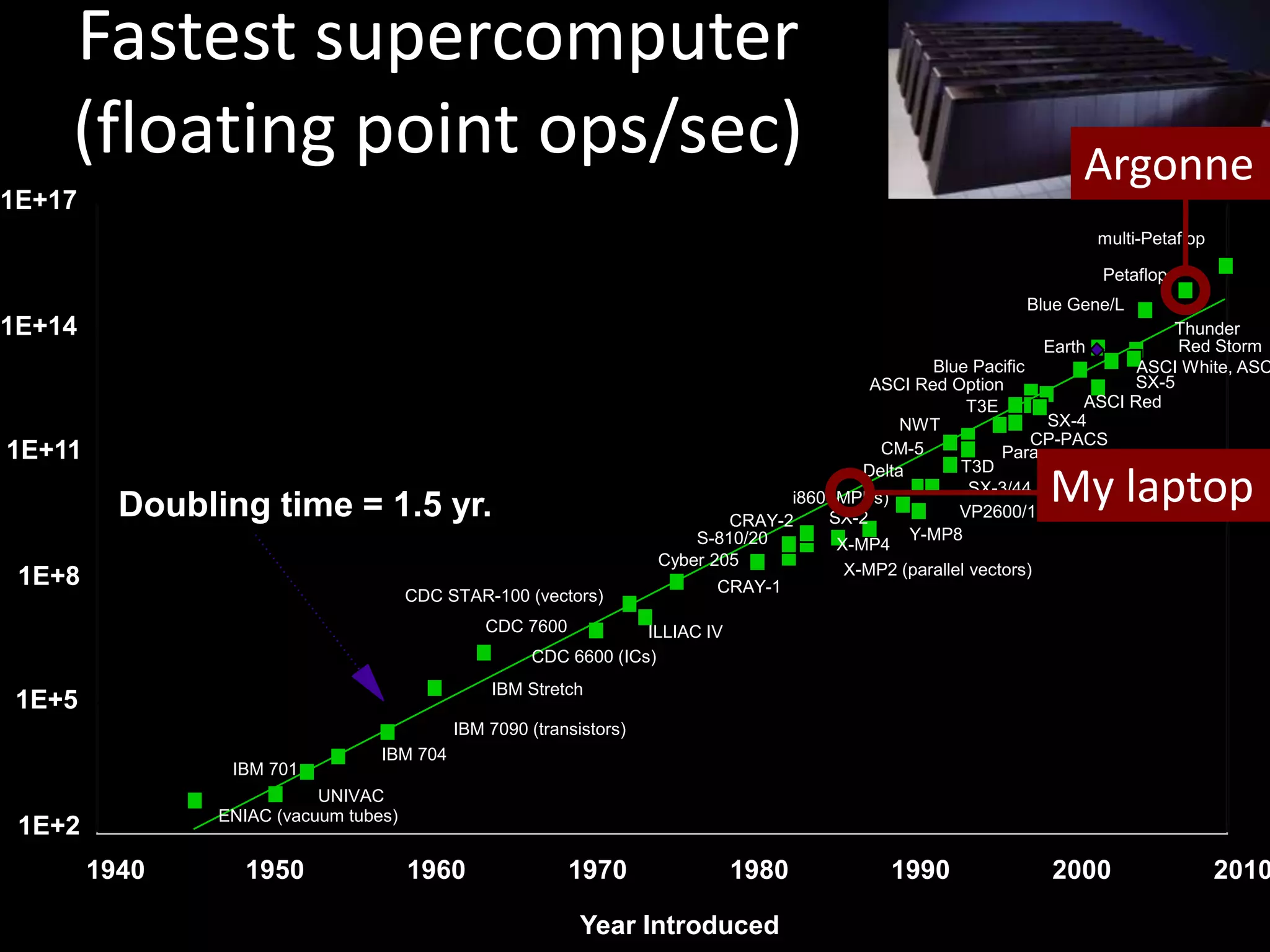
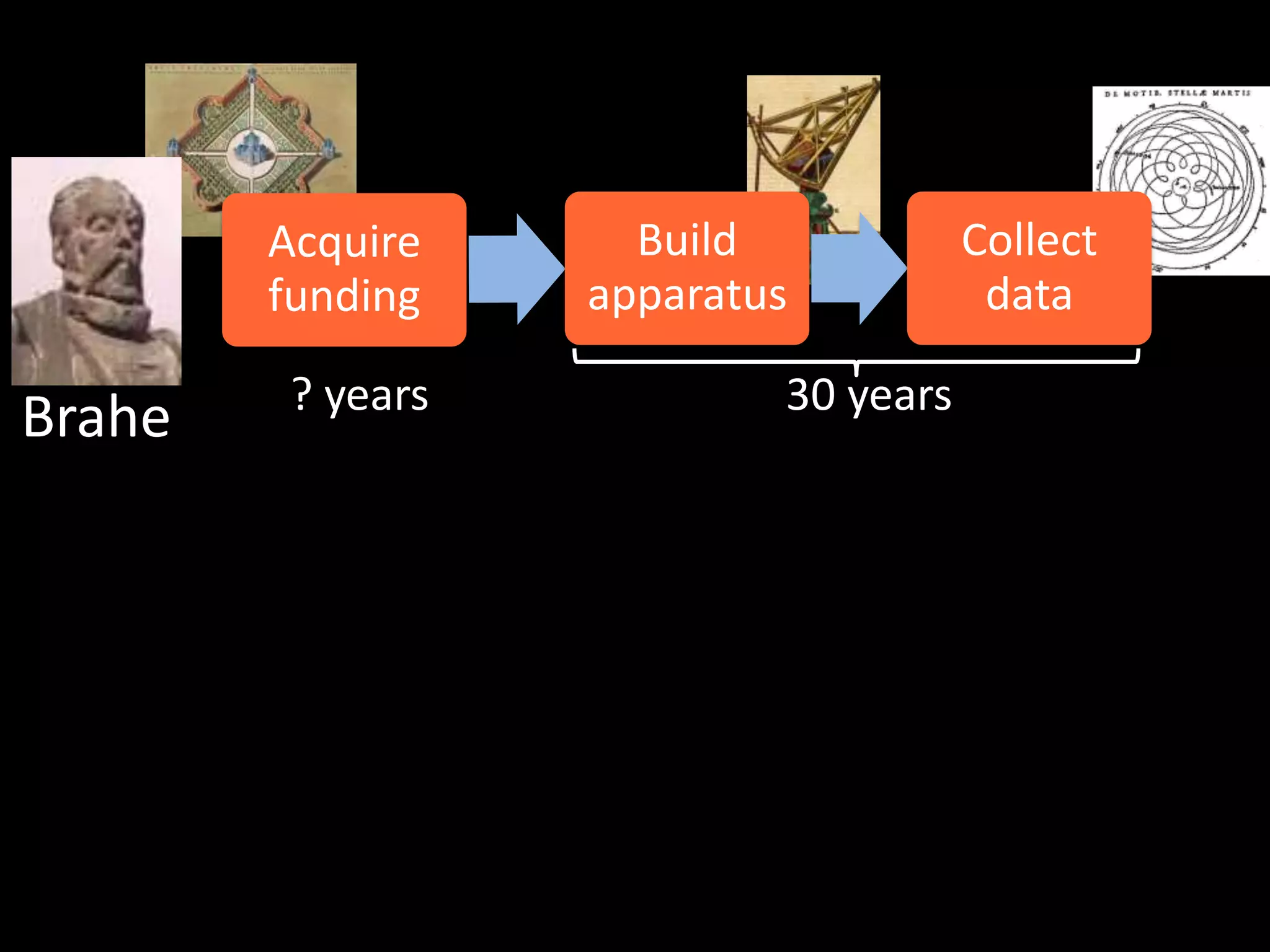
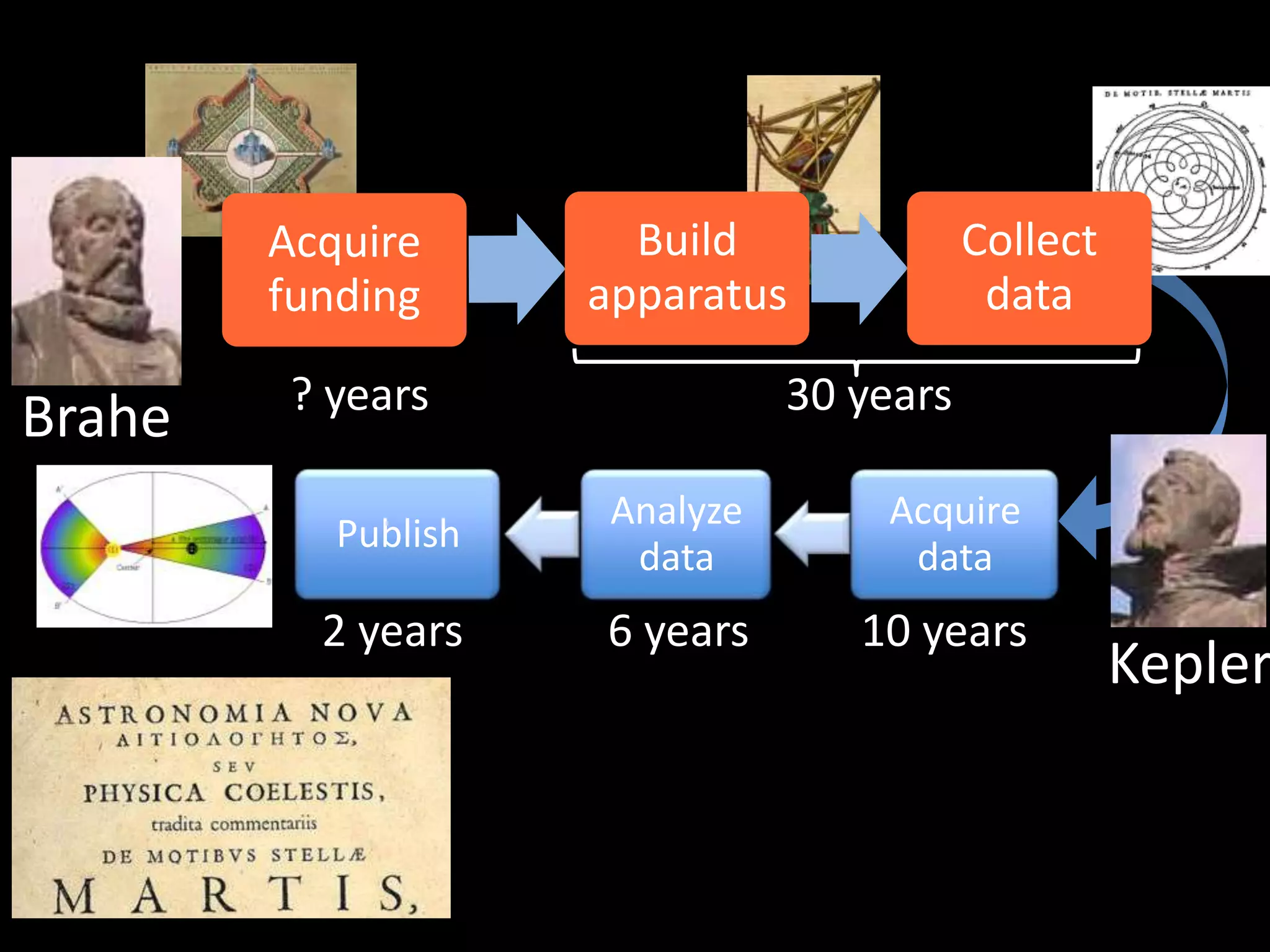
The document discusses advancements in computing architecture, highlighting trends such as petascale and cloud computing, with implications for x-ray science and facilities. It emphasizes the importance of massive parallelism, large data handling, and economic aggregation in future computing challenges. The document also touches on various computational methods and the necessity for automation in scientific processes to enhance discovery and efficiency.






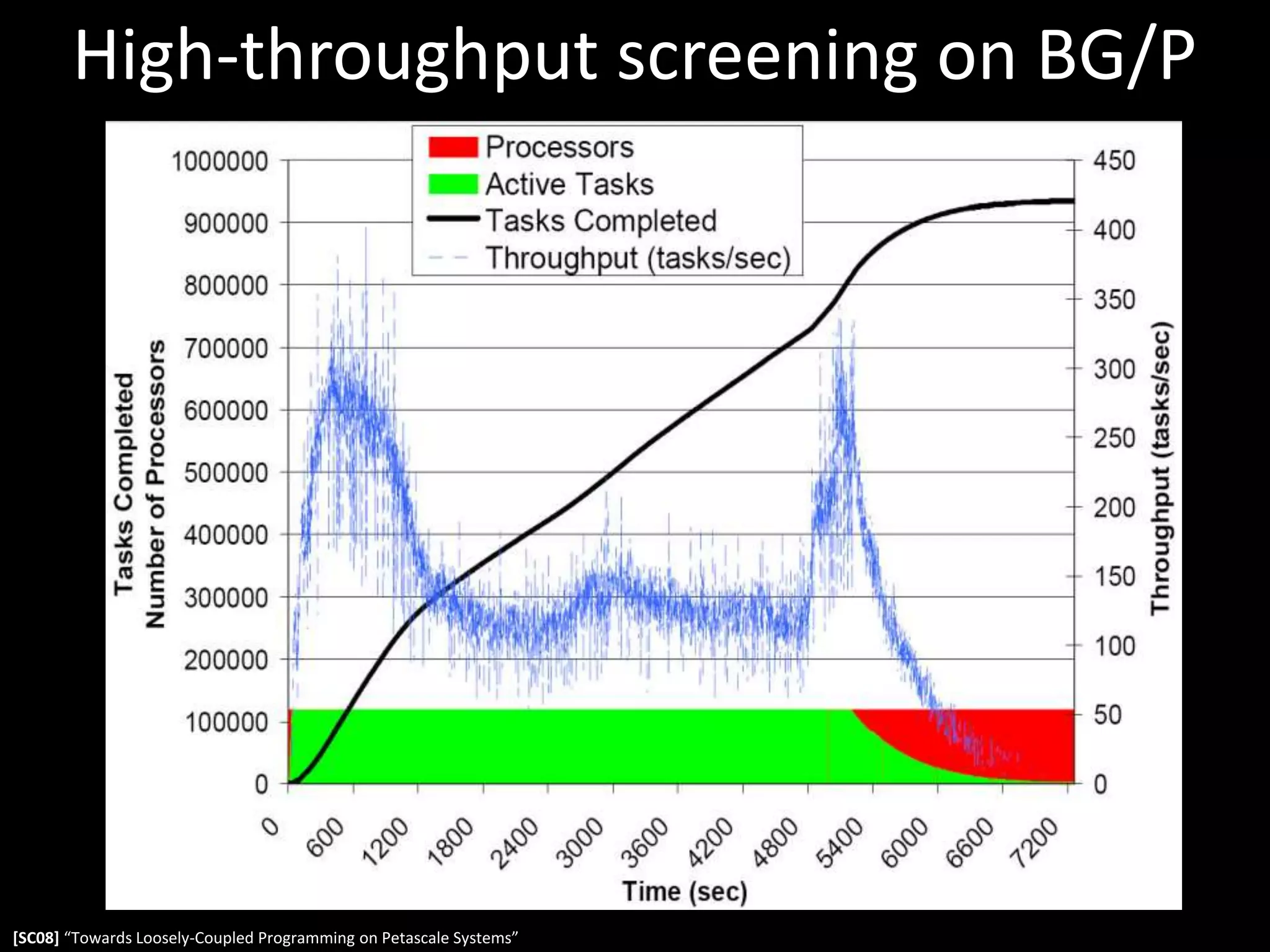
![17High-throughput screening on BG/P[SC08] “Towards Loosely-Coupled Programming on Petascale Systems”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apsfosterfebruary2011-110211130654-phpapp02/75/Opportunities-for-X-Ray-science-in-future-computing-architectures-17-2048.jpg)
![Datacomplexity also increasingID MURA_BACSU STANDARD; PRT; 429 AA.DE PROBABLE UDP-N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINE 1-CARBOXYVINYLTRANSFERASEDE (EC 2.5.1.7) (ENOYLPYRUVATE TRANSFERASE) (UDP-N-ACETYLGLUCOSAMINEDE ENOLPYRUVYL TRANSFERASE) (EPT).GN MURA OR MURZ.OS BACILLUS SUBTILIS.OC BACTERIA; FIRMICUTES; BACILLUS/CLOSTRIDIUM GROUP; BACILLACEAE;OC BACILLUS.KW PEPTIDOGLYCAN SYNTHESIS; CELL WALL; TRANSFERASE.FT ACT_SITE 116 116 BINDS PEP (BY SIMILARITY).FT CONFLICT 374 374 S -> A (IN REF. 3).SQ SEQUENCE 429 AA; 46016 MW; 02018C5C CRC32; MEKLNIAGGD SLNGTVHISG AKNSAVALIP ATILANSEVT IEGLPEISDI ETLRDLLKEI GGNVHFENGE MVVDPTSMIS MPLPNGKVKK LRASYYLMGA MLGRFKQAVI GLPGGCHLGP RPIDQHIKGF EALGAEVTNE QGAIYLRAER LRGARIYLDV VSVGATINIM LAAVLAEGKT IIENAAKEPE IIDVATLLTS MGAKIKGAGT NVIRIDGVKE LHGCKHTIIP DRIEAGTFMI[source: GlaxoSmithKline]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apsfosterfebruary2011-110211130654-phpapp02/75/Opportunities-for-X-Ray-science-in-future-computing-architectures-21-2048.jpg)